Based on the observations of the interaction-virgin electrically charged bodies, the American Canan Physicist Benjamin Franklin called some bodies charged positively, while others are negative. According to this I. electric chargescall polo-residents and negative.
Bodies with the charges of the same name are replicated. Bodies with multi-chain charges are attracted.
These charge names are completely conditional, and their only meaning is that the body having electrical charges can either attract or repel.
Electrical charge sign of the body determined by interaction with the conditional embarrass of the charge sign.
The charge of an ebony stick was taken as one of these standards, shabby fur. It is believed that the ebonite wand after rubbing the fur always has a negative manner.
If it is necessary to determine which sign of the charge of this body, it is under-worn to the Ebonite stick enshrined in a light suspension, a furry fur, and is observed. If the wand is repelled, then the body has a negative charge.
After opening and studying elementary particles, it turned out that negative charge always has the elementary part-CA - electron.
Electron (from Greek. - Amber) - Stable elementary part-Central Asia with negative electric hoaxe \u003d 1,6021892 (46). 10 -19 CL, restingm E \u003d. 9,1095. 10 -19 kg. Opened in 1897 by English physicist J. J. Thomson.
As a reference of a positive charge taken a chaaming of a glass stick, a shabby-rally silk. If the wand is repelless from the electrified body, then this body has a positive charge.
Positive charge always has proton,which is part of the atomic poison. Material from site.
Using the above rules, to determine the body charge, you need to remember that it depends on the substance of interacting tel. So, the ebonitea pa-pet may have a positive charge if it is lost to a cloth from synthetic materials. The glass wand will have a negative charge if it is lost by meh. Therefore, planning to get a denial charge on an ebony stick, be sure to use the fur or wool tissue when scattered. It also applies to the electrification of glass stick, which is rubbed with natural silk cloth to obtain a positive charge. Only an electron and proton always and uniquely have a negative and polo charges, respectively.
On this page, material on the themes:
What is the conventional standard of negative charge?
What is a conventional standard of negative charge
What is the conditional reference of a positive charge?
Then be a conditional non-discharge charge
-
Electric charge- The physical quantity characterizing the ability of bodies to join electromagnetic interactions. Measured in the coulons.
Elementary electric charge- minimum charge that have elementary particles (proton and electron charge).
The body has a chargeSo it has extra or missing electrons. This charge is denoted q.=ne. (It is equal to the number of elementary charges).
To electrify the body- Create an excess and disadvantage of electrons. Methods: electric frictionand electrization contact.
Cottage daryd - body charge, which can be accepted for the material point.
Trial charge(
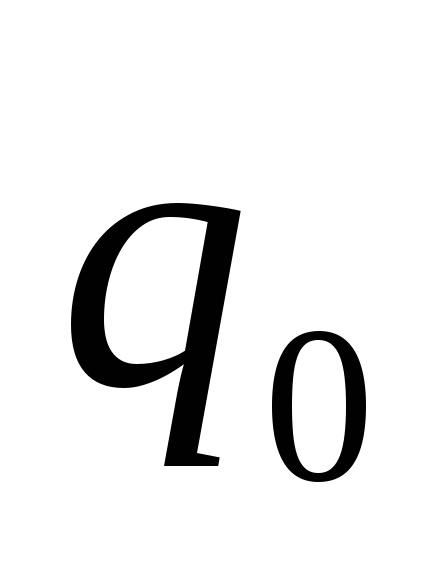 ) - point, small charge, be sure to be positive - used for research electric field.
) - point, small charge, be sure to be positive - used for research electric field.The law of saving charge:in an isolated system, the algebraic amount of charges of all bodies remains constant for any interactions of these bodies.
The law of Kulon.:the strength of the interaction of two spot charges proportional to the product of these charges, inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, depend on the properties of the medium and are directed along the straight line connecting their centers.
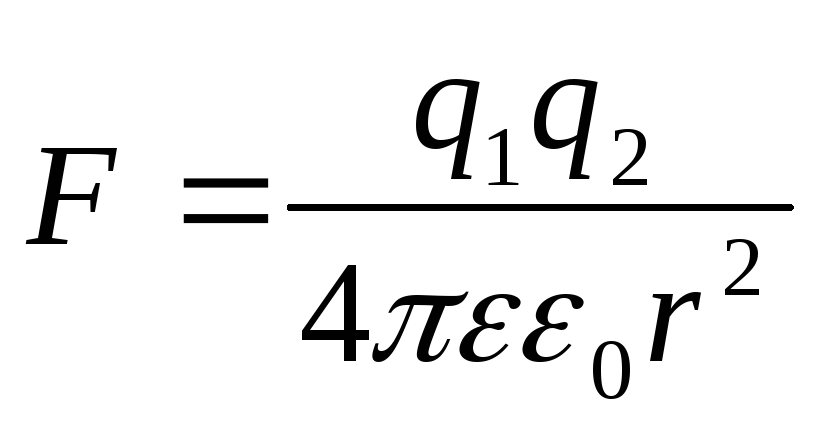 where
where 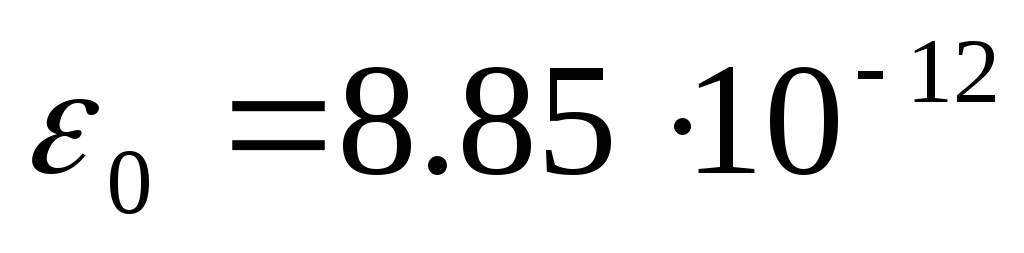 F / M, CL 2 / Nm 2 - Dielectr. fast. Vacuum
F / M, CL 2 / Nm 2 - Dielectr. fast. Vacuum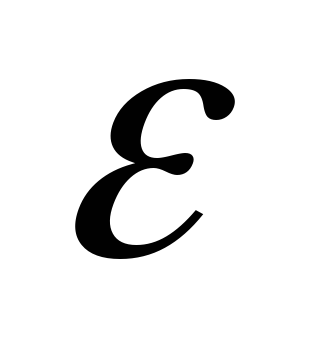 - relates. Dielectric constant (\u003e 1)
- relates. Dielectric constant (\u003e 1)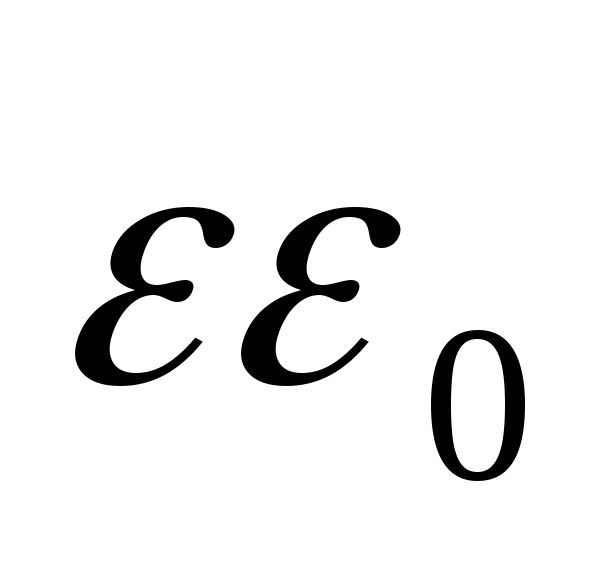 - Absolute dielectric penetration. Environments
- Absolute dielectric penetration. EnvironmentsElectric field- Material medium through which electric charges are interacted.
Electric field properties:
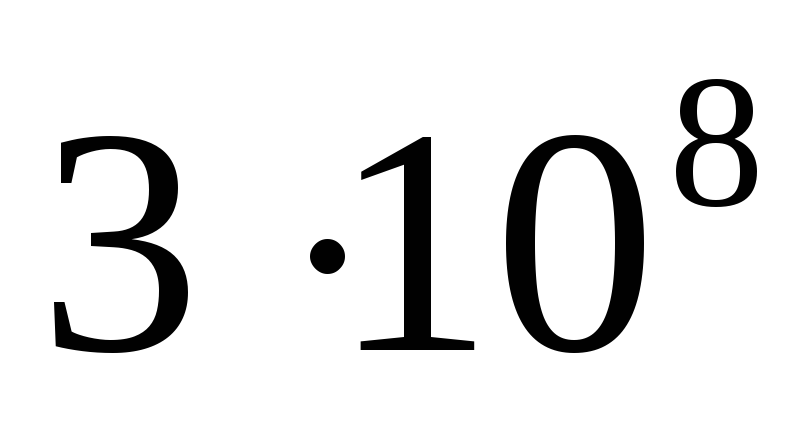
Electric field characteristics:
Tension(E.) - vector magnitude, equal poweracting on a single trial charge placed at this point.
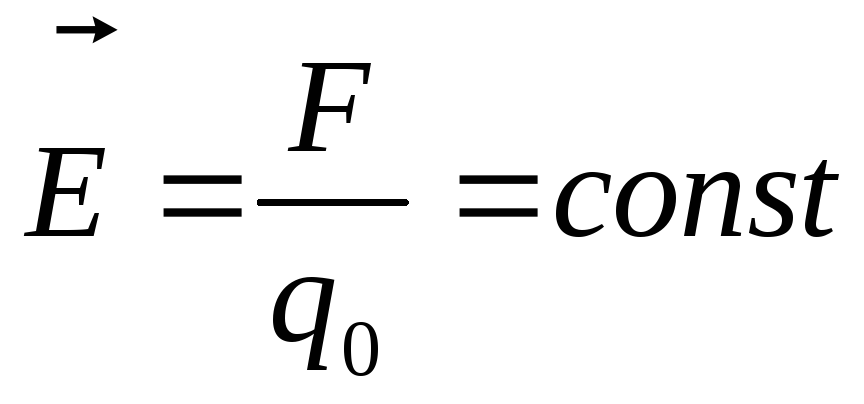 Measured in N / CL.
Measured in N / CL. 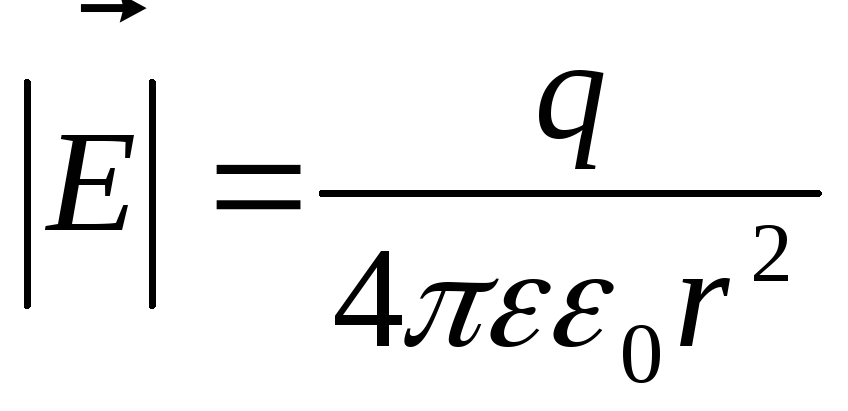
Direction- The same as in the current strength.
Strength does not dependnone of the strength nor from the value of the test charge.
Superposition of electric fields: The voltage of the field created by several charges is equal to the vector sum of the fields of fields of each charge:
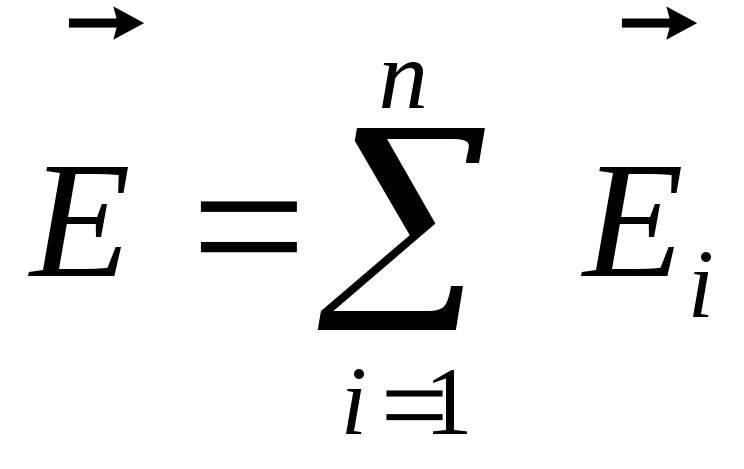
Graphicallythe electronic field is depicted using voltage lines.
Line of tension- The line tangent to which at each point coincides with the direction of the voltage vector.
Properties of tension lines: They do not intersect, through each point you can spend only one line; They are not closed, come out of a positive charge and included in negative, or dissipate into infinity.
Field types:
Uniform electric field- field, the voltage vector of which at each point is the same modulo and direction.
Heterogeneous electric field- field, whose voltage vector at each point of unequal modulo and direction.
Permanent electric field- Vector voltage does not change.
Non-permanent electric field- Vector voltage changes.
The operation of the electric field to move charge.
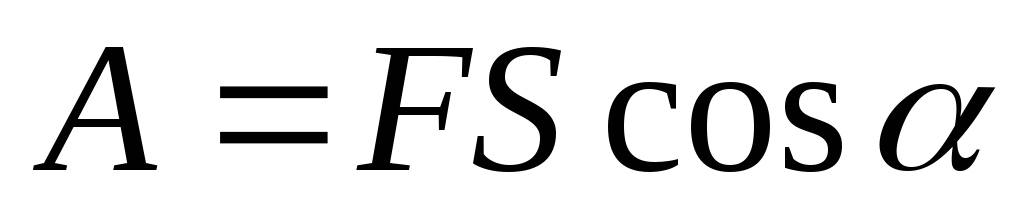 where the power, S- Move,
where the power, S- Move,  - Angle of Memfi.
- Angle of Memfi.For uniform field: Power constant.
The work does not depend on the form of the trajectory; Work on moving along a closed trajectory is zero.
For an inhomogeneous field:


Electric field potential- The ratio of work that makes the field by moving the test electrical charge into infinity, to the magnitude of this charge.
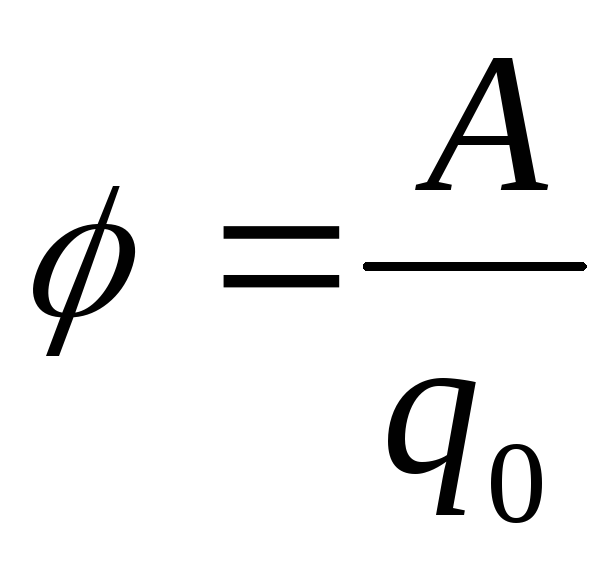 -potential- Energy characteristics of the field. Measured in Volta
-potential- Energy characteristics of the field. Measured in Volta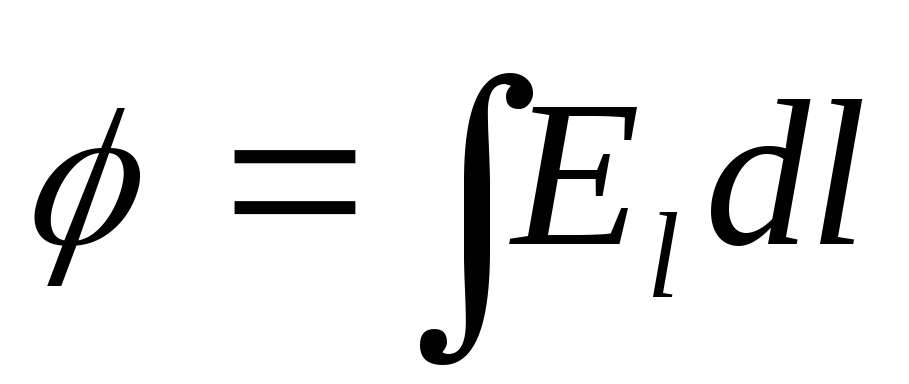
Potential difference:
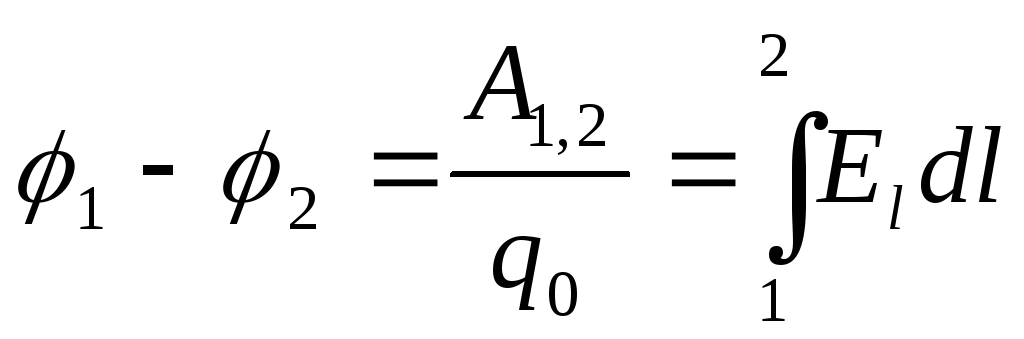
If a
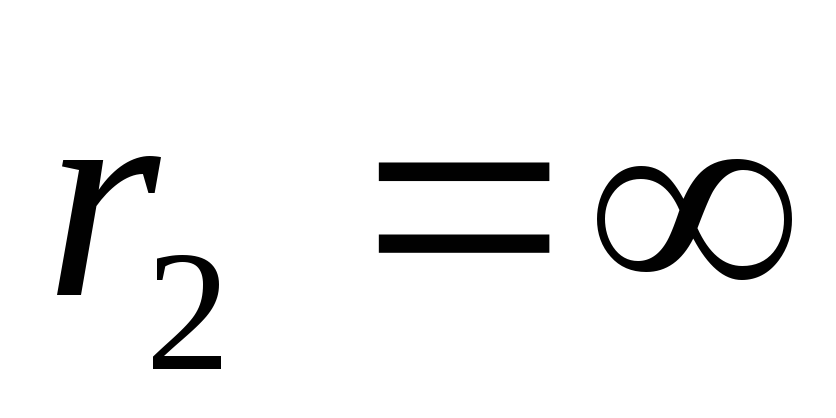 T.
T. 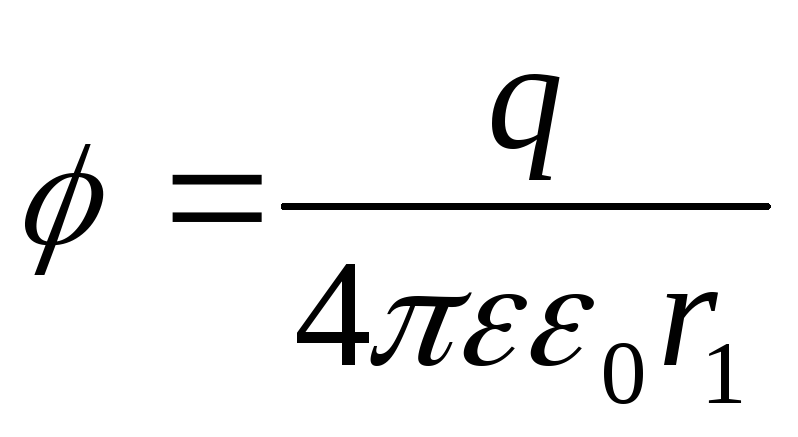
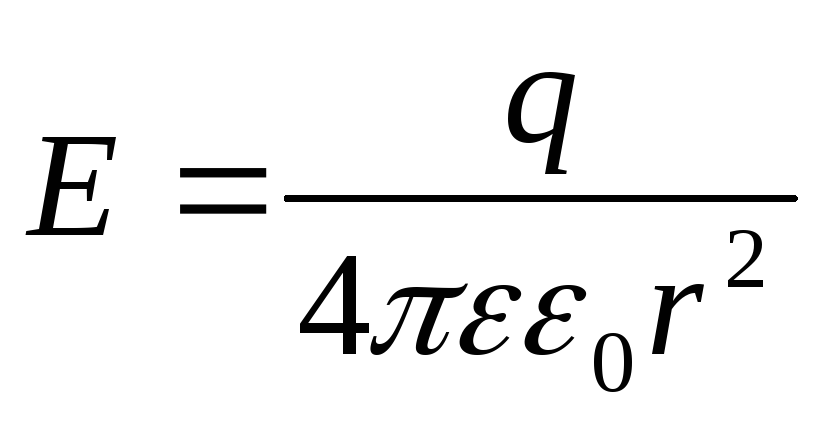 So
So 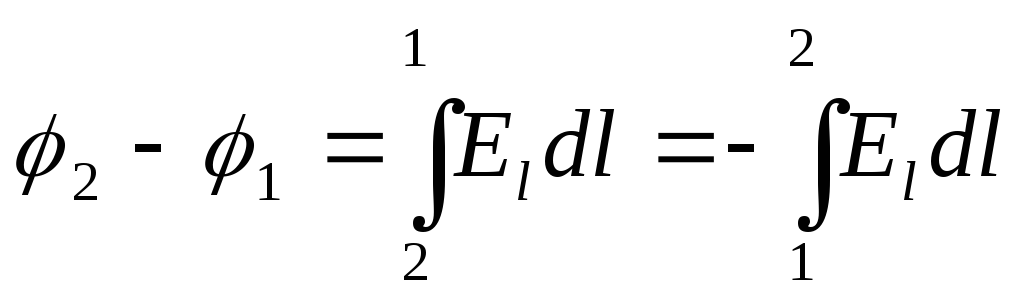
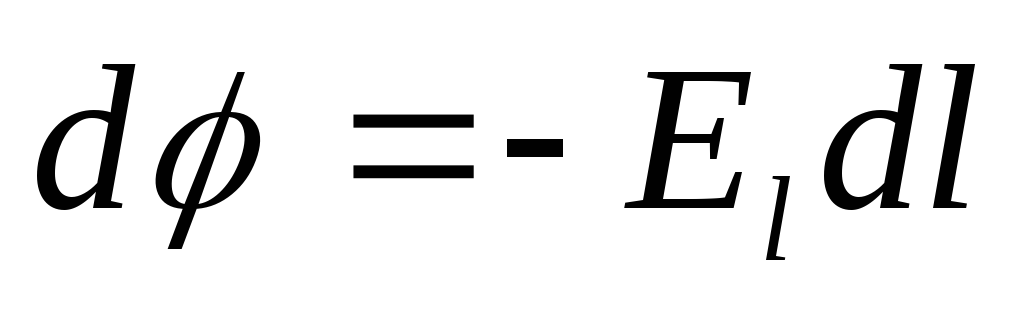
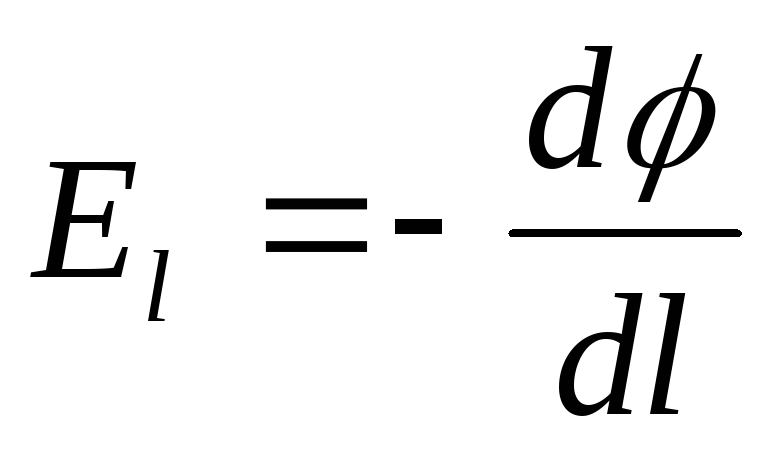 -capacity gradient.
-capacity gradient.For a homogeneous field: Potential difference - voltage:
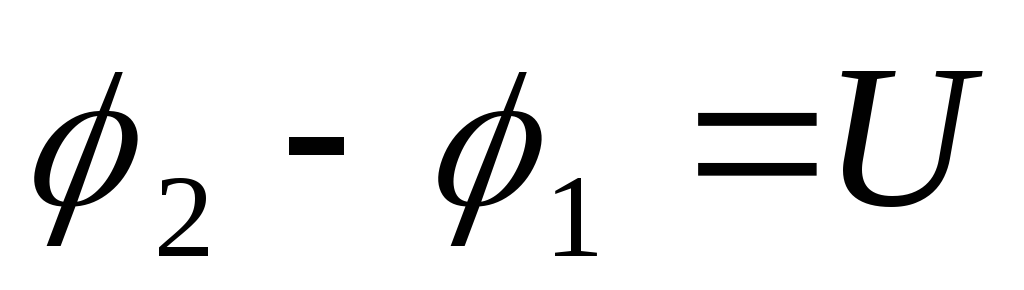
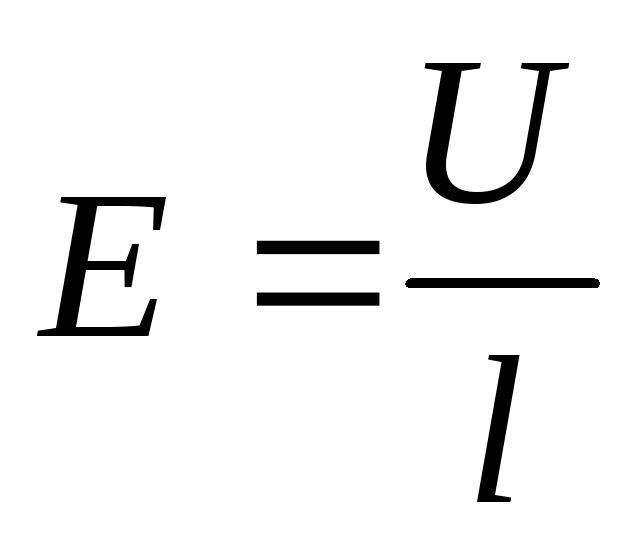 . It is measured in volts, instruments - voltmeters.
. It is measured in volts, instruments - voltmeters.Electricity- body ability to accumulate electrical charge; The ratio of the charge to the potential that is always constantly for this conductor.
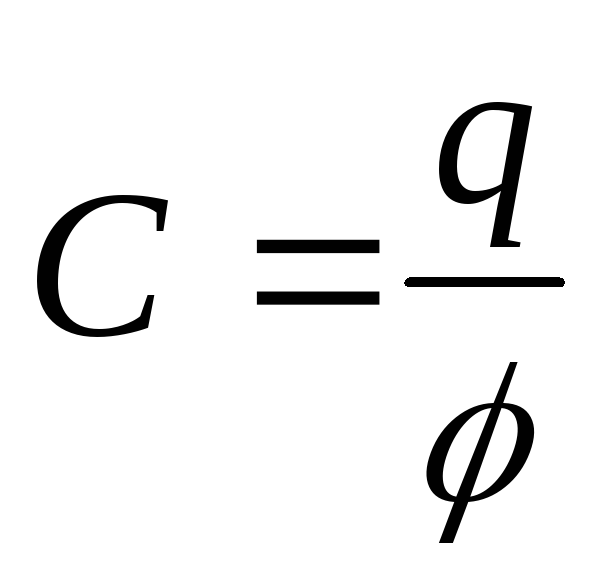 .
.Does not depend on the charge and does not depend on the potential. But depends on the size and form of the conductor; from the dielectric properties of the medium.
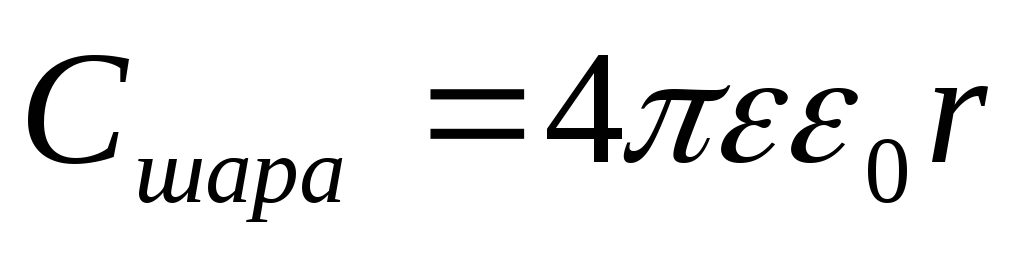 wherer- size,
wherer- size, 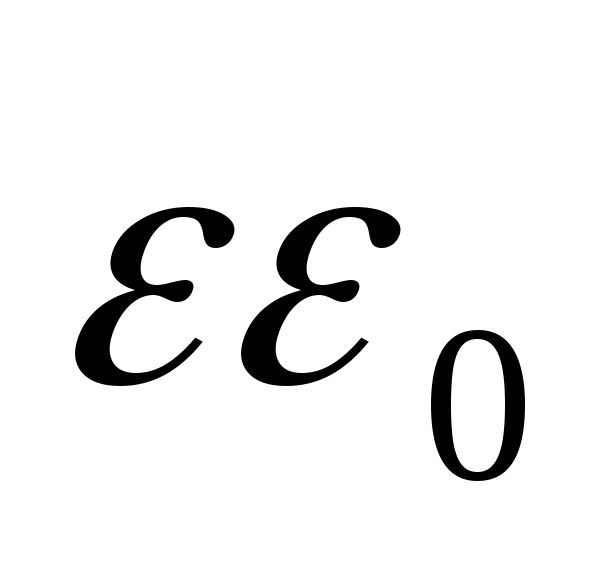 - permeability of the medium around the body.
- permeability of the medium around the body.Electricity increases if any bodies are located nearby - conductors or dielectrics.
Capacitor- A device for accumulating charge. Electricity:
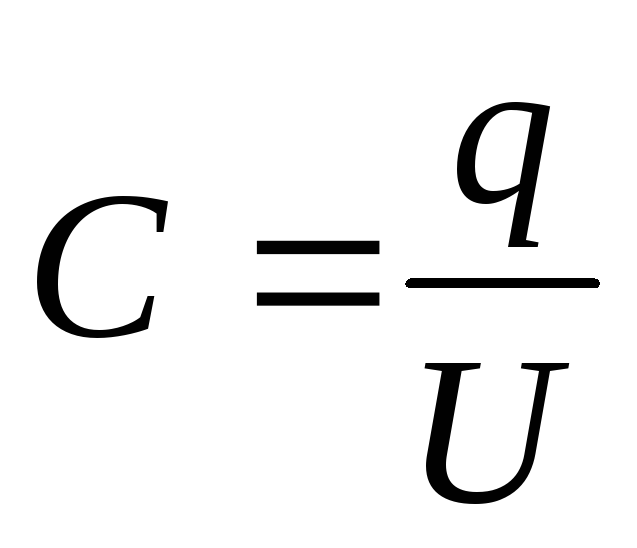
Flat condenser- Two metal plates, between which the dielectric is located. Flat condenser electric capacity:
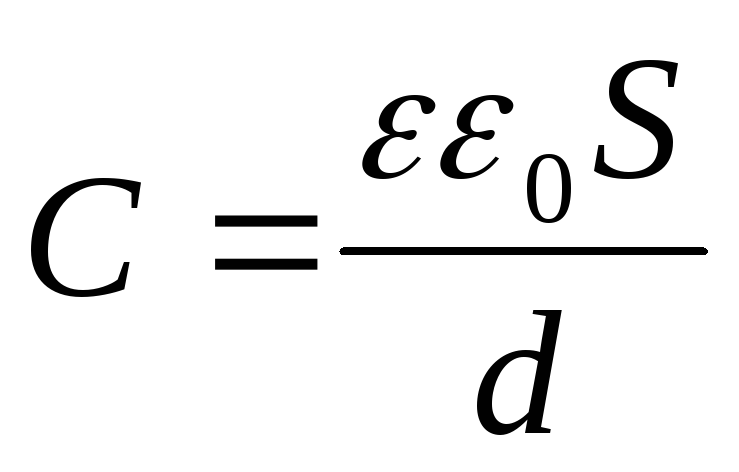 wheress is the area of \u200b\u200bthe plates, the distance between the plates.
wheress is the area of \u200b\u200bthe plates, the distance between the plates.Energy charged condenserit is equal to the work that the electrical field performs when the charge is transferred from one plate to another.
Transferring a small charge
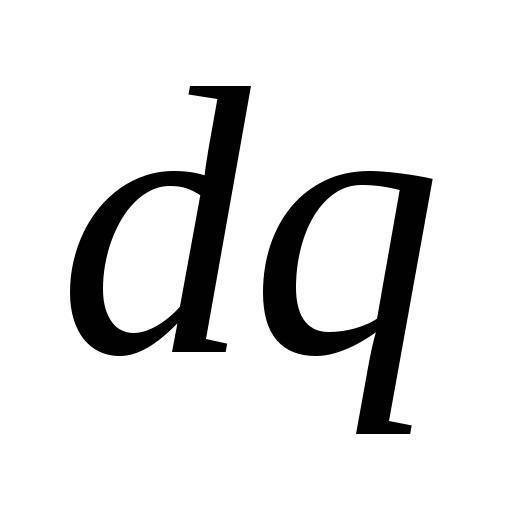 , voltage change to
, voltage change to 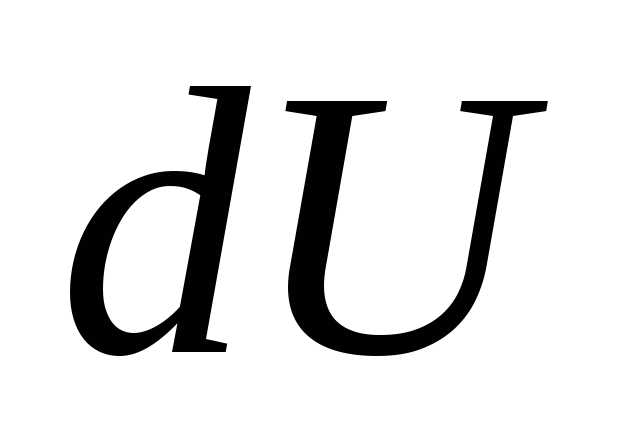 , work will be done
, work will be done 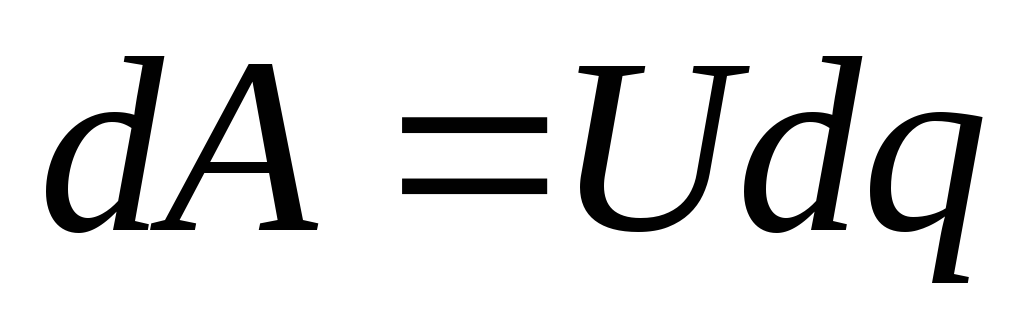 . Because
. Because 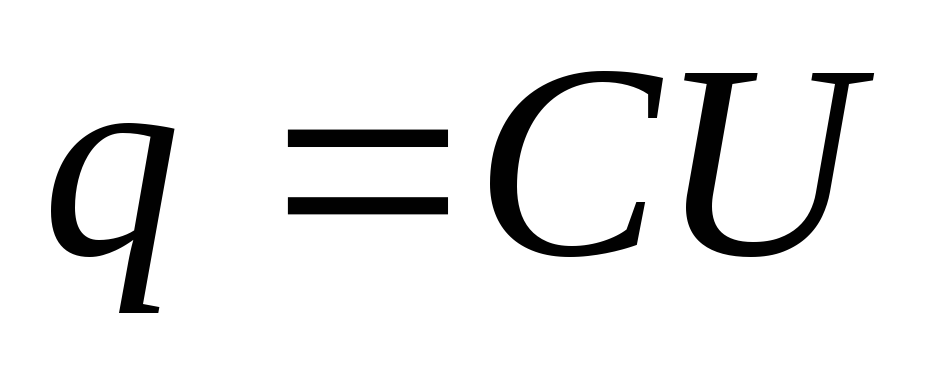 , and c \u003d const,
, and c \u003d const, 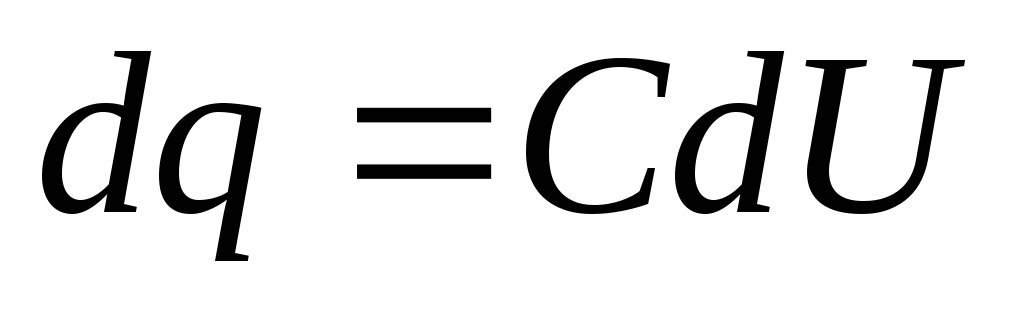 . Then
. Then 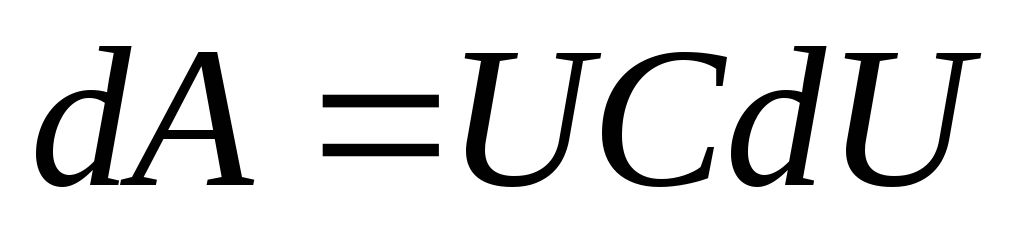 . We integrate:
. We integrate: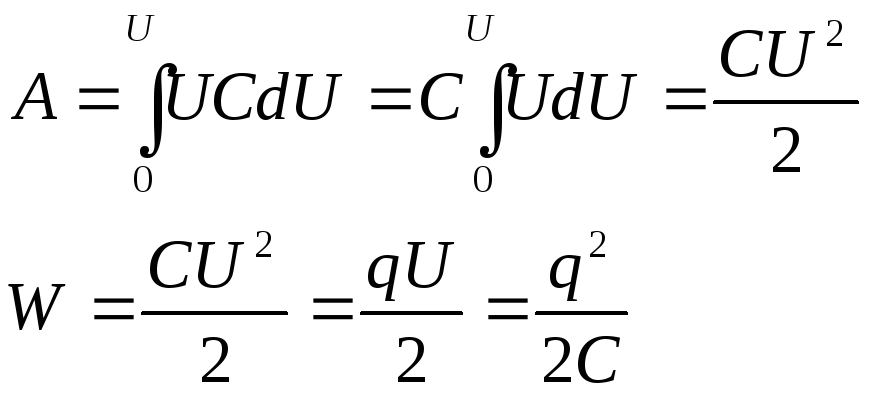
Electric field energy:
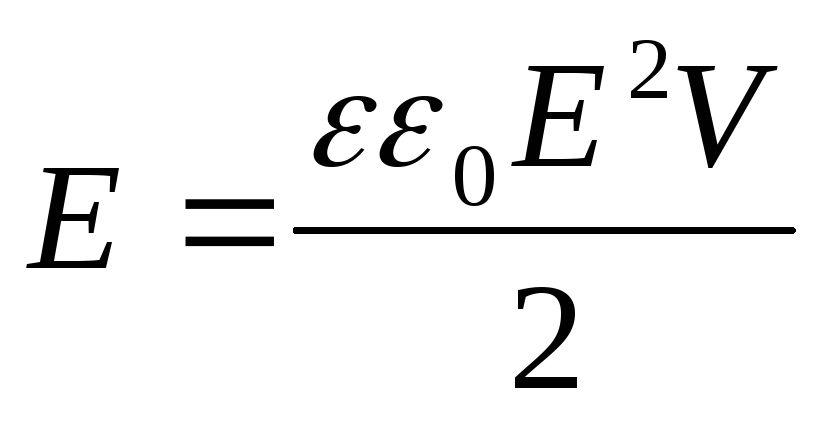 wherev \u003d SL-volume occupied by an electric field
wherev \u003d SL-volume occupied by an electric fieldFor an inhomogeneous field:
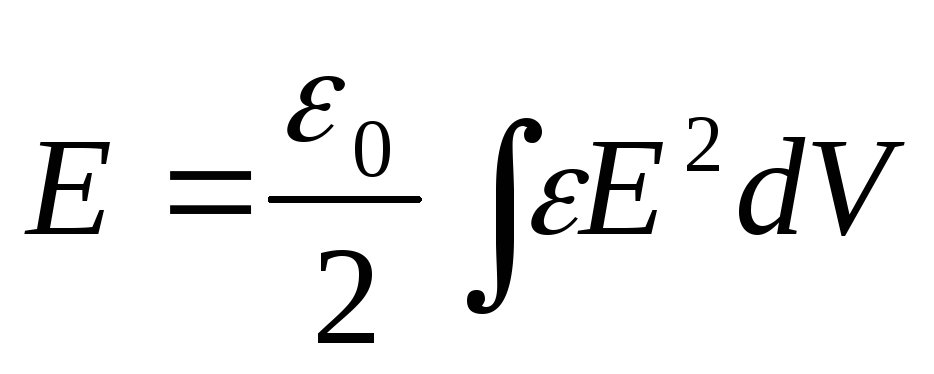 .
.Volume density of the electric field:
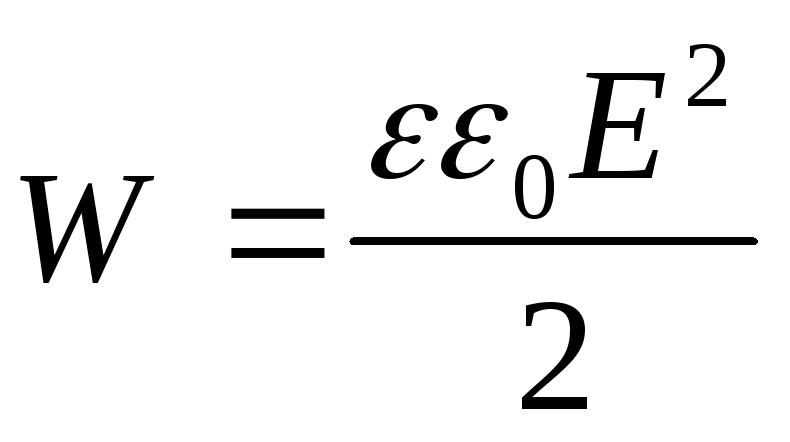 . Measured in j / m 3.
. Measured in j / m 3.Electric dipole.- A system consisting of two equal, but opposite on the sign of point electrical charges, located at some distance from each other (Dipole -L shoulder).
The main characteristic of the dipole - dipole moment- Vector equal to the work of the charge on the shoulder of the dipole, directed from the negative charge to the positive. Denotes
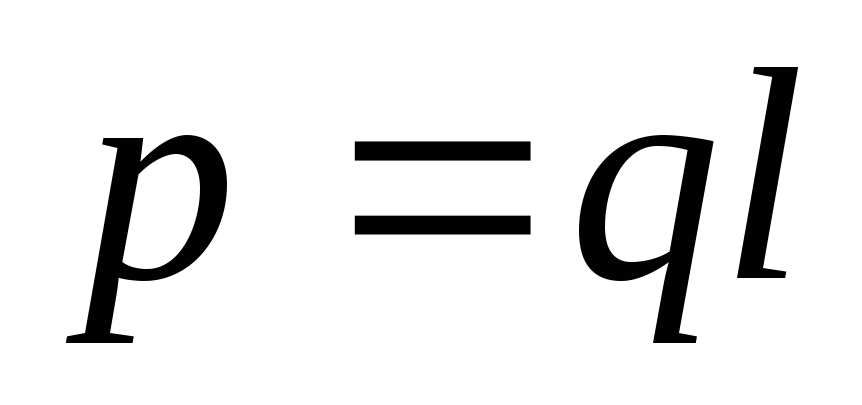 . Measured in pendant meters.
. Measured in pendant meters.Dipole in a uniform electric field.
For each of the charges of the dipole, the forces act:
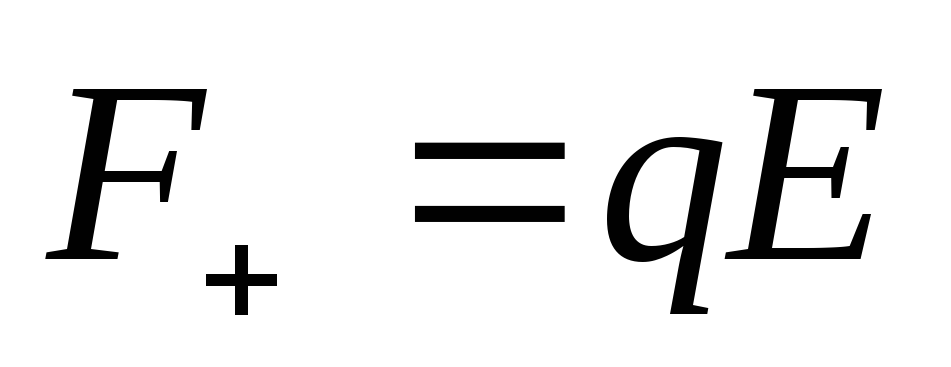 and
and 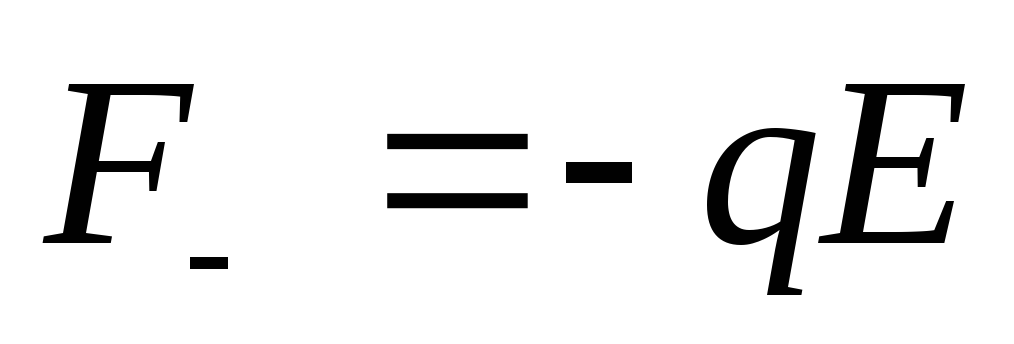 . These forces are oppositely directed and create a moment of pair of forces - torque :, where
. These forces are oppositely directed and create a moment of pair of forces - torque :, whereM - Rotating moment of F-forces acting on the dipole
d-Shouldvo Single-Shoulder Dipole
p- dipole moment- voltage
 - Embossing angle
- Embossing angleUnder the action of the torque, the dipole turns and will be installed in the direction of voltage lines. Vectors of the PI e will be parallel and unidirectional.
Dipole in an inhomogeneous electric field.
The torque is, it means the dipole will turn. But the forces will be unequal, and the dipole will move to where the power is more.
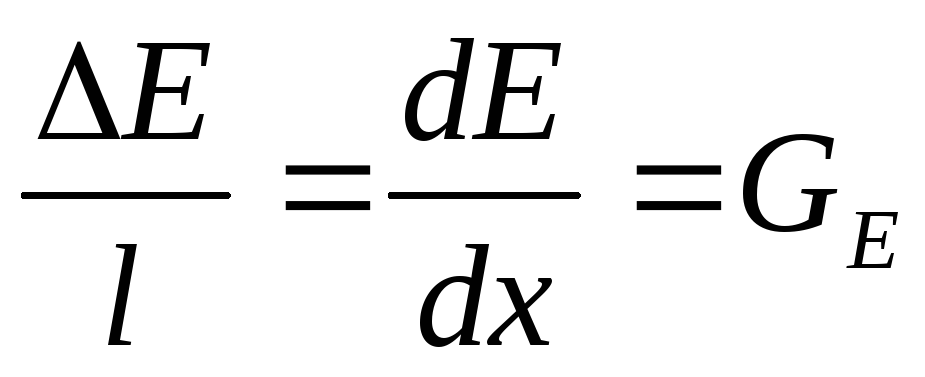 -tension gradient. The higher the tension gradient, the higher the lateral force that the dipole becomes. The dipole is focused along the power lines.
-tension gradient. The higher the tension gradient, the higher the lateral force that the dipole becomes. The dipole is focused along the power lines.Own dipole field.
But. Then:
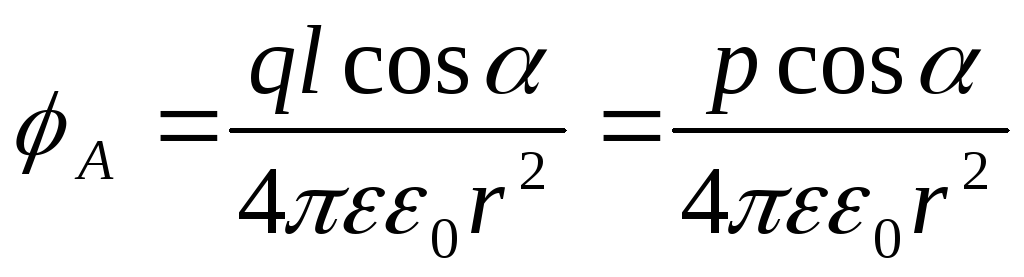 .
.Let the dipole be at the point oh, and his shoulder is not enough. Then:
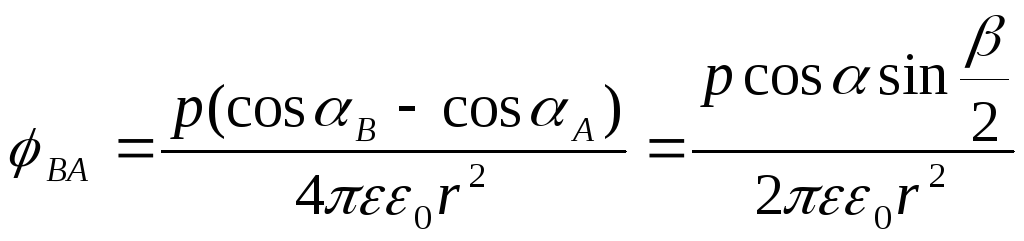 .
.The formula was obtained taking into account:
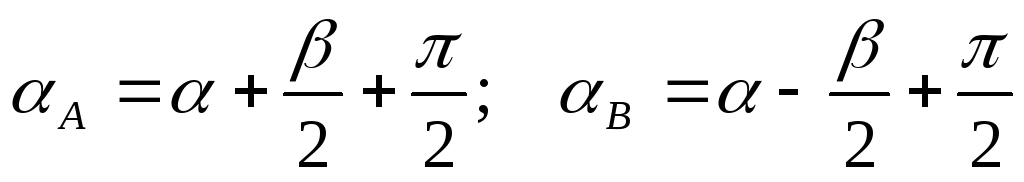
Thus, the potential difference depends on the sinus of a half angle, under which the dipole points are visible, and the projection of the dipole moment to the direct connecting these points.
Dielectrics B. electric field.
Dielectric- A substance that does not have free charges, which means that the non-conductive electric current. However, in fact, conductivity exists, but it is negligible.
Dielectric classes:
with polar molecules (water, nitrobenzene): Molecules are not symmetrical, the masses of the masses of positive and negative charges do not coincide, and therefore they have a dipole moment even in the case when the electric field is not.
with non-polar molecules (hydrogen, oxygen): Molecules are symmetrical, centers of masses of positive and negative charges coincide, and therefore they do not have a dipole moment in the absence of an electric field.
crystal (sodium chloride): a set of two cerebrals, one of which is charged positively, and the other is negative; In the absence of an electric field, the total dipole moment is zero.
Polarization- The process of spatial separation of charges, the appearance of associated charges on the dielectric surface, which leads to the weakening of the field inside the dielectric.
Polarization methods:
1 method - electrochemical polarization:
On electrodes - movement to them cations and anions, neutralization of substances; The areas of positive and negative charges are formed. The current is gradually decreasing. The rate of setting the neutralization mechanism is characterized by the relaxation time is the time during which the polarization EMP increases from 0 to the maximum from the moment of the imposition of the field.
 \u003d 10 -3 -10 -2 s.
\u003d 10 -3 -10 -2 s.2 Method - Orientational polarization:
On the surface of the dielectric, noncompensated polar, i.e. Polarization phenomenon occurs. The tension inside the dielectric is less external tension. Relaxation time:
 \u003d 10 -13 -10 -7 p. Frequency 10 MHz.
\u003d 10 -13 -10 -7 p. Frequency 10 MHz.3 Method - Electronic polarization:
Characteristic for non-polar molecules that become dipoles. Relaxation time:
 \u003d 10 -16 -10 -14 s. Frequency 10 8 MHz.
\u003d 10 -16 -10 -14 s. Frequency 10 8 MHz.4 Method - ion polarization:
Two grilles (NaCl) are shifted relative to each other.
Relaxation time:

5 Method - microstructure polarization:
It is characteristic of biological structures when charged and uncharged layers alternate. The redistribution of ions occurs on semi-permeable or impenetrable partitions.
Relaxation time:
 \u003d 10 -8 -10 -3 s. Frequency 1 kHz
\u003d 10 -8 -10 -3 s. Frequency 1 kHzNumerical characteristics of the degree of polarization:
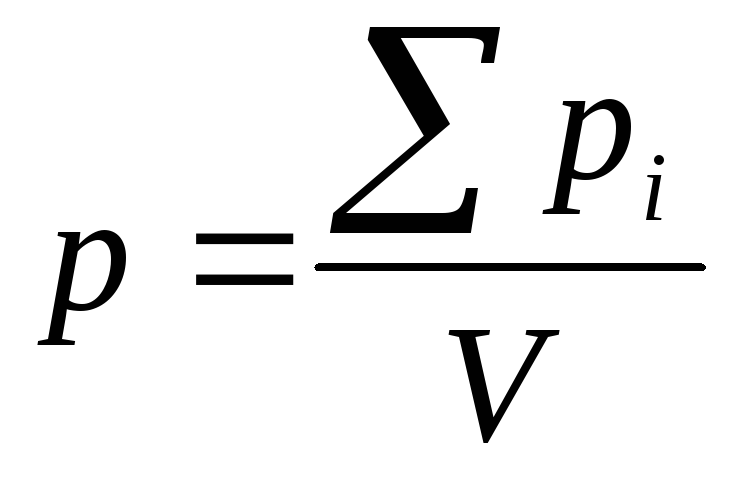
Electricity- This is an ordered movement of free charges in a substance or in a vacuum.
Conditions of the existence of electric current:
availability of free charges
the presence of an electric field, i.e. Forces acting on these charges
Tok Power- The value equal to the charge, which passes through any cross section of the conductor per unit of time (1 second)
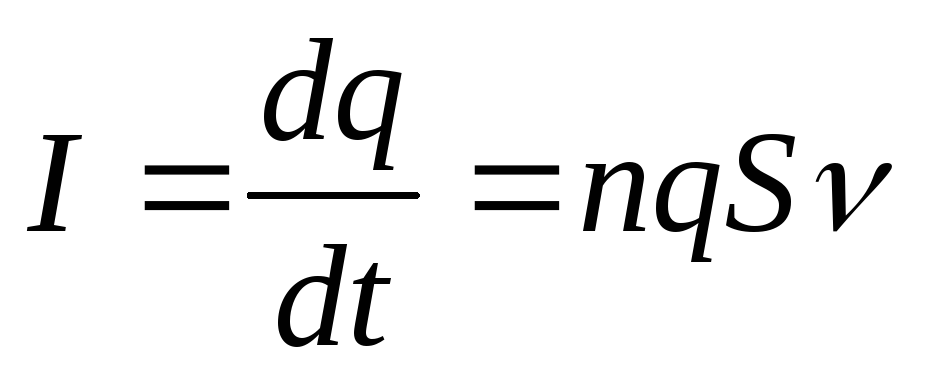 Measured in amperes.
Measured in amperes.n- Concentration of charges
q- The value of charge
S- Cross section of the conductor
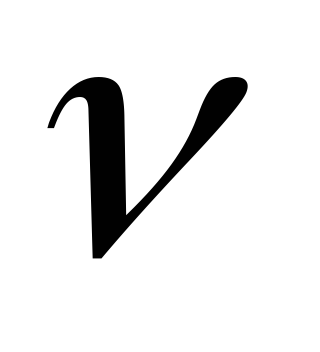 - The speed of the directional movement of particles.
- The speed of the directional movement of particles.The speed of movement of charged particles in the electric field is small - 7 * 10 -5 m / s, the speed of propagation of the electric field 3 * 10 8 m / s.
Cone density- The value of the charge passing in 1 second through the section in 1 m 2.
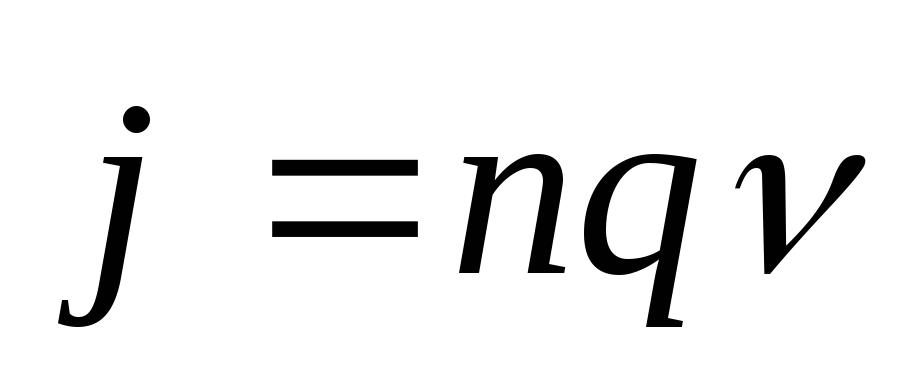 . Measured in a / m 2.
. Measured in a / m 2.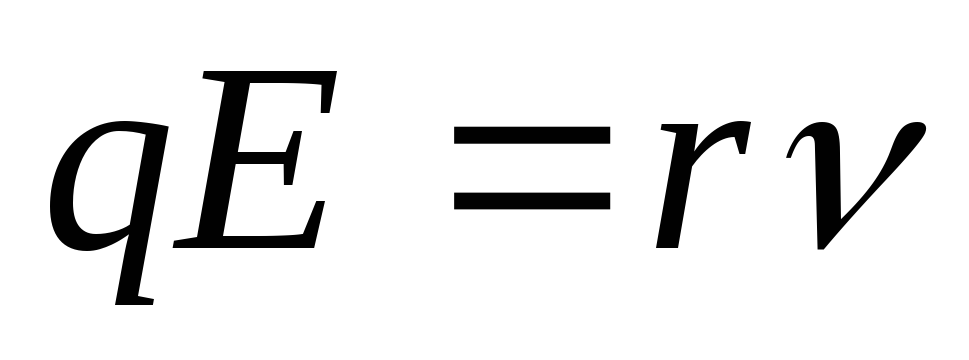 - The force acting on the ion from the field of the field is equal to the power of friction
- The force acting on the ion from the field of the field is equal to the power of friction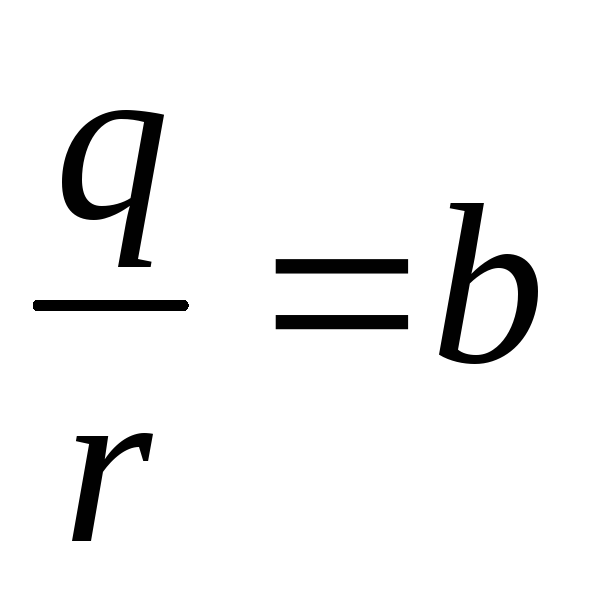 - Mobility ions
- Mobility ions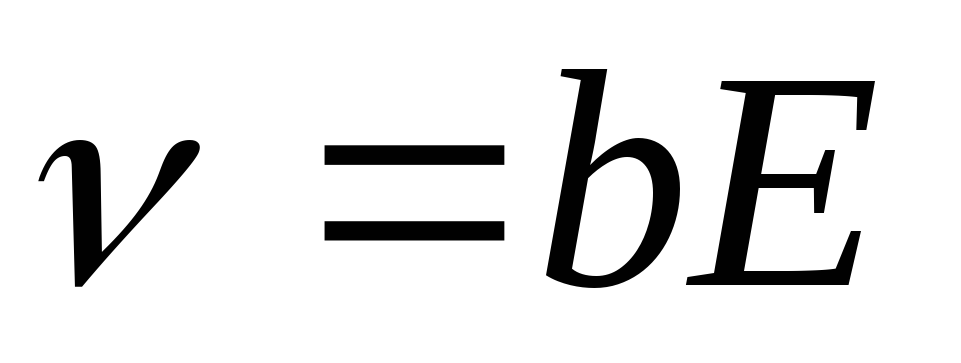 - the rate of directional movement of ions \u003d mobility, field strength
- the rate of directional movement of ions \u003d mobility, field strength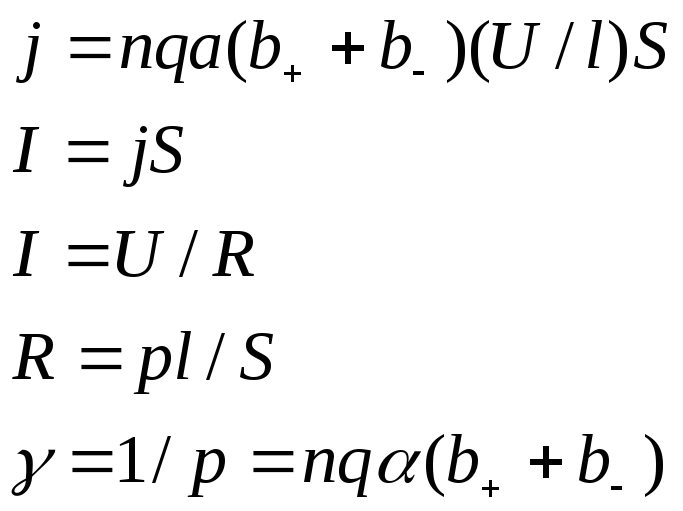
The specific conductivity of the electrolyte is the greater, the greater the concentration of ions, their charge and mobility. When the temperature rises, the mobility of ions increases and the electrical conductivity increases.
Tied with material carrier; The internal characteristic of the elementary particle that determines its electromagnetic interactions.
The electrical charge is a physical quantity characterizing the property of bodies or particles to enter into electromagnetic interactions, and the determining values \u200b\u200bof forces and energies in such interactions. Electrical charge is one of the basic concepts of electricity exercise. All totality electrical phenomena There is a manifestation of existence, movement and interaction of electrical charges. The electrical charge is an integral property of some elementary particles.
There are two types of electrical charges, conventionally called positive and negative. The charges of one sign are repelled, different characters - attract each other. The charge of the electroded glass sticks conditionally began to be considered positive, and the resin (in particular, amber) - negative. In accordance with this condition, the electrical electron charge is negative (Greek. "Electron" is amber).
The charge of the macroscopic body is determined by the total charge of the elementary particles from which this body consists. To charge the macroscopic body, you need to change the number of charged elementary particles contained in it, i.e. transfer to it or remove a certain number of charges of one sign. In real conditions, such a process is usually associated with the movement of electrons. The body is considered charged only if it is an excess of charges of one sign, the body charge, indicated usually by the letter q. or Q. . If the charges are placed on point bodies, the strength of the interaction between them can be determined by the law of the coulon. The charge unit in the SI system is a pendant - CL.
Electric charge q. any body is discretened, there is a minimum, elementary electric charge - e, which is multiple all electrical charges tel:
\\ (q \u003d n e \\)
The minimum charge existing in nature is the charge of elementary particles. In units, the module of this charge is: e. \u003d 1.6.10 -19 CL. Any electrical charges for an integer once more elementary. Elementary electrical charge has all charged elementary particles. At the end of the 19th century An electron-carrier of a negative electric charge was opened, and at the beginning of 20 V, the proton, which is the same largest charge; Thus, it was proved that electric charges exist in themselves, but are associated with particles, are an internal property of particles (other elementary particles carrying a positive or negative charge of the same value were opened). The charge of all elementary particles (if it is not zero) the same in absolute value. Elementary hypothetical particles - quarks whose charge is 2/3 e. or +1/3 e.have not been observed, but in the theory of elementary particles, their existence is supposed.
The invariance of the electrical charge is established experimentally: the value of the charge does not depend on the speed with which it moves (i.e. the value of the charge is invariant with respect to inertial reference systems, and does not depend on whether it moves or rests).
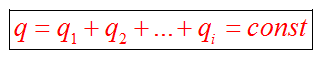
Electric charge additive, i.e. the charge of any system of bodies (particles) is equal to the sum of charge charges (particles) in the system.
The electrical charge is subordinated by the conservation law, which was set after the set of experiments. In an electrically closed system full summary charge It remains and remains constant for any physical processes occurring in the system. This law is fair for isolated electrical closed systems, in which charges are not made and of which they are not taken out. This law acts for elementary particles that are born and annihilated by pairs, the total charge of which is zero.
We have to literally to win one of the other freshly resistant and delivered things from the dryer, or when we cannot put the electrified and literally standing your hair. And who did not try to hang the air ball to the ceiling, after friction about his head? Similar attraction and repulsion is a manifestation static electricity. Similar actions are called electrification.
Static electricity is due to existence in nature electric charge. The charge is an integral property of elementary particles. The charge that occurs on the glass upon friction it is about silk is conventionally called positiveand the charge arising on the ebony with friction about wool - negative.
Consider an atom. An atom consists of a kernel and flying around it, electrons (in the figure of blue particles). The kernel consists of protons (red) and neutrons (black).
.The negative charge carrier is an electron, positive - proton. Neutron - neutral particle, has no charge.
Value elementary charge - electron or proton, has a constant value and equal
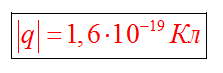

The entire atom is neutrally charged if the number of protons corresponds to electrons. What happens if one electron breaks off and flies? Atom will be more proton, that is, positive particles are greater than negative. Such an atom is called positive ion. And if one electron is joined extra - we get negative ion. Electrons, having broken off, may not join, and some time move freely, creating a negative charge. Thus, in the substance with free charge carriers are electrons, positive ions and negative ions.
In order to have a free proton, it is necessary that the core collapsed, and this means the destruction of the atom of the entire one. Such methods for obtaining electric charges we will not consider.
The body becomes charged when it contains an excess of some or other charged particles (electrons, positive or negative ions).
The magnitude of the body charge is a multiple elementary charge. For example, if in the body 25 of the free electrons, and the remaining atoms are neutral, the body is charged negatively and its charge is. Elementary charge is not divisible - this property is called discreteness
Charges of the same name (two positive or two negative) repel, variepetes (positive and negative) - attract
Point charge - This is a material point that has an electric charge.
Electric charge conservation law
The closed system of bodies in electricity is such a system of bodies, when there is no exchange of electrical charges between external bodies.
The algebraic amount of electrical charges of bodies or particles remains constant for any processes occurring in an electrically closed system.
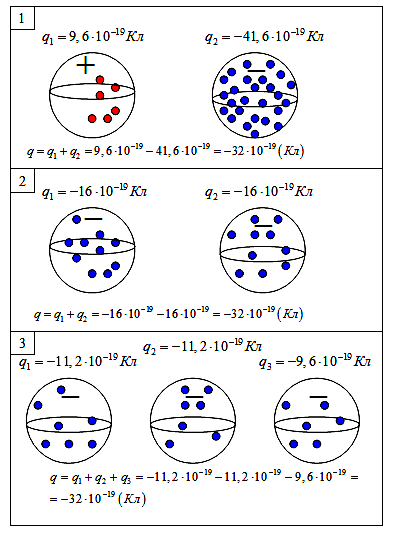
In the figure, an example of the law of conservation of an electric charge. In the first picture, two bodies of a variety of charge. On the second drawing the same body after contact. In the third figure in an electrically closed system, the third neutral body and the body brought to interact with each other.
In each situation, the algebraic charge charge (taking into account the charge sign) remains constant.
The main thing is to remember
1) Elementary Electric Charch - Electron and Proton
2) the magnitude of the elementary charge is constant
3) positive and negative charges and their interaction
4) carriers of free charges are electrons, positive ions and negative ions
5) Electric charge discrete
6) Electrical Charge




