Mechanical work this is energy characteristic Movement of physical bodies having a scalar look. It is equal to the module of the force acting on the body multiplied by the movement module caused by this force and on the cosine of the angle between them.
Formula 1 - mechanical work.
F - force acting on the body.
s - Moving the body.
cOSA - Cosine angle between force and movement.
This formula has a general view. If the angle between the applied force and the movement is zero, the cosine is equal to 1. Accordingly, the work will be equal only to the work of force on the movement. Simply put, if the body moves in the direction of the application of force, then the mechanical work is equal to the work of force to move.
The second special case, when the angle between the force acting on the body and its movement is 90 degrees. In this case, the cosine of 90 degrees is zero, respectively, the work will be zero. And indeed, what happens we, apply power in one direction, and the body moves perpendicular to it. That is, the body moves obviously not under the action of our strength. Thus, the work of our strength to move the body is zero.
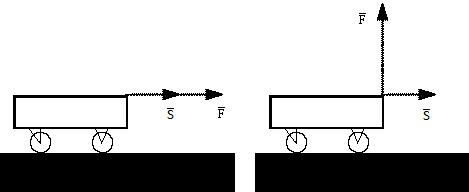
Figure 1 - Work forces when moving the body.
If there is more than one strength on the body, then calculate the total force acting on the body. And then it is substituted in the formula as the only force. The body under the action of force can be moved not only straightly, but also in an arbitrary trajectory. In this case, the work is calculated for a small portion of movement, which can be considered straightforward and then summarized throughout the path.
Work can be both positive and negative. That is, if moving and strength coincide in the direction, then the work is positive. And if the force is applied in one direction, and the body moves in the other, then the work will be negative. An example of negative work can be the work of friction force. Since the strength of friction is aimed at moving. Imagine the body moves along the plane. The force attached to the body pushes it in a certain direction. This force makes positive work on the movement of the body. But at the same time the friction force makes negative work. It slows down the movement of the body and is directed towards its movement.
Figure 2 - Movement and friction power.
Work in mechanics is measured in Joules. One Joule is a work performed by force in one Newton when moving the body for one meter. In addition to the direction of the body movement, the value of the accompanying force may vary. For example, when the spring is compressed, the force of the attached to it will increase in proportion to the distance traveled. In this case, the work is calculated by the formula.
Formula 2 - the work of the springs compression.
k is the rigidity of the spring.
x - coordinate of moving.
Do you know what work is? Without any doubt. What is work, knows every person, provided that he is born and lives on the planet Earth. What is mechanical work?
This concept is also known to most people on the planet, although some individual personalities have a rather vague idea of \u200b\u200bthis process. But it's not about them now. An even fewer people have an idea what mechanical work in terms of physics. In physics, mechanical work is not a person's work for food, it is physical quantitywhich can not be completely connected with anyone with any other living being. How so? We'll see now.
Mechanical work in physics
We give two examples. In the first example of the water of the river, encountered with the precipice, falling down in the form of a waterfall. The second example is a person who holds a heavy item on the elongated hands, for example, holds the roof over the roof over the porch of the country's house from falling, while his wife and children seek convulsively than to rest. In which case is the mechanical work?
Determination of mechanical work
Almost everything, without thinking, will answer: in the second. And they will be wrong. The situation is just the opposite. In physics, mechanical work is described the following definitions: Mechanical work is performed when the power acts on the body, and it moves. The mechanical work is directly proportional to the applied strength and the path traveled.
Formula of mechanical work
The mechanical work is determined by the formula:
where a is work
F - force,
s - traveled path.
So, despite all the heroism of the tired roof holder, the work done by them is zero, but water falling under the action of gravity from a high rock, makes the most that neither there is mechanical work. That is, if we push the heavy wardrobe unsuccessfully, then the work that we did from the point of view of physics will be zero, despite the fact that we make a lot of strength. But if we slide the closet for a while, then we will do the work equal to the product of the applied force at a distance that we moved the body.
The unit of work is 1 J. This is a work performed by force in 1 Newton, on the movement of the body for a distance of 1 m. If the direction of the applied force coincides with the direction of the body movement, then this force makes positive operation. An example is when we pushing any body, and it moves. And in the case when the force is applied to the opposite body movement, for example, the friction force, this force makes a negative work. If the attached force does not affect the movement of the body, the force performed by this work is zero.
Let the body on which the force acts is passed, moving along some trajectory, the path s. At the same time, the force either changes the body speed, telling it acceleration, or compensates for the effect of another force (or forces) opposing the movement. The action on the path S is characterized by the value called the work.
The mechanical work is called a scalar value equal to the work of the projection of force on the direction of movement of the FS and the path S, the passing point of the application of the force (Fig. 22):
A \u003d fs * s.(56)
The expression (56) is valid if the value of the FS force projection on the direction of movement (i.e., on the direction of speed) remains all the time unchanged. In particular, this takes place when the body moves straight and permanent force forms a permanent angle α with the direction of movement. Since FS \u003d F * COS (α), expression (47) you can give the following form:
A \u003d F * S * COS (α).
If - the movement vector, then the work is calculated as a scalar product of two vectors and:
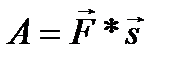 . (57)
. (57)
Work is an algebraic value. If the force and direction of movement form a sharp angle (COS (α)\u003e 0), the work is positive. If the angle α is stupid (COS (α)< 0), работа отрицательна. При α = π/2 работа равна нулю. Последнее обстоятельство особенно отчетливо показывает, что понятие работы в механике существенно отличается от обыденного представления о работе. В обыденном понимании всякое усилие, в частности и мускульное напряжение, всегда сопровождается совершением работы. Например, для того чтобы держать тяжелый груз, стоя неподвижно, а тем более для того, чтобы перенести этот груз по горизонтальному пути, носильщик затрачивает много усилий, т. е. «совершает работу». Однако это – «физиологическая» работа. Механическая работа в этих случаях равна нулю.
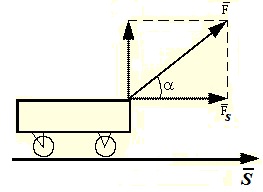
Work when moving under the action of force
If the value of the projection of force to the direction of movement does not remain constant during the movement, then the work is expressed as an integral:
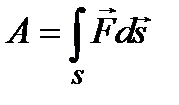 . (58)
. (58)
The integral of this type in mathematics is called a curvilinear integral along the trajectory S. The argument here serves as a vector variable that can vary both by module and direction. Under the sign of the integral is a scalar product of the strength and vector of elementary movement.
For a unit of work, a work carried out by force equal to one and acting in the direction of movement, on the way equal to one. In S. the unit of work is Joule (J) who equal to workPerformed by force in 1 Newton on the way to 1 meter:
1J \u003d 1H * 1m.
In the SSS, the unit of work is ERG, equal workMade by force in 1 Dina on the way to 1 centimeter. 1J \u003d 10 7 ERG.
Sometimes an extra-system unit of a kilogram meter (kg * m) is used. This is a job made by force of 1 kg on the way to 1 meter. 1kg * m \u003d 9,81 J.




