1. The wording of the law of Kulon.
but)the interaction of two point charged bodies is directly proportional to the production of charges of these bodies and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
2. Formulation of the Law of Joule - Lenza.
b)the amount of heat dedicated to the current in the conductor is proportional to the square of the current force, the resistance of the conductor and the current time
3. The wording of the Ohm law for the circuit site.
in)the strength of the current on the plot of the chain is directly proportional to the voltage drop in this section and inversely proportional to the resistance of this section.
4. Ohm's law for full chain.
d)the strength of the current in the entire circuit is directly proportional to the EMF of the power supply and inversely proportional to the full resistance of the external and inner section of the chain
5. What value is an energy characteristic electric field?
but)voltage
6. What value is the power characteristic of the electric field?
d)tension
7. What value is determined by the number of electrical charges passing through the cross-section of the conductor per unit of time?
b)tok Power
8. What physical quantity has a unit measurement unit?
in)charge
9. What physical value has a unit of measure?
but)tok Power
10. What physical value has a unit of measure in?
b)voltage
11. What value has a unit of measurement OM?
d)resistance
12. FormulationThe 1st Law of Kirchhoff.
but)algebraic amount of currents in the node is zero
13. Formulation of the 2nd Kirchhoff Law.
b)the algebraic amount of EDC contour is equal to the algebraic amount of stress drops in separate areas of the circuit
14. Physical meaning Voltage.
d)voltage is numerically equal to the operation of the field forces when the charge is moving between two field points to the magnitude of this charge
15. What value is characterized by the ratio of the force acting on the point charge placed at this point of the field, to the magnitude of this charge?
but)tension
16. What kind of body is called electrically neutral?
in)the number of positive charges is equal to the number of negative
17. Which charge has an electron?
d)negative
18. Which charge has a proton?
but)positive
19. What conditions are required to exist in the circuit?
b)the presence of a power supply, consumer, free charges, closed chain
20. What device is considered a power source?
in)generator
21. What is an electrical chain?
in)a combination of devices to obtain electric current
22. With which measuring instruments determine the electrical current?
but)ammeter
23. With what measurement instruments determine the voltage?
b)voltmeter
24. With which measuring instruments determine power?
in)wattmeter
25. With which devices determine the consumption of electrical energy?
d)counter
26 . What device relates to electrical energy consumers?
d)engine
27. What is constant with a consistent connection of the resistance?
but)tok Power
28. What is a constant value with a parallel connection of the resistance?
b)voltage
29. What is the general resistance to a sequential connection?
but) RO \u003d R1 + R2 + R3
30. What is equal to the overall resistance with a parallel connection?
but)1 / RO \u003d 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3
31. Resistance:R.1 \u003d 2 ohms;R.2 \u003d 4 ohms;R.3 \u003d 6 ohms are connected sequentially.
DetermineRo..
b)12 Oh.
32. Resistance:R.1 \u003d 4 ohms;R.2 \u003d 6 ohms;R.3 \u003d 8 ohms are connected in parallel.
DetermineRo..
in)1.8 Ohm.
33. Which of the modes of the electrical circuit is considered an emergency?
d)short closure mode
34. In what mode of the chain does not have a load?
b)work in idle mode
35. What is called an electric node?
d)connection point 3 or more wires
36. What is the magnitude characterizes the intensity of the magnetic field in any environment?
but)magnetic induction
37. What is the magnitude characterizes the intensity of the magnetic field in vacuo?
b)magnetic field tension
38. What letter is the magnetic induction?
39. What letter is the magnetic stream indicate?
40. In which units is the magnetic induction?
41. In which units is the magnetic stream measured?
but)[WB]
42. Formulation of the law of electromagnetic force.
b)if the conductor with the current is placed in a magnetic field, it will move
43. Formulation of the law of electromagnetic induction.
in)if the conductor move to the magnetic field, crossing the power lines, then the EMF of electromagnetic induction is guided.
44. What rule is the direction of electromagnetic force determined?
d)rule "Left Hand"
45. What rule is the direction of EMF electromagnetic induction is determined?
b)right hand rule
46. \u200b\u200bWhat law of magnetism is the basis of the operation of the generator?
d)
47. What law of magnetism is the basis of the engine work?
but)electromagnetic power law
48. What phenomenon is the basis of the operation of the transformer?
b)phenomenon of mutual induction
49. What is the hysteresis loop area?
in)losses on the process of cyclic magnetization of the material
50. What is the work mode under load?
in)in electrical chain There are consumers of energy
51. What is the current called variables?
d)current, which changes over time largest and direction
52. What is the period?
but)time of one oscillation
53. What is the frequency?
b)number of fluctuations per unit of time
54. What is the instantaneous value of alternating current?
in)the value of variable value at different times
55. What is the amplitude AC value?
d)most of the instantaneous values
56. What is the meaning of the AC indicate the measuring device?
but)existing meaning
57. What value is measured in seconds?
b)period
58. What value is measured in Hz?
but)frequency
59. What value is indicated in alternating current letterZ.?
b)impedance
60. What value is indicated in the alternating current of the letterX.L.?
in)reactive inductive resistance
61. What value is indicated in alternating current letterXC.?
d)reactive capacitance resistance
62. What value is indicated in alternating current letterR.?
but)active resistance
63. In which units is the active power of P?
in)[W]
64. In which units the reactive power is measuredQ.?
b)[Var]
65. In which units the total power is measuredS.?
but)[Va]
66. Stress resonance condition.
in)XL \u003d XC.
67. What is equal tos.φ With stress resonance?
but)Cosφ \u003d 1.
68. In which chains the stress resonance is created?
b)in chains with a consistent compound of active, inductive and capacitive resistances
69. In which chains the current resonance is created?
but)in chains with parallel compound of active, inductive and capacitive resistance
70. Conduance condition of currents.
d)Il \u003d IC.
71. With which mechanisms it produces three-phase alternating current?
but)synchronous generators
72. For which synchronous machines are used.
in)to obtain a three-phase alternating current
73. What voltage is called linearU.l?
b)voltage measured between linear wires or principles
74. What voltage is called phaseU.f?
but)voltage measured between the beginning and end of the phase
75. What connection is called a "star"?
in)this is a connection in which the ends of the three phases are connected to one point, and linear wires are connected to the beginning of the phases.
76. What connection is the "triangle" called?
d)this is a connection at which the end of the previous phase is connected to the beginning of the subsequent
77. What is the ratio between linear phase voltages in the "Triangle" scheme?
b)Ul \u003d UF
78. What is the relationship between linear and phase currents in the "Star" scheme?
but)Il \u003d IF.
79. What is the zero wire?
in)zero wire lines phase voltages in the case of uneven loads of the phases and is the fuse of the system from overload
80. What is the load of the three-phase chain called uniform?
in)if the three phases have a load of the same largest and character
81. Why protective devices Do not install in zero wire?
but)zero wire itself is the fuse system from overload
82. Which device refers to direct assessment devices?
d)ammeter
83. What device refers to comparison devices?
b)measuring bridge
84. What devices are needed to determine the power indirectly?
in)ammeter and Voltmeter
85. What devices are needed in order to determine the power directly?
d)wattmeter
86. The device, which system is used only in DC circuits?
but) magnetoelectric
87. The device, which system is used in constant and alternating circuits?
b)electromagnetic
88. What can be measured using an electrodynamic system instruments?
d)current, voltage and chain power
89. What system of instruments are used in electric meters?
d)induction
90. Instruments, with what accuracy class are standards?
91. How many are the accuracy classes of measuring instruments?
92. Why are DC machines are reversible?
d)machines can operate in the generator and engine mode
93. What is the basis of electromagnetism under the basis of the operation of the DC generator?
d)electromagnetic induction law
94. What is the basis of electromagnetism under the basis of the operation of the DC motor?
in)electromagnetic power law
95. What is the stator of the DC machine?
b)the main poles of the stator create the main magnetic field of the machine
96. What should be done with an electrical machine to work in the generator mode?
but)it is necessary to rotate the rotor in the magnetic field of the main poles of the stator
97. What should be done with an electrical machine to work in the engine mode?
b)it is necessary to give a current into the rotor winding, which will interact with the main magnetic field stator
98. For what is needed in a direct current collector?
c) collector is an electromechanical rectifier
99. What form should be the pole of the constant current machine?
c) hiking
100. What phenomenon is called "anchor reaction"?
a) this is the phenomenon of distortion of the main magnetic field of the machine
Potential energy Charge q. 0, located in the charge field q. on distance r. It is equal to the work performed when moving the charge q. From this point to the point of zero potential, i.e. on infinity
Potential A scalar value that characterizes the energy that has a charge placed at this field point and numerically equal to the potential energy of a single positive charge at this point point.
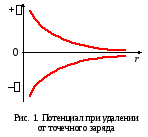
 .
(2)
.
(2)
The potential is numerically equal to work on the movement of charge from infinity at this field.
 .
(3)
.
(3)
Superposition principle
 ,
,

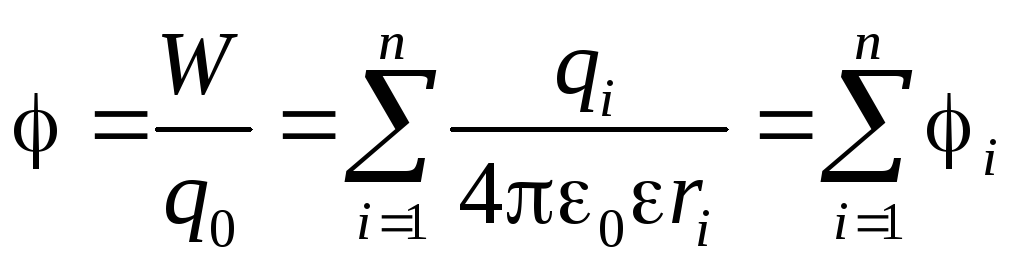 ,
,
those. The potential of the field created by the dot charge system is equal to algebraic sum Potentials created by each charge separately.
those. The work performed by electrical forces when moving the charge between two points of the field is equal to the product of this charge on the potential difference in the initial and endpoints of the path.
Corollary:
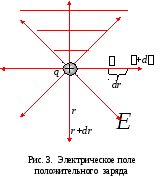
Graphic image of electric fields. Equipotential surfaces

Properties of equipotential surfaces
the work performed on the movement of the charge along this surface is zero;
coulomb force is directed perpendicular to this surface;
equipotential surfaces do not intersect;
the thickness of the lines of equal potential (the number of lines passing through the unit area) is proportional to the gradient of the electric field strength;
Communication between tension and potential
Equating the right parts of equations (10, 11), we get
 ,
(7)
,
(7)

 ,
(8)
,
(8)Example. For uniform field Flat condenser ( E.\u003d const)
 ,
,
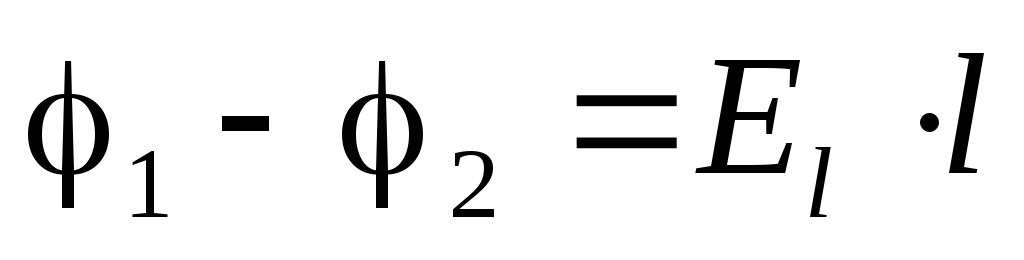 ,
,
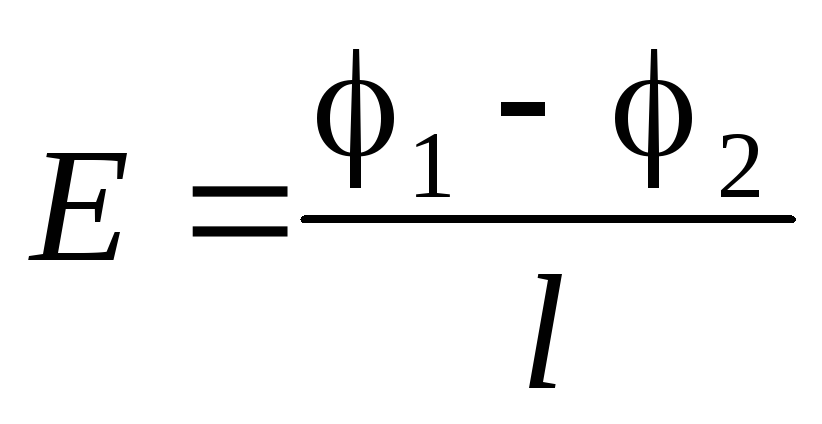 .
.
Units
 (Volt);
(Volt);

 ;
;
So, the electric field, being a potential field, has two characteristics - vectoror Silia
 , I. scalaror energy
, I. scalaror energy
 .
.
24. Conductors in the electric field. Electrostatic protection. Conductor electrical capacity. Condencators
The main task of electrostatics is the task of finding tension  and the potential of the electric field at each point of space.
and the potential of the electric field at each point of space.
Theorem Gaussa

Stream (F. E.) Vector  electric field through a flat surface area
electric field through a flat surface area  called scalar The physical quantity characterizing the intensity of the field in this place of space and is numerically equal to the number of power lines that permeate this platform in the direction of normal to it.
called scalar The physical quantity characterizing the intensity of the field in this place of space and is numerically equal to the number of power lines that permeate this platform in the direction of normal to it.
 ,(1)
,(1)
FlowF. E. , created by a single positive charge
 ,(2)
,(2)
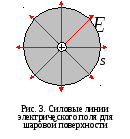
square Shara 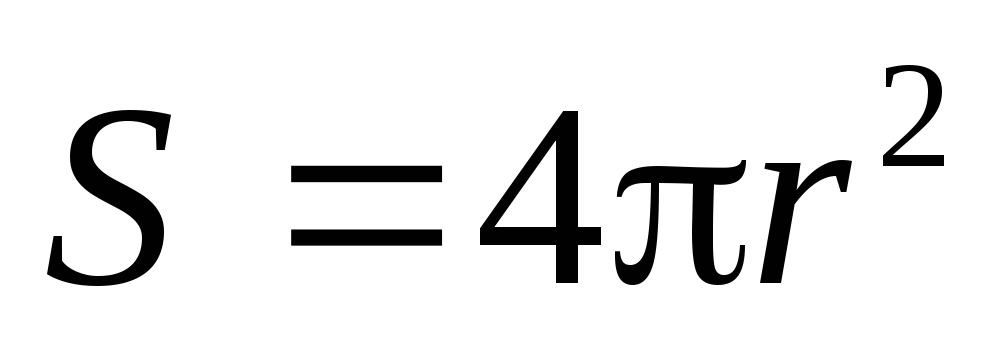 , Point Dot Charge Field Tension
, Point Dot Charge Field Tension  ,
,
 .
.
In general:
 .(3)
.(3)
The flow of the electrostatic field strength through an arbitrary closed surface is equal to the algebraic amount of charges enclosed inside this surface divided by 0.
Conductor The medium in which there is a sufficient number of free electrical charges. For example, in metals in 1 cm 3 contains about 10 23 free electrons.
The combination of free electrons in the metal is called electronic gas. If the conductor is placed in an electric field, then free electrons are moved inside it under the action of the field against the power lines, as a result, under the action of an external electric field on the surface of the plate will appear induced charges with superficial densities 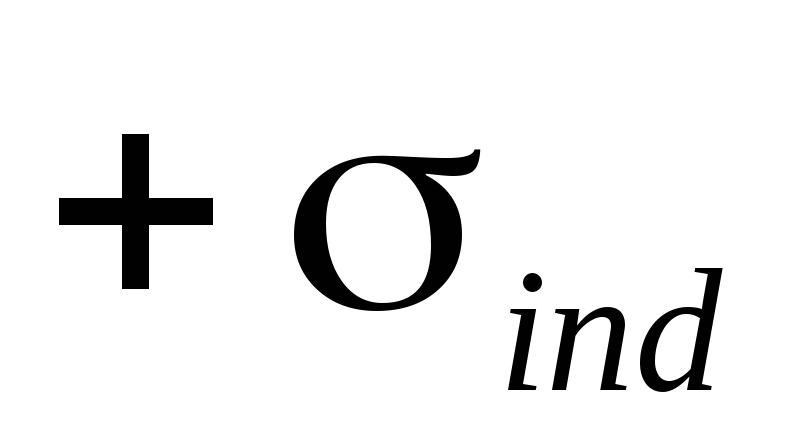 and
and  . The electrical field of induced charges compensates for the external electric field, i.e.
. The electrical field of induced charges compensates for the external electric field, i.e.

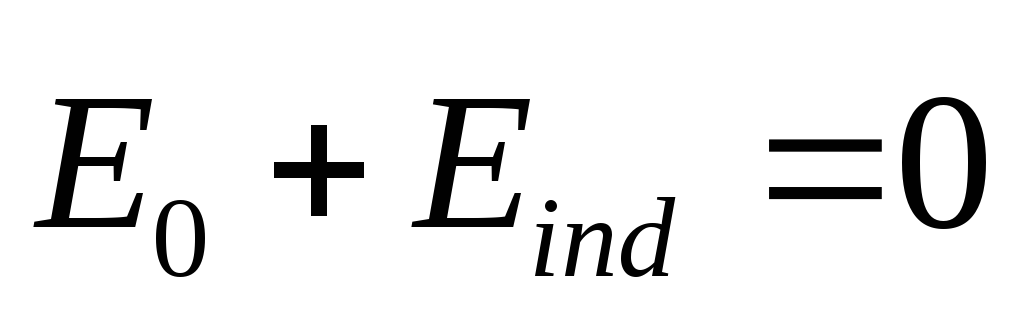 because
because  T.
T.
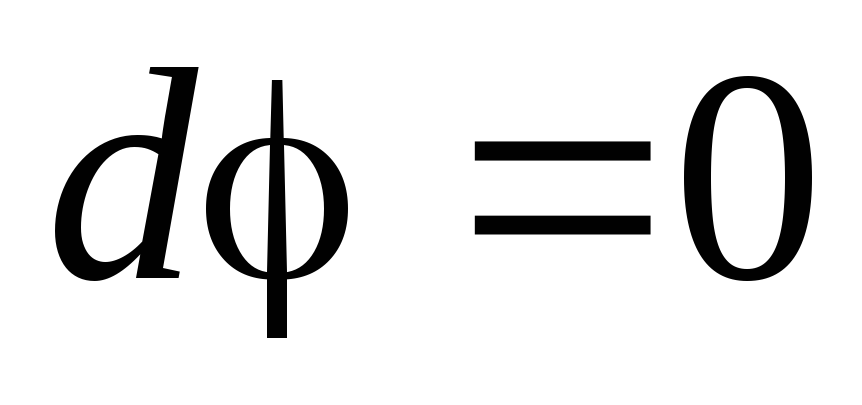
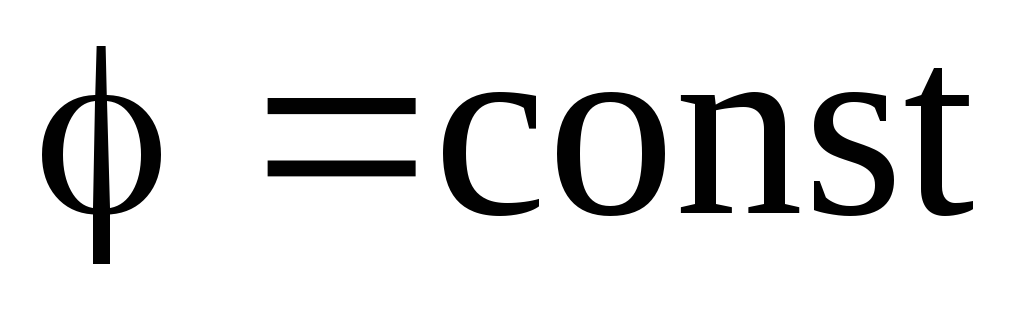 , (4)
, (4)
those. there is no electrostatic field inside the conductor, and the potential of the conductor is permanent(explorer Equipotencilen).

In the curvilinear surface of the conductor, the power line of the electrostatic field strength should be directed by normal to this surface, otherwise under the action of the tangential component of the field  the charges would move according to the conductor, which contradicts the condition (4).
the charges would move according to the conductor, which contradicts the condition (4).
In the charged conductor, overweight is located only on the surface, because According to the Gauss Theorem for a closed areaS. There is no charge inside the conductor.




 .
(5)
.
(5)
Energy characteristics of the electric field of meatnikov G. I. Teacher of Physics
Charge B. electric field For a charge, placed in an electrostatic field, the power on the part of this field acts. When the charge is moved, this power can work. This work is often referred to as the operation of the electric field.
Potential energy The "charge + field" system has the ability to work. The system capable of doing work has potential energy.
Change potential energy change in potential energy? WP is associated with a perfect system of work and as a relation :? WP \u003d - and if a\u003e 0, then WP decreases. If A.<0, то WP увеличивается.
Features of the electric field operation of the field when the charge is moved from point 1 to point 2 in the electrostatic field depends only on the position of these points in the field and does not depend on the charge trajectory. + Q 1 A1. 2 A2 |A1| \u003d |A2|
The physical field is potentially if: work in it does not depend on the form of the trajectory; Work on a closed contour in it is zero. The electrostatic field is potential.
Potential of the electrostatic field by the potential of the electrostatic field? At this point, is the physical value equal to the ratio of the potential energy of WP charge Q, placed at this field point, to the magnitude of this charge: WP? \u003d Q.
Energy characteristics of the electric field potential - the value is scalar. The potential is the energy characteristics of the electric field. The physical meaning has no point potential, but the potential difference between two points. It is it that is related to the work of the field when the charge is moved from one point to another.
Potential difference The difference of potentials between points 1 and 2 is equal to the function of the field when the charge is moved from point 1 to point 2 to the magnitude of this charge: a? 1 -? 2 \u003d Q
Voltage The difference in potentials in the electrostatic field has another name - voltage between two points. Voltage between two points 1 and 2 fields: U \u003d? 1 -? 2
Sex measurement units: [? 1 -? 2] \u003d in (volt) 1 j [? 1 -? 2] \u003d 1 in 1 CL The difference of potentials between the two points of the field is 1 V, if when moving the charge in 1 cl down Dots to another electric field makes a job in 1 J.
The principle of superposition The potential of the electrical field of the charge system is equal to the algebraic amount of field potentials created by each of the charges :? \u003d? 1+? 2+? 3+ ... +? N
The relationship between potential difference and tension Trial charge Q\u003e 0 moves in a uniform field with tension E in the direction of power lines. E d f q f \u003d qe a \u003d fd a \u003d qed u \u003d a q u \u003d ED D
The definition in a homogeneous electrostatic field with the tension E the potential difference between the points connected by the vector d, the direction of which coincides with the direction of the field strength, is determined by the formula: U \u003d ED
The ratio between the tension and the potential difference can also be written as: u E \u003d D the field strength is directed toward the decrease in the potential.
Units of field strength in C: [E] \u003d m in H 1 \u003d 1 m cl prezentacii.com




