Nuclear energy: Atomic energy - the internal energy of the atoms of the nuclei, released under nuclear reactions. Nuclear energy is based on the use chain reactions dividing nuclei and the reaction of thermonuclear synthesis.
Nuclear power plant (NPP) - the energy sector using atomic energy or nuclear. In the Soviet Union in 1943 the laboratory of atomic energy was created. V. I. Kurchatov, in which in 1946 a nuclear reactor was built. The laboratory in 1955 was renamed the Atomic Energy Institute.
Nuclear radiation is originally particles and gamma quanta emitted during the radioactive decay of the nuclei. In the further flow of particles and gamma radiation from accelerators, charged particles, nuclear reactors, etc., as well as cosmic radiation.
Nuclear fuel serves to obtain energy in a nuclear reactor. Typically, a mixture of substances containing both the codes and the kernels are capable of forming the coders as a result of neutron bombardment.
Building atom
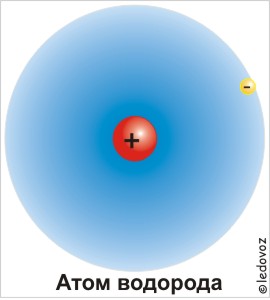
The atomic theory of the structure of the substance originated in ancient Greece. Great merit in the wording of scientific atomic hypothesis belongs to V.M. Lomonosov. He wrote that the atom is characterized by a certain mass, it has chemical properties, in molecules atoms are connected in certain quantitative relations. In 1913, the Danish physicist of the Bohr, by the basis of the nuclear model of the atom, gave a detailed picture of the structure of an atom electronic shell. He proceeded from the fact that the absorption and emission of light in the atom occurs with certain portions, quanta. From the provisions of Bor, it follows that the farther the kernel is the electron, the greater the energy of the energy it possesses. Atom, despite its insignificant dimensions 10 "13 - 10" "2 cm is a complex formation. An atom is represented as a kernel consisting of severe elementary particles - nucleons (protons - having a positive charge, and neutrons - non-charge), around which is rotated at high speed elementary particles-electrons carriers negative charge. Protons and neutrons in the kernel are firmly related through nuclear clutch forces. In the neutral atom, the total electron charge is equal to the total charge of protons. Electrons have a negative charge and thanks to this hold near positively charged kernels. The mass of the electron is negligible and is 1/1240 part of the mass of nucleon. The acquisition or loss of an electron atom changes it chemical propertiesHe is unstable and easily enters into a chemical bond with other atoms and molecules and is called an ion. The mass number of the atom is determined by the number of protons and neutrons in the kernel. The number of protons for chemical elements is strictly defined in the Mendeleev table it indicates the sequence number. In the nuclei of atoms of a substance, the number of neutrons may be different and they are called isotopes. In the Mendeleev table, they are in the same cell.
Natural radioactivity
The phenomenon of radioactivity was open in 1896 by Henri Becquerem.
In 1898, M. Slabovskaya-Curie found that radiation emit not only uranium salts, but also the element of the thorium and its compounds. She and her husband Pierre Curie allocated two new radioactive elements from uranium ore, which were called polonium and radium.
Natural radioactivity is a spontaneous disintegration of a radioactive substance with the formation of A-in and U-radiation and a new substance with the separation of energy.
The activity of the radioactive substance is a measure of a radioactive substance, expressed by the number of decays of atomic nuclei per unit of time. Unit of radioactivity decay atom per second.
Curie is a unit of measurement of activity, symbolic designation C. I Curie \u003d 3.7 x 1010 decay acts per second. Curie derivatives 1 MLKURN / 1 MCURI \u003d 0.001 Curie microcures / I MK Curie 0.00001 Curi.
Beckel is one decay of one second.
Radium - translated into Russian means radiant. Natural radioactive substances are elements that have the property spontaneously emit invisible rays. Radiy emits three types of radiation, which were named according to the first three letters of the Greek alphabet: and rays, 0 rays, U-rays.
Alpha - radiation is a flow of particles with a mass equal to 4 and a double positive charge. The alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons and is the helium element cores. Alpha particles occur during the decay of radioactive substances (natural radioactivity) or at the phenomenon of artificial radioactivity - in a nuclear reactor. They have a very small penetrating ability that makes up 50 - 70 microns in human tissues. But causing a high ionization density of 3-4 thousand pairs of ions per unit of run. In the air, one alpha particle forms 200 thousand pairs of ions. High ionization density causes high biological efficiency. Alpha particles carrying high energy (up to 800 MeV) obtained in atomic reactors have a high penetrating ability.
Beta radiation is positive or negatively charged particles. They are formed during the decay of radioactive substances (natural radioactivity) or the phenomenon of artificial radioactivity in a nuclear reactor, as well as in linear or cyclic accelerators (linear accelerator, betatron). The penetrating ability of beta-radiation, formed during the decay of the radioactive substance in the tissue is 8-10 mm. The ionization density from beta particles is 100 times less than alpha particles. At the same time, the electron flow can have a large penetrating ability formed in accelerators and depends on the energy they have.
Gamma rays - electromagnetic oscillations in their properties resemble X-rays. The energy of y-rays is usually more x-ray, so penetrating ability is much larger.
Gamma radiation is an electromagnetic oscillation arising from the change in the energy state of the atomic nucleus.
Table 4.
Properties of radiation
|
View, Nature of Radiation |
Speed |
Energy (E) |
Air Length Air - Fabrics |
Ionization density in tissues |
|
|
Kernel Gelia |
3000-4000 pairs of ions per 1 m |
||||
|
Electron flow |
87-298 thousand km / s |
50-70 pairs of ions per 1 m |
|||
|
Electromagnetic oscillations |
300 thousand km / s. |
3000 pairs of ions all over the way |
|||
The kernel of the atom contains protons, charged positively (+).
Around core but electrons are rotated negatively(-).
Modules (values) of charges of protons and electrons are equal.
The number of electrons of the neutral atom coincides with the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the total charge of such an atom is zero.It is clear that it is zero and a body charge consisting of such neutral atoms - In it, too, the number of "minuses" - electrons is equal to the number of "pluses" - protons.
If any body has the number of charges of one sign, does not coincide with the number of charges of the opposite sign, it is charged.
Note that rotons are connected by the nuclei of atoms and cannot leave the body, and the electrons located on the orbit removed from the nucleus (valence electrons) are completely able to run away from the atom. Therefore, the charge of the body depends on how many electrons it leaves. Or how much the body contains excess electrons.
If the body leaves part of the electrons, it turns out that there are more protons left. Therefore, the body is charged positively.If the body is excess electrons, the body is negatively charged.
The more surplus or the deficit of electrons on the body, the more his charge.
Charging both proton and electron elementary (Minimal existing in nature), equal to 1.6 * 10 ^ -19 CL. There can be no smaller charge.
therefore the charge of any body can only be multiple
1.6 * 10 ^ -19 CL,those., it changes not smoothly, but discretely (jumping), depending on how much this body contains unnecessary electrons, or how much they are missing. There is not enough single electron - body charge is1.6 * 10 ^ -19 CL, extra one electron - charge is minus1.6 * 10 ^ -19 CL (electrons are charged negatively). Lack of three electrons - charge 4, 8 * 10 ^ -19 CL and so on.BUT
1 pendant is a total charge of 6.24 * 10 ^ 18 electrons (or protons).So decided: the charge is of such a number of electrons to call 1 pendant.
The liter of water contains approximately 3 * 10 ^ 25 molecules. We do not say: pour me 3 * 10 ^ 25 Water molecules, say: liter, floor liters, one and a half liters, etc. Also with a pendant. Pendant - measure of a large number of elementary charges, just like liter (or mol) - a measure of a large number of molecules.
By the way, the mass of water also changes discretely: one molecule was added - the mass of water changed to the mass of this molecule itself - the jump. Like water, so the charge will not be able to divide into parts infinitely, for there is a minimum unit and the other.
It is easy to figure out that two numbers - charge of one electron
1.6 * 10 ^ -19 CL and 6,24 * 10 ^ 18 - the number of electrons, the total charge of which is 1 clinverse: Move them to get a unit.
Analogy: Oda Rota is 100 soldiers. One soldier is a hundredth share of the company. These numbers are also reverse to each other. Multiplying one hundred one hundred per hundred we get a unit:
0.01 x 100 \u003d 1.
Charged bodycreates around him electric field, and reacts to other people's fields as follows:
attracts to bodies having the opposite charge(body with spinning electrons attracts to the body with a deficit of electrons) and repelled from bodies charged just like it itself (Minus is repelled from the minus, plus from the plus).In general, behaves heterosexually.
The charged body interacts with the magnetic field, but only when the body moves relatively magnetic field. The more body charge, the stronger it interacts with electrical and magnetic fields.
To electrify the body is the easiest to lose it about another.
Video YouTube.
As mentioned above, charged bodies are either attracted to each other or repel.
Video YouTube.
The strength of their interaction is described by the law of Coulomb
The strength of the interaction of two bodies F. Directly proportional to the work of their charges q.1 q.2 and inversely proportional to the square of R between them. The charge of one body (in the coulters) multiply on the charge of the second body. And we divide the distance between them (in meters). The result multiply on k.. In different environments, the strength of the interaction of charges may vary." k."In the law of the coulon - the coefficient for specific environments in which there are charges. There will be one in vacuo k., in water - the other.
Repeat: 1 pendant is a charge of 6.25 * 10 ^ 18 electrons. If it is so much electrons in the body lacks, its charge is 1 pendant (1 CL). If the same excess of electrons is the charge of the body minus 1 CL (electrons are negatively charged). It is clear that if excess electrons, for example, is 10 times less, the charge of the body, respectively, minus 0.1 CL. Not difficult.
According to the formula, it can be seen that if at least one body is not charged (Q1 or Q2 \u003d 0), there will be no power of interaction.
Why the power of the interaction decreases in proportion to the square R between them? Because in proportional to the square of the radius area of \u200b\u200bthe sphere:
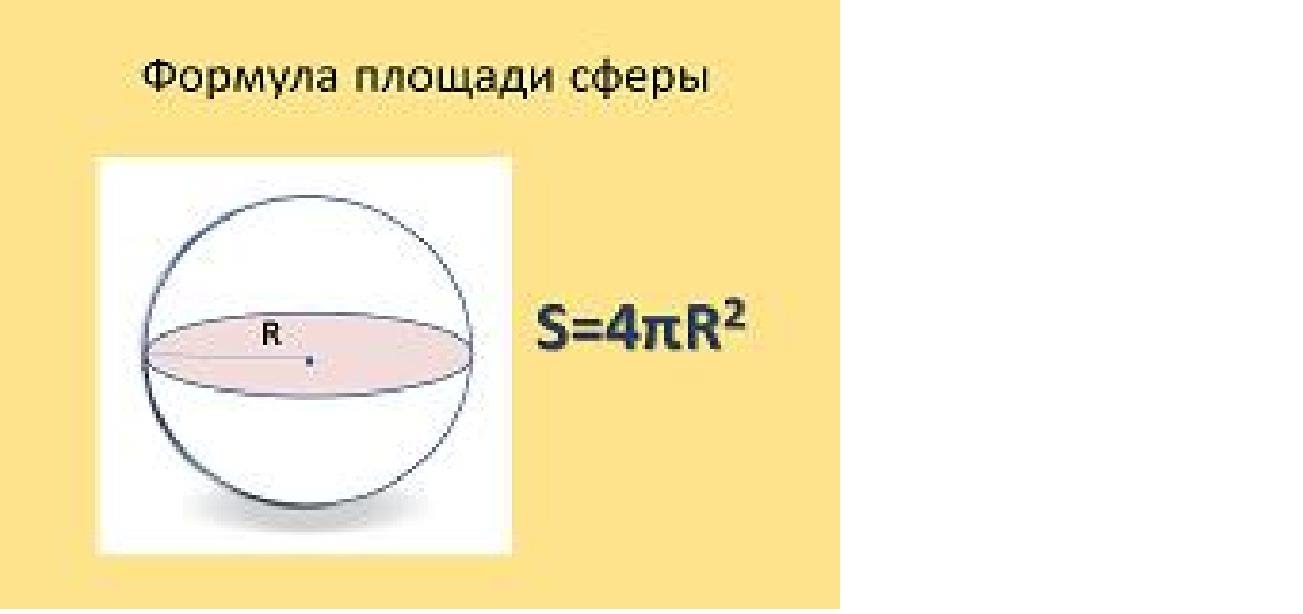
By the same law, the shock wave of the explosion decreases: if there is a wave in the meter from the place of explosionit is distributed over area 4 * 3.14 * 1 ^ 2 \u003d approximately 12 sq.m., then two meters, the energy of the explosion is already 48 sq. M.: Each unit of the area will get four times less - when doubling the distance . With an electric field of point charge the same picture. With an increase in distance between charges, the interaction force decreases fourly. With increasing distance of ten times - decreases in a hundred.
And why the charges in the formula are multiplied, not, let's say, develop?
If we, for example, double the charge of one of the interacting bodies, this will mean that the amount of missing or unnecessary electrons has doubled on it. And the power of the second body acts the same for each elementary charge. So, the strength of the interaction will double. Approximately as the Earth attracts a two-kilogram weight of a twice as stronger than a kilogram. What, in fact, reflects the law of Coulomb - the power is painted by charge.
Note that the law of Culon practically copies the law of the World Committee:
There is also a coefficient, the product of the two masses (instead of the work of two charges) and the square of the distance between them.
Electric field is created around the charged bodies. The electric field is something that affects the charged bodies, regardless of whether they are moving or not, in contrast to the magnetic field, which acts solely on moving charges. But about this later.
By the way, person is able to determine the presence of a strong electric field. If you spend the back of the palm near the very electrified body, you can feel how the hairs are moving on it. If they are.
Like any physical phenomenon, the electric field must be measured somehow.If on Earth try to raise the weight of the mass, for example, 16 kg, it will become noticeable that the earth attracts it with some force. The same girches of the moon attracts with a force of about 6 times lower.And in weightlessness, the weight (but not the mass - the measure of inertia!) Giri and disappears at all.Measuring the power with which the ice attracts various planets, you can determine the force of their grave.
The same approach is used to measure the parameters of the electric field: it is judged by the strength of which it attracts (or repels) trial positive charge:
E \u003d F / Q.
Electric field tension E. proportional to power F.acting on a point charge q.. (Point charge - concentrated on a small body, the sizes of which can be neglected).The stronger the field pulls or pushes the same charge, the greater the tension of this field.The force F is measured in Newton, the charge Q is in the coulons. Therefore, the unit of measuring the electric field e -newton / Peal.
Left body weighing 102 grams in the field of land. On the right is a weightless body carrying a charge of 1 CL, located in an electrical field of 1 Newton tension / pendant. On both bodies there are strengths of the same value - 1 Newton. The left body attracts the gravitational field of the Earth, the right - electric field.
Let me remind you: 1 Newton is a force capable of accelerating the body weighing 1 kg per 1 meter per second for one second. 1 Newton \u003d 1kg * m / s ^ 2.If the body weigh 1 kg accelerated by 1 m / s, it means for 1 second, the force acting on the body is 1 Newton. A ten-mlarogram body accelerated per second for 3 m / s - the force 30 Newton (10 kg * 3 m / s ^ 2 \u003d 30 H).
Once a free charge is positive, and pulls it down, mean, the power lines of the exterior electric field are directed from top to bottom. That is, plus fields at the top, minus below. The probe is repelled from the charge of the same name and stretches to the opposite.
Why does the field strength formula have this kind? What if you take a trial charge, let's say twice as much?
Then exactly twice will grow and the force with which the field acts on the charge. And therefore, the ratio of the power of the power and the magnitude of this charge will remain the same:E. = 2 F / 2Q.= F / Q..
We can write this formula otherwise:F \u003d E * Q.
The force acting on the charge at a given point of the field is proportional to the field strength and charge - as well as body weight(Pressure Pressure on Support) On this planet depends on the gravity of this planet and the body weight.
Another blow on the lid: q \u003d F / E.In such a form mit is possible to calculate the amount of charge according to the power, with which the electric field of the known tension affects it (as it is possible to calculate the body weight, measuring the force with which the land is attracted - actually, the scales of this force are shown). The strength in Newton is divided on Newton's tension / pendant. Cutting Newtons, we get the answer in the coulons.
As in the case of measurement of gravity, the trial charge must be small in order not to make distortion in the electrical field itself.
In fact, the kilogram weight will allow the gravity of the Earth. But if you try to use the moon as a Giri, it will become a noticeable effect of its mass. And we need to know how much the items attracts objects (measure its gravitational field), and not how power is attracted by each other two massive bodies.
If you bring to the charged body trial charge - a small body with a positive charge (hereinafter referred to as the "Prober"), the latter will either attract to the body (if their charges are opposite), or repel from it.And move the probe to the body or from it will be on a certain trajectory. The trajectory of the traffic of the probe is called the power line of the electric field.
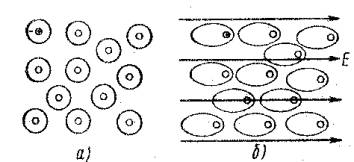
Power lines Draw with arrow indicating the direction in which the probe will move. The bodies of various shapes the power lines are different: Single spot charges - radially divergent or converging straight (a).The same form has the power lines near the sharp protrusions of charged bodies.
If there are bodies with charges of opposite characters nearby, some of the power lines begins on positive charges and ends on negative (b).
At the same-name point charges line is approximately the same, but "divergent" in the zone between charges (B).
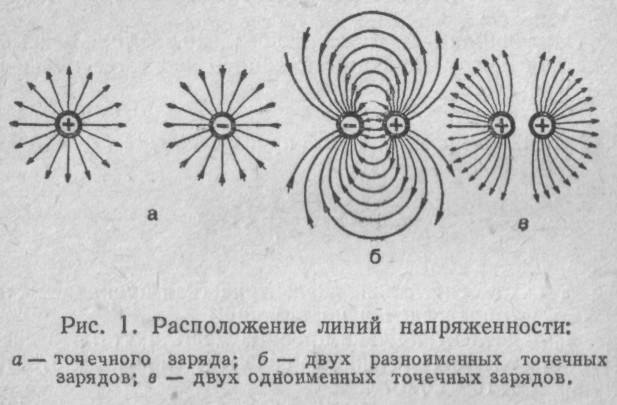
Do not forget: power lines show the trajectory of motion of a positive test charge.
It is noticeable that the lines thickness falls with the removal from charges. But it happens not always.
Remember the explosion example? The power of the shock wave drops in proportion to the square of the distance. But if the explosion occurs in a narrow corridor or mine, the shock wave without weakening can leave quite far away - simply because it has no place to dissipate: the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe corridor (hence the shock wave) does not change with removal.
The same picture is close to a flat plate of a large area. Power lines are parallel to each other, and the electric field (its tension) E. Does not change at a fairly large distance from her.
Superposition principle
The thing is obvious. If we had another land under our feet, the strength of gravity would double. If two are tripled.AND the fact: the fact: the strength of the moon "punches" to the Earth, causing tides and fed in the coastal areas of the oceans. This phenomenon does not interfere with the presence of its own gravitational field of the Earth. Pthe rinjip superposition says: The electrical field of each body spreads in space, regardless of the presence of other electric fields around . Fields do not affect each other, but simply summed (fold).Let's go back to the drawing with two charges of the same name:
It seems, it can be seen that the fields of these two bodies affect each other? Otherwise, why are the power lines such curves?
Let's try to understand why the lines have such a form. Suppose the probe (small gray circle in the figure) is on the surface of the right body, at the point where its left upper power line begins.Since the body and the probion are charged the same, the latter will push away from the body surface and will begin movement towards the center of the right body, perpendicular to its surface. At this point, the influence of the right body on the probion is large (as it is close), the effect of the left body is unnoticed (we remember: the fields of point charges decrease in proportion to the square of the distance from them). As the probe is removed from the right body, the influence of the latter decreases, but the effect of the left body is growing (which also repels the probe). As a result, the testament "There is no way to go", except to the top: it is pushed and on the right and left. What demonstrate the power lines. The individual power lines of both bodies both were and remain radial (directed from the center to the parties, like the rays of the sun).
You can depict the forces acting on the probes in the form of vectors (arrows). Vector direction will show the direction of strength, vector length shows the size of this power.
Forces acting on body probes A. marked a.body B., accordingly, b.. Vector c. - resulting (sum of vectors a. and b.). Remember how vectors are folded and lay down on the probes of force.
On a straight line between centers A. and B. Vectors are mutually destroyed. Their amount is zero. And a trial positive charge, which is in the midpoint, will not move to the left or right. It is understandable even without addition - it pulls it and left and right in the same way. (If this probion was originally not in the center, it will still be poured into the center, to the point of "equilibrium" for the closest body pushes more than far). If the probe is closer to the body A.(the second on top in the picture), vector a.depicting the force acting from this body long (since the force acting on the side of the close body is greater). Vector b. forces acting on the part of the body B., short. Summing vector c. Shows the direction of the resulting force, and it became - and the direction where the platoon moves. BUT the direction of movement of the probe and there is a power line.
Exactly the same picture will be between multi-chain charges. Want - fold the vectors, want to follow the movement of the positive probe at each point - the result is one.
The probe departs from the left body perpendicular to its surface. As it removes from the left body, the influence of the latter decreases, but the effect of the right, attracting probe is growing. Therefore, the trajectory (path) of the probe is bent in the direction of the right body. From here curves power lines. It can be noted that the power lines are tangents to arroges-vectors.
If our charged bodies are placed in any dielectric, the field strength around them (or between them) will decrease several times:E \u003d E. 0 / ε, whereε - coefficient dielectric permeability showing how many times the tension decreased compared to the vacuum.
That in practice gives thisε? The reduction in the electric field strength means that the strength will act on our favorite probe, than in vacuum. How many times less - showsε. If this design
move from vacuum to distilled water (ε water \u003d 81), the right spring stretches 81 times less! Reduces dielectric interaction charges. If you put a dielectric with a bigε Between the capacitor plates (the device stored), this condenser will be able to store inε times more energy.
Surface density charge
Recall how the bodies look like with a great magnification:

Red balls - atoms charged positively (because part of the electrons leave them), the blue balls are negative electrons.If the number of body protons is equal to the number of electrons, the body is not charged. If the body has, for example, excess electrons, it is charged negatively. But there is an interesting point -all excess electrons will be ousted on the surface of the body!No charge charge.
This happens for a simple reason: Lyland Electrons are repelled from each other, since they are charged the same name. And where will the electrons be at the maximum distance from each other? On the body surface, where else.
If the electrons in the body lacks (the body is charged positively - protons are greater than electrons), the picture is reverse - ithe dum will attract electrons by driving them inside. Outside T. e.lA will be a deficit of electrons. But this means that the surface of the body is charged positively. Again charge on the surface!
The above applied to conductors (substances inside which electrons are not attached to atoms) - electrons have the ability to move inward or outward. However, with insulators(In the insulators electrons still) The same picture - the charge is always outside. And just because of the impossibility of moving electrons: electrons are either closed from the surface of the insulator, or extra electrons are made to the surface of the insulator.And if so, physicists introduce the concept of "superficial charge density".
σ =
The surface density of the body charge is equal to the ratio of charge to the surface of the body surface.
We remember: the charge is what electrons and protons are worn. It is clear that two bodies with the same charge(i.e., the same snuff or electron deficit) may have different surface density Charge - if they have a different surface area. Electrons can be "smeared" along a large area, or concentrated on a small patch.
Closing ahead, we note that it is the form of the body is determined his electrical capacity - As far as "closely" on it electrons. And the more electrons are gathered on a unit area, the higher it turns out potential Body.
Two different charged plates
capped by an electrical capacitor. Their electric field looks like this:
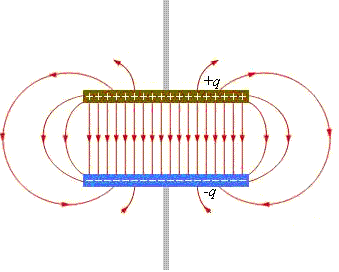
Between the plates, the power lines go, it is clear from the plus to minus, and above and below the plates of the electric field there, for the field of one plate compensate for the fields of the second plate.
The electrical capacitor keeps the electrons themselves, not their excess or deficiency, but the difference: how many electrons are not enough on a positive plate (it is called a clamp), as many extra electrons on a negative plate. To charge the capacitor, it is required to overtake part of the electrons from one plate to another.
Electric dipole.
These are two identical spot chargeSpace in space and rigidly connected with each other. Design, like dumbbells, which one ball is charged positively, the second is negative.
Since the charges are separated, dipoles react to an external electric field (unfold by a positive end of the field) and interact with each other - the oppositely charged ends of the neighbors attract each other.
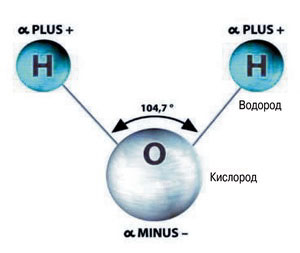
Such structures with separated charges exist in nature. Water molecules just represent such dipoles ("di" means "two") - two related separated charges ( in the water molecule of separated charges, three, but two positive charges can be represented as one double, which is approximately in the middle between them).
In water molecule H2 O Electrons connecting atoms are shifted to oxygen atom. Therefore, an oxygen atom is negatively charged. The atoms of hydrogen H are devoid of electrons and therefore are positively charged (alone protons remained from atoms).
Due to the dipole, the water molecules briefly stick into clusters - groups of molecules - the positive ends of some molecules are attracted to the negative ends of other molecules:
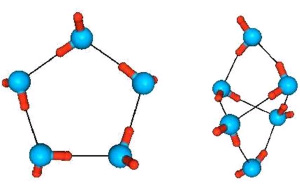
The dipoleness of water molecules explains the high coefficient of its surface tension. Water molecules behave like a bunch of magnets - stick together with each other. And if there are such "magnets" next to water also in the surface - polar molecules, then the water will wipe such a surface. If not - water molecules. And this effect can be.
Conditions
Atoms of some substances weakly hold their electrons that are at the most remote orbits.(valence electrons). Such substances are called conductors. Electrons that broke away from atoms are capable of moving inside the conductor. And since there are charged particles capable of moving, these substances carry out the current, sincecurrent is an ordered movement of charged particles. Actually, the name "Explorer" and means the ability to conduct electricity. In particular, the conductors are metals:
Video YouTube.
The general condition for the belonging of the substance to the conductors is the presence of free (capable moving inside the substance) of charged particles. In addition to electrons, such charged particles can be, for example, ions in ionized gases and aqueous solutions of salts and acids.
NaCl salty molecules at dissolution in water are split into ions: Na + and Cl-. Sodium atom, giving one electron of chlorine atom, turns into a positive ion, chlorine, with an external electron, selected from sodium to a negative ion. And if there are two wires in the aqueous solution of salt and supply voltage on them, sodium atomsNa +. Move in the direction of "minus" (negative electrode), chlorine atomsCl- In the direction of positive. Why - it is clear: the opposite charges are attracted. Atom sodium lacks one electron, it can get it on a negative electrode. The chlorine atom can reset an excess electron on a positive electrode. Reaching electrodes, both types of ions are converted into source substances - sodium and chlorine. But we were distracted, because now we are not talking about electrolysis, but about electric current - the motion of charged particles. The movement of chlorine and sodium ions in the direction of the electrodes and there is an electric current.
Video YouTube.
Conductors in the electric field.
We remember that the conductor contains moving charged particles. We also know that the opposite charges are attracted, and the same names are repelled. Based on this, you can guess what will happen in the conductor when it turns out to be in the electric field.
The left-hand picture shows the metal in the absence of an electric field. Positively charged kernels and free electrons are distributed evenly. Otherwise, it cannot be: if in some kind of metal region there will be overhang of electrons (such a short-term local change in the concentration of electrons is called fluctuation), they, by mutual repulsion, will quickly leave this place. If the local electron deficiency arises, it will mean that positively charged nuclei there are more. And the electrons will be attracted to this area by Coulomb forces.
When an external electric field appears (the middle picture), the electrons are understandable, move in the direction of the "plus" of this field, that is, left (power lines, remind, draw from the plus to minus field). But. Once the electron is "left left", the excess of positively charged cores turned out to the right. That is, inside the metal formed its electric field due to the movement of the part of the electrons. And since the "plus" of this own field on the right, and "minus" on the left (where the electrons gathered), it means that the conductor's own electric field is directed on the external. And at the moment when the internally comes with an external, the electron movement stops (the right picture shows the equality of external and internal fields). It is clear that the stronger the external electric field, the more electrons shift to the left.
The redistribution of charge carriers under the influence of an external electric field is called electric induction.
It is clear that turning off the external field, we will restore the status quo: electrons will leave the left surface and will be evenly distributed via the conductor.
Note: if the conductor is divided into an electric fieldoverall (across the field), each half of the conductor will be charged: on half from the plus of the field there will be an excess of electrons, on the second half - a deficit.
If within the conductor there is a cavity (emptiness), there will be no electric field in it - precisely because of compensating for the external electric field with its own conductor field. The inner cavity in the conductor is protected (they say "shielded") from external fields. Electrostatic protection is based on this: items are placed in a grounded (connected conductor with a soil) Metal shell, not necessarily solid, it is also suitable for a mesh (the so-called "Faraday Cell"). Very effectively demonstrates the action of such protection one of the "destroyers of the myths" Adam Sev(Adam Savage):
Video YouTube.
The voltage of artificial lightning can be judged by the following fact: the dielectric strength of the air is 3,000 volts per millimeter - if the electrodes that are at a distance of one millimeter from each other, to file a voltage of 3,000 volts, an electric sample occurs between them - an electric arc. Accordingly, one meter is required to break through a thousand times more - 3,000,000 (three million) volts. Recall that in the voltage household electrical network 220 volts are enough to kill a person. Nevertheless, Adam, apparently, feels nicely at the length of lightning hitting the cell, clearly longer than two meters.
By the way, music in this roller reproduces the lightning themselves: the voltage on the Tesla coil is served from the audio amplifier. The air in the channel of the electrical breakdown is expanding due to heating and ionization, creating sound. Even more effectively watch lightning strikes incurrent suit.
Dielectrics in the electric field.
So that the substance spends the current, that is, so that the charges can order in it, the presence in the substance of the carriers of this charge is required, and movable. And dielectrics do not have them. More precisely, the charge carriers themselves are ( anyone The substance consists of atoms, and atoms contain positively charged protons in nuclei and negatively charged electrons in orbits around the cores), but these carriers cannot move by dielectric. In dielectrics, electrons are tightly held by atoms, and free electrons are very small.You can read about the reasons on the page. "
When heated, the conductivity of dielectrics is growing: the temperature is a measure of the speed of the atoms and electrons of the substance. The faster Mov. atoms and electrons of the substance, the higher its temperature. Therefore, the larger number of electrons is broken away from atoms (as highly overclocked satellites can leave the Earth orbit) and become free (and therefore can be transferred to the charge).
Metals, when heated, on the contrary, the current is worse. In metals already at low temperatures there are enough free electrons that provide conductivity. With increasing temperature, the amplitude of oscillations of atoms fixed in nodes crystal lattice, and the electrons are harder to get through this lattice.
Polar and non-polar dielectrics.
What does an atom look like, for example, a hydrogen atom? This is a proton in the kernel and the electron rotating around the kernel at such a speed, which one can say that the "minus" of the atom of the smeared around the "plus". "Centers of gravity" of both charges coincide. The properties of such an atom are the same in all directions - he is a ball.
If such an atom turns out to be in an electric field, what happens to it? Probably the atom core will shift along the field (in the direction to minus, like a trial charge), and an electronic cloud - in the opposite direction?
For sure. That is exactly what happens. Now our atom appeared poles: negative left and positive right. That is, the atom polarized. This type of polarization is called electronic or deformation polarization. The meaning is clear: electronic - because the electronic cloud shifted relative to the kernel. Deformational - see that the electric field made with our perfect ball: it deformed him, flattened.
Now take the water molecule. It originally ears the poles, since the oxygen atom pulls the electrons of both hydrogen atoms. Therefore, the oxygen atom becomes the negative pole of the molecule, and the hydrogen atoms (more precisely the point of approximately in the middle between atoms of hydrogen) is a positive pole.
And since the molecule has a positive and negative pole, it is clear that in the electric field it will unfold a plus to minus, minus - to the plus of the field:
This type of polarization is called orientational (polarization due to the orientation of molecules).
It is clear that when removing the external electric field, the position of molecules will happen.
However, there is a trick: if to polarize such a dielectric in liquid form, and then give it to frozen, the molecules will not be able to return to the chaotic state. Dielectric, for a long time retaining polarization, is called an electrofem. The electrotte itself creates an external electric field. You can read more.
Another type of polarization is ion polarization. Its usually demonstrate on the example of the crystals of the table salt Na CL:
Salt crystals consist of positive sodium ions and chlorine negative ions (why it is - on the page in the "ion connection" section).
It is clear that in the electric field, sodium ions will be shifted along the field, chlorine ions - against the field.
From the above, you can make a cramole conclusion: dielectrics are also carried out electric current. After all, what is the current? Current is an ordered movement of charged particles. What happens in the process of polarization? It is such a massive direction. The only difference is that the movement of charges in dielectrics is limited to an atom limits during a deformation polarization and a turn of molecules - with orientational polarization. Well, and the displacement of atoms in lattices with ion polarization. That is, current flows, but very short-term. While the charges "do not disappear into the wall" - in the same way as this happens during the polarization of conductors in the electric field (it is called electrical induction, see above).
Such currents are called polarization - current only at the time of polarization of the dielectric.If we are very quickly and often change the direction of the external electric field, then, by constant changing the direction of polarization, the current will flow in the dielectric. Clearly, exceptionally variable. It is polarization currents that hears food into the microwave stove.
When the polarization of dielectrics on their surface (and only on the surface), negative charges appear to the plus of the external field, and there are positive charges on the surface from the minus of the external field.
These charges are associated (with substance molecules), that is, they cannot be removed from the surface.
Inside the same dielectric, total charges are zero, and the electrical fields of polarized molecules are directed against the external electric field. This is currently visible to another analogy with conductors. But if there is no electrical field inside the conductor, it is present inside the dielectric, although weakened several times. For example, in distilled water (we remember, it has orientation polarization), the electric field decreases 81 times. This the attenuation coefficient of the external electric field is called dielectric constant.
The dielectric constant
Take two differently charged plates. The power lines between them are directed from the plus to minus, the length of the arrow lines symbolizes the field strength.
Now imagine that between the plates we have some designs in the form of spaced point charges on chopsticks (electric dipoles), capable of rotating around your own center of gravity.
If our plates are charged, these structures turn out to be clearly as: plus to a minus plate, minus to the plus. What is happening now? The electric field created by the plates is superimposed by an electric field existing between the balls on the stick (short arrowers along the sticks). And this field is essential opposite to the field created by the plates. And if so, the field strength between the plates will fall! Therefore, on the right drawing, the arrow between the plates is shown shorter.
If you pour distilled water (it consists of dipoles) between charged plates, the water molecules turn on oxygen atoms to a positive plate, hydrogen atoms to negative. The interaction (attraction) of the plates will decrease - as well as the electric field strength between them (action per test charge). And 81 times! This figure is 81 and called dielectric permeability of dielectric. It shows how many times the interaction of charges in this dielectric is weaker than in vacuum.
For different dielectrics, this figure is different - It depends on the specific location of atoms in the molecules of the polar dielectric. Table of dielectric constant of some substances - .Work of the power of the electric field.
For the charge, which is in the electric field, the force acts. If the charge, yielding to the action of this force, will begin to move, it means that the field makes work. How else? If something happens, then someone (or something) works.
In physics work is equal to a change in body energy - object application object.
For example: the kinetic and potential brick energy lying on the ground is zero. If we stamp brick, then let us give him kinetic energy - the energy of movement. It is equal to the product of the mass M of the brick (in kilograms) to the square of its velocity V (in meters per second) divided by two E \u003d M * V ^ 2/2.The resulting result, measured in Joules (J) is equal to our work (and the acceleration of the brick, i.e., transmitting energy to it, and there is a job) A.Also measured in Joules.
If we raise the brick on some height, perfect work will be equal to potential energy Bricks at this height: E \u003d M * G * h. The mass of bricks in kilograms M multiply on the gravitational constant G (rounded 10) and to the height of the lift in meters h. And in this case, the brick energy will be equal to the perfect work. A. In the same joule. It can be seen that the greater the mass of the brick, the power of gravity on this planet and the height of the lift, the greater work we do. our work Describes formula
A \u003d m * g * s * cos a
The work is equal to the product of M mass, accelerating the free fall (it is the same gravitational constant of the Earth) G, the path passed. About cosine just below.
Now take a look at the formula describing the work of the electric field when the charge is moving, on that part of the formula that after the second sign of the equality:
Electrical field work A. Equal to the product of the charge q, the intensity of the field E and the change in the distance of Delta L.
All the same as our brick: the work of the gravitational field A. It is equal to the product of M mass (its analog in electrostatics - charge q), gravitational constant G (analogue - field strength E) and changes in the height of the delta H (distance L).
Still in the formula there is a cosine. You can read about it on the page. Its meaning is this: we can raise our brick vertically (along the line with in on the left triangle), or insert along the inclined plane and in the same height. Regardless of the lifting trajectory, the height of the brick at the end point in, and therefore, its potential energy will be the same.Therefore, and the work perfect by us is the same in both cases.
However, the path of brick up along the roller coaster is longer than the vertical lift. If we stupidly substitute the traveled path s. in the formula
A \u003d f * l * cos a
ignoring cosine, it will come out that the more common hill (the longer our way), the greater work we made. And this does not correspond to reality (gently gear easier, though longer). Cosine same just shows how many times the way is shorter than the common Lifting (for this angle). Suppose our slide is twice the straight path. This ratio happens when the angle between the vertical and a slide is 60 degrees (we look at the cosine table). The cosine of an angle of 60 degrees is 1/2, or that the same, 0.5.Suppose height of lifting 3 meters. Raising brick vertically, we substitute in the formula these 3 meters (s). The cosine in this case is equal to one (COS 0 \u003d 1).
Raising the same brick on a six-meter slide, we multiply its length on the cosine of the angle between the plane of the slides and the vertical, that is, on 1/2 and we get the same troika.
Now everything converges: regardless of the trajectory, lifting the brick on the same height means performing the same work.
On the table of cosines, you can learn how many times rolls with in shorter hypotenuses A B for any angle, for example, for the right triangle with an angle of 45 degrees.
But it only makes sense with the cosine in the direct trajectory of the movement at least the charge. More often the trajectory is more complex. However, as mentioned above, the work depends only on the difference in the potential energies of the manipulation object - brick or charge - in the initial and endpoints of the trajectory.
Since we went from the brick, you can present the situation: your work is to deliver bricks from the lower floor of the building of the bricklayer, working on the second floor. The bricklayer is indifferent to how bricks fall into it: on the vertical lift, along the fire or access ladder, and even a transit through the ninth floor. He is important only the result - the brick was initially lying on the ground, and now it is, he has in his hands. And you will get a salary for your work regardless of pretzels with brick: solely by the result. That is, by the difference in the energies of the brick.
It is clear that if the brick moves down, the work of its movement makes a gravitational field. At the same time, the potential energy of the brick decreases.
To the movement of charge in the electric field, the above is fully: the operation of electrostatic forces when moving the charge q in the electric field is equal to the potential energy of this charge:
A1-2 \u003d wp1 - wp2 \u003d q φ1 - q φ2 \u003d q (φ1 -Φ2).
Similarly, the measure of the work of the gravitational field of the Earth is to decrease the potential energy of the body:A 1-2 \u003d W P1 - W P2.
The body mass M (in kilograms) at the height G (in meters) has potential energy (in joules) equal to M * G * H, where H is the height of the body above the ground level. Since at the level of the Earth height H is zero, then the potential body energy on zero altitude is equal to zero(W p2 \u003d 0): Multiply the product M * G to zero (it is logically understandable: the body on zero height cannot make any work. There is no energy). Therefore, the work of gravitational forces when moving the body from the height H to zero is equalm * G * H - 0 \u003d M * G * H \u003d W P1. In short: a \u003d w p1.
So the work of electrostatic forces when moving the charge Q from the point where this charge has potential energy to a point with zero potential energy equal
A \u003d w p1 \u003d Q * φ.Another aspect: our brick, lying on Earth, does not have potential energy only with respect to the surface of the Earth. But imagine. Which in the ground was pulled by a well. In relation to the bottom of the well. Brick will have energy will already be, and falling there can make business.
But the brick. Lying at the level of the second floor has energy only relative to the Earth. Regarding the second floor, its energy is zero. Conclusion: The potential energy depends on the point of reference. From what level we accept for zero.
Electric field potential.
Tutorials say: electric field potential - scalar valuepotential energy W P. single charge Q, placed on this point φ \u003d w p / q.
Let's return to gravitational-massalogs.We define the potential of the gravitational field. Let's call it the same:φ. FROM We will do the gravitational formula, not forgetting that the charge Q for gravity is Mass M
φ \u003d W p / m:
the potential of the point of the gravitational field is equal to the ratio of the potential energy of the body to the mass of this body. But sinceW p \u003d. m * G * H (formula of potential body energy), it turns out that the potential of the field φ \u003d M * G * H / M.
But - to practice. The "point of the gravitational field" will, say, the windowsill window of the second floor at an altitude of 5 meters from the ground. How to determine the potential of this point?
We take our favorite brick. Let his mass of 2 kg.
φ \u003d W p / m \u003dm * g * h / m.
We multiply the mass of bricks (2 kg) to accelerate the free fall (roughly 10 m / s ^ 2) and height (5 m). The result (100) is divided by the mass of the same brick (2 kg). We get: the gravitational potential at the level of the windowsill is 50.
And 50, in fact, what? Which units to measure? In which it will work out, in such a measure:
kg * m / s ^ 2 * m / kg.
Kilograms in a numerator and denominator will reduce. Meters too. There will remain a square square in the denominator: 1 / s ^ 2. The potential is 50 / s ^ 2.
Wikipedia We agree with us: "The gravitational potential is the scalar function of coordinates and time characterizing the gravitational field in classical mechanics. It has the dimension of the square of the speed, is usually indicated by the letter φ . The gravitational potential is equal to the ratio of the potential energy of the material point placed in the point of the gravitational field under consideration, to the mass of this point. ".
Note that we would have walked perfectly without bricks: what's the point of multiplying on his mass, and then share it? We will reduce the mass in the numerator and denominator:
φ = m * G * H / M \u003d G * H.
The potential is equal to the product of speeding free fall and the height of this point:
φ = G * h.
Main Question: Cheren? Why do we need to know the potential of the gravitational field?
It's simple: from this figure, for example, the energy that the hydroelectric power station produces is producing - the greater the height and acceleration of the free fall at the water fence point, the more power station will give energy. And do not think that the acceleration of the free incidence is permanent: it depends on the location of the rocks in the earth's thicker, from geographic latitude (the land rotates, it became, the acceleration of the free fall from the equator less) and even on the time of day and the position of the moon - marine rings And the lowers are just caused by the fact that the potential of the gravitational field "walks" due to the imposition of the gravitational fields of the Sun and the Moon on the ground field (remember the principle of superposition).
However, it's time to return to electricity.
Remember, the parameter of the electric field "tension", equal to the ratio of force acting on the charge to the magnitude of this charge (E \u003d F / Q)? Is this field characteristic not enough? Of course not. The field strength corresponds to the strength of gravity. But the water with the same force is attracted by the Earth both on the meter altitude and in Staterova. And an electric field, for example, between the capacitor plates, all over the negative plague to positive with the same force acts a trial charge. The charge may be far from the end point of the following, and maybe near. It is clear that on a long way the charge (like water in the power plant) is able to make more work than on a short one. Therefore, this parameter is necessary - the potential of the electric field.In the international system of units (s) unit of potential is"Staining" with the "height" of 1 B, charge in 1 CL is able to work in 1 J.
And the load of a mass of 0.1 kg, going down from a meter height, can take the same work. More precisely, the same work.
And yet: we found out the potential of the gravitational field at the level of the second floor window sill. The height difference between the windowsill and the earth is 5 meters. It is clear that if it is above this windowsill, there will be another one, above the first on the same 5 meters, the potential difference between the windowsills will be the same 50 / s ^ 2.
In electrostatics, too, for zero (base), "Earth" is not always taken - a conductor with zero potential. More often they talk about the "potential difference" between the points of the electric field or between the conductors.
Reset the ball with some height. Falling, it loses potential energy (remind you by the formula: Ep \u003d M * G * H, where m is the mass of the ball, G is the acceleration of the free fall, H is height). It is clear, the loss of potential energy occurs due to the parameter H - height, since M and G are constant. However, losing height, the ball is gaining speed, which means that the kinetic energy is EK \u003d M * V ^ 2/2, where V is the speed. And the sum of these two energies - kinetic and potential - at any time standing (const) and is equal to the initial potential energy of the ball: EP + EK \u003d const.
Or:m * V ^ 2/2 \u003dm * G * H1 - m * G * H2. BUTg * H, as we remember, this is the potential of the point of the gravitational field.
This is also valid for the body with the charge Q and mass M, accelerating in the electric field:
m * V ^ 2/2 \u003d Q * φ1q *Φ2.
Q * ( φ1Φ2.)
Page 3.
The substances surrounding us (bodies) consist of atoms and molecules that have positively charged kernels and adversely charged electrons. Atoms and molecules are electrically neutral, since the nucleus charge is equal to the total charge of electrons surrounding the kernel. Under some conditions, for example, with an increase in temperature, an atom or molecule is losing an electron. Such an atom (molecule) turns into a positive ion.
Each atom when it is in good condition, the total electron charge is equal to the charge of the kernel. In such a state, the atom is electrically neutral, since the charge of the nucleus and the total electron charge is neutralized.
As noted, in the usual state of the body are electrically neutral, since the total charge of electrons and protons included in the atoms is zero.
In the absence of a magnetic field of plasma behaves like ordinary gas. The reason is that the plasma is quasi-lineatrical: even in sufficiently small (but not microscopic) volumes, the total charge of electrons and positive ions is zero. Therefore, in the absence of an external magnetic field, the plasma phenomena is described by conventional hydro-or gas dynamics equations (see ch.
Thus, the molecule both in relation to the field created by it and in relation to those experienced in the external field of the forces equivalent to the dipol. The positive charge of this dipole is equal to the total charge of the nuclei and is placed in the center of gravity. positive charges; A negative charge is equal to the total charge of electrons and is placed in the center of gravity of negative charges.
With the length of the gaps of about dozens of centimeters and more before breakdown, the volumetric charge embedded with avalanches and rigs, significantly levels the gap field at a considerable distance from the surface of the electrode. At the same time, the field strength in the region, permeated with the streamer, is not lower than 5 - - 10 kV / cm. Under these conditions, the length of the streamer is also dozens of centimeters, and the total charge of electrons QEZZ (L - i - 2) LQ - U to. K, What is enough for thermal ionization of gas.
As is known, all substances consist of molecules, which are a combination of individual atoms. Each atom consists of a positively charged nucleus and adversely charged electrons moving around the kernel in electronic shells on various elliptic orbits. The total electron charge is equal to the charge of the nucleus, so the atom generally is electrically neutral. Electrons moving along the nearest to the kernel orbits are firmly connected to the nucleus, do not participate in chemical reactions And do not affect electrical conductivity. Electrons of external orbits are the so-called valence electrons - determine the chemical properties of the substance and the ability to carry out electrical current.
The appearance and disappearance of electrical charges on bodies in most cases is due to the transitions of elementary charged particles - electrons - from some bodies to the other. As you know, the composition of any attendance is consistent with a positively charged core and negatively charged electrons. In the neutral atom, the total electron charge is accurate equal to the charge of the atomic nucleus. The body consisting of neutral atoms and molecules has a total electric chargeequal to zero.
Around the kernel on closed (elliptical) orbits, electrons are moving, forming an electronic shell of an atom. The kernel charge is equal in the absolute value of the total charge of electrons.
According to this theory in the center of the atom there is a positively charged core around which electrons rotate. In general, the atom is electronically, since the overall charge of electrons is numerically equal to the positive charge of the kernel. The mass of electrons is negligible, therefore, almost the entire mass of the atom is concentrated in its core. The size of the kernel compared to the size of the atom is extremely small. The volume occupied by atomic nuclei is approximately 10-13 of the total volume of atoms. It follows that the density of atomic nuclei is very large.
Currently, it has been established that the atom of each element consists of a positively charged nucleus and rotating around negatively charged electrons. The mass of electrons is negligible, therefore the mass of the atom is mainly concentrated in the kernel. In general, the atom is electronically, since the overall charge of electrons is equal to the charge of the kernel.
Currently, it has been established that the atom of each element consists of a positively charged Yadea and rotating around negatively charged electrons. The mass of electrons is negligible, therefore the mass of the atom is mainly concentrated in the kernel. In general, the atom is electronically, since the overall charge of electrons is equal to the charge of the kernel.
on - negative. Therefore, the kernel holds electrons in the atom; The force of attraction to the CCU makes the electrons move around it.
The same electrical forces are determined by the size of atoms. With a very close convergence of two atoms, there are huge repulsion forces between their electrons. These forces impede further rapprochement and determine the volume occupied by an atom; Another atom cannot penetrate this volume.
Repulsion forces between atoms arise when orbits (paths) of their electrons intersect. Therefore, the size of the atom is approximately determined by the diameter of its largest electronic orbit (see Fig. 2).
Electrization tel friction
Why don't we observe electric forces Attraction and repulsion between the bodies around us? After all, all bodies consist of atoms, and atoms are from particles with electrical charges.
The reason is that atoms are generally neutral. The general negative charge of all electrons in the atom is equal to the positive charge of the kernel. The total charge of the atom is zero. And once neutral atom, - neutral and molecule. And the body consisting of atoms or molecules is also neutral; It does not have an electrical charge.
Take a glass wand and pull it hard with a piece of dry silk. In this case, part of the electrons belongs to the glass molecules and moves to Molyulam Silka. There is a so-called both glass of glass molecules, converting them from neutral particles into electrically charged particles - and about n. Glass molecules that have lost one or more electrons are no longer neutral. The positive charge of the nuclei in such a molecule is greater than the negative charge of the electrons remaining in it. The molecule is charged with n oh oh and t a n n n oho german bodies of ion. An atom or molecule that captured one or more extra electrons is called negative ions.
If you touch the bats to two sheets of cigarette paper suspended on the threads, then the part of the electrons from the leaves will be attracted positively
a charged wand and goes on it. Feltism will be charged positively and become repelled from each other, Jac is shown in Figure 3.
Leafs can be charged and negative. For this, instead of glass it is necessary to take an ebonite or mesh palmistry, and instead of Silka - fur or woolen fabric. When rubbed Surguche or ebonite with fur, some electrons moves from fur on a wand and it charges negatively. Eleitrons are pulled out from each other. Therefore, when the wand touches the leaf of cigarette paper,
Fig. 3. Dae Olyiacoao charged papers repel.
Fig. 4. Major Different Charged
papers are attracted.
part of Eleitron goes to it. Two foreheads, which we are inherent ebonite or mad chicken, dress up negatively. Between themselves, they are thawing taia, as pozano in drawing 3, and 1ris is attracted to positively charged sheets. four).
Page 1.
The total charge of the electrons is equal to the charge of the proton, however, under certain conditions, part of the electrons that are the most movable particles can move from one atom to the other, as a result of which the electrical equilibrium inside the atom is broken and the way is positively or negatively charged.
If the total electron charge is equal to the positive charge of the ball, the atom as a whole is neutral.
The charge of the nucleus of the atom and the total charge of electrons rotating around the kernel is the same in size, but differ in the sign. Therefore, the atom as a whole has no charge; He is electronically.
If the nucleus charge is equal to the total charge of electrons, then the atom is called neutral, and in the case when this condition is not performed - ion. The simplest of all is a hydrogen atom, which has only one electron. The kernel of the hydrogen atom is called a proton. In the following complexity of an atom - helium - the core, four-solidly superior to the mass of the hydrogen atom, consists of two protons and two particles, called neutrons, devoid of charge and very close by their mass to Proton.
All dielectric molecules are electrically neutral: the total charge of electrons and atomic kernels included in the molecule is zero. Nevertheless, the molecules have electrical properties. Here Q is the total positive charge of all atomic nuclei in the molecule, 1 is a vector conducted from the center of gravity of electrons in the molecule to the center of gravity of positive charges of atomic nuclei.
Since the atom general is neutral, the total electron charge must be equal to the charge of the kernel.
Since the atom general is neutral, the total electron charge must be equal to the charge of the kernel. The latter managed to calculate in the proportion of OS particles scattered at a certain angle.
Since the atom generally electronized, the total electron charge should be equal to the charge of the kernel.
Since the atom general is neutral, the total electron charge must be equal to the charge of the kernel.
Each atom when it is in good condition, the total electron charge is equal to the charge of the kernel. In such a state, the atom is electrically neutral, since the charge of the nucleus and the total electron charge is neutralized.
Atoms and molecules are electrically neutral, since the nucleus charge is equal to the total charge of electrons surrounding the kernel. Under certain conditions; For example, with an increase in temperature, an atom or molecule is losing an electron.
Atoms are electrically neutral, therefore, the charge of the core in the module is equal to the total charge of electrons. The electron electron-moving orbit should emit energy (according to the electrodynamic laws, with any uneven movement of the charged particle, the electromagnetic wave and the particle will lose energy), while kinetic energy Electron, its speed and radius of orbits should decrease and it should fall on the kernel. However, it is known that atoms are stable and ray raned spectra.
Under normal conditions, atoms are electrically neutral, since the charge of the nucleus is equal to the total charge of electrons surrounding the kernel. However, under certain conditions, the atom can give or attach one or more electrons to itself. A atom having an excess or disadvantage of electrons is called a negative or positive ion. Thus, either negative or positive charges will prevail in the body.




