Currently, due to the emergence of not just new materials, but entire systems of enclosing structures (consisting of heterogeneous materials), great attention should be paid to understanding the physical processes occurring in the upper enclosing structures - roofs. Without this, it is impossible to competently design and erect.
Fig. 1. External and internal factors affecting roof
The roofs are exposed to a number of forces closely related to processes both outside the building and inside it (Fig. 1). These factors, in particular, include: atmospheric precipitation; water vapor, located in the outer and inner air of the building; wind; solar radiation; temperature differences; Chemically aggressive substances contained in the air, as well as some other components.
The effect of atmospheric precipitation and wind
The wind with force throws water or snow to the roof, which, with an insufficiently thought-out structure of the roof and roof in general or individual nodes, can lead to a roof leakage as a result of water or snow in the seams of roofing materials. In addition to the rain, the influence is influenced by the roof. The most vulnerable plates of the roof are framed by smoke and ventilation pipes And the roof adjoining to various vertical surfaces: walls, frontones, auditory windows.
The traditional technical solution of the roofs of the roofs to the walls and parapets, both frontal and lateral, provides for the manufacture of niches and strokes on the walls (parapets) of niches and strobes along the entire length of the adjuncing and installing the aprons from roofing steel roofing. It is allowed to install aprons from black roofing tin, twice the hot oil turned from two sides and painted at least two times. Installation of the apron without a niche or a shorter way by tight pressed to the wall does not provide proper adjunctions, and the node occurs. There is at least two reasons for this: first, the walls are not so smooth so that it is possible to close the apron tightly to them; Secondly, the sun heats the apron and it is lengthened as a result of the temperature expansion and will cross between the fasteners with a waste from the wall (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Traditional solutions of nodes of adjacent roofs to walls and parapets
The installation of the top of the apron in the niche or the stroke eliminates this problem, here the looseness is covered on top of the wall material, which reliably closes them from rainwater, but does not protect them from snow. Therefore, when installing apron in a niche, it is recommended to do the top of at least 100 mm high, and when installing in the stroke - it is desirable to close it cement-sandy solution. It is necessary to add immediately, a simple sealing with a high niche solution is virtually useless, the solution from there will take it over time, winter frosts and wind will help, but for 5-10 years he will still serve. Protecting apron with a solution will not allow the wind to whine snow in the stroke, where it melts and melting water will be required under iron. The fastening of the aprons is carried out by nails to wooden antiseptic corks, pre-laid in the wall, for example, when erected brick masonry. The plug installation step is about 1 m. If you attach wooden triangular bruks before installing the apron, then the plugs can be installed less often, and the apron's edge is tight. Fixing apron by the second triangular bar will make the node with almost waterless. The stroke can be laid down and forget about it until it rotches the apron.
In length, the elements of the aprons are mounted in the vane in the direction of the water skate. The backstage is made at least 10 cm. If the docking of the aprons does not make a mustache, but with a false fold, the node will be more reliable.
To protect the roof adjoining node to parapets, the "roof" is installed on the roof of roofing, equipped with drippers (hooked "hook" edges). The parapertic apron with drippers released by the walls protects the rain parapet: the water on the droplets is removed from the walls, there is a separation of droplets and drop them directly on the roof or on the apron of the adjoining node. Water flowing directly along the walls becomes less. Parapete apron is fixed with tensioning on T-shaped crutches, installed in increasing about 1 m and attached, in turn, nails to wooden antiseptic corks. In order for the parapet apron does not reduce the strong wind, it is allowed to the top mount with screws (self-plugs in a wooden plug) through the roofing tice with the installation of rubber washers under the screw head.
Similarly, the components of roofs are solved to smoke trumpet and ventilation mines. Brick tubes are framed by aprons from galvanized or treated black tin. The lower and side parts of the apron are stacked over the roof, and top part start at her. From above, the aprons are covered by a brickwork with a brickwork. In the manufacture of apron, it is recommended to stick to the size shown in Fig. 3, they provide protection against melting snow. With abundant winter snowfall, the snow falls under the inner side of the iron, the indicated the dimensions of the apron will not give meal water to penetrate the roof. She, overcoming a long way, simply dry.
Fig. 3. Traditional solutions of tubular cutting nodes (sizes in mm)
In the pipes, especially smoke, the installation of wooden plugs is unacceptable, so the attachment of the apron is carried out on the lying fold, connecting all the roofing iron around the pipe into one. If the roofing cutting is done around the ventilation mines, then the apron can be mounted with nails to wooden antiseptic corks. Cutting around round, for example, asbestos-cement or PVC pipes, clamping a different tube of larger diameter. The slot between the pipes is poured molten bituminous mastic or any other sealant. Big gap, Before filling the sealant, it is boosted with a fibrous material, for example, flax strands or rope impregnated with oil paint or bitumen primer. After boiling, the slit is poured with a sealant or smeared with a fatty cement-sandy solution.
When the device is roofing from piece materials, for example, slate, ondulin, and their similar, the magnitude of the side and front alone adjacent sheets should be the one that the material manufacturer recommends to do it. An increase in the size of the adolescence leads to unreasonable overruns of roofing material, and the decrease is to possible roof leaks. Short alternates can create a blowable junction, in which snow or rainwater will be made, driven by the wind, or melt water as a result of the capillary suck of the junction.
Free sv, the roof should also be as it recommends that the manufacturer of the roofing material recommends. Short OTL does not provide water removal from the roof. Part of the water, rolling through the edge of the roofing material, will be reduced by the wind and thrown onto the wall, and the other part, as a result of the surface tension of the water overcoming the force of the earth's attraction, will flow up along the bottom plane of the roof and will make the wooden crate and the rafalinks of the rafter. Long Sve is well assigned water, but it can be cut or bent (at flexible roofs) Sliding with the roof of snow (Fig. 4). And well, if the roof breaks at the free sink, it happens more often, roofing material It is premounced much higher, right above the room, which should protect the roof.
Fig. 4. The roof of this house was on the summer of 2008, the photograph was made in the spring of 2009. As it should be expected, in March 2011 sliding snow climbed the sinks of the roof, shifting slate above the middle of the sheet. There is no photos of destruction (there was no camera with me). Outcome: Roofing with a free sink of 20-25 cm was able to "survive" without loss, only two spring
Rainwater and lowered snow bags are dangerous on endowes - inner corners The intersections of two perpendicular skates. There are two water flows flowing into the angle, and the endow becomes a water tray. To prevent the roof of the roof in the endows, in all cases and for any kind of roofing, a solid doomle is made and is trimmed with roofing tin (Fig. 5), and already fits them roofing. Either in this place is settled by a special waterproofing carpet provided for such nodes by the manufacturer of a particular roofing material.
Fig. 5. Traditional Device Solution Roofing End
Infrequent hurricanes passing through the middle lane of Russia, it is extremely rarely destroyed by a truly roof system, but they are able to remove the dilapidated or poorly fixed roof from the house. The tangent winds of the wind, acting along the roof of the roof, can disrupt its individual elements. That this does not happen, they establish anti-conflict brackets for roofs from wavy roofing sheets, T- and M-shaped brackets for metal roofs (Fig. 6), tie the special type of tiles to the crate. From the front of the building of the building, the wind board is installed (Fig. 5). Anti-standard brackets can perform a double function: to hold the roofing material from breaking the wind and resist the separation from the action of the sliding snow. This is especially true for the attic roofs with a large slope slope, where the snow does not lie, and the roofing material is fixed almost vertically, the weight can be partially shifted onto the brackets. For hold of piece roofing elements on cool mansard roofs The brackets must be previously treated with hot oil and painted at least two times.
Fig. 6. Traditional anti-confer decisions of roofing nodes
Effect of water vapor and air temperature
The topic of ventilating the underground space is considered in the section "Warming of the roofs".
Solar radiation and temperature drops
Various materials have different sensitivity to solar radiation. For example, solar radiation practically does not affect ceramic tile, as well as on materials from metals without polymer coatings applied on them. On the other hand, paints and varnish materials are subject to significant destruction, which is manifested in the form of paint cracking on metal roof. A number of materials do not change their physical propertiesBut loses external attractiveness - for example, fades (paints and some polymer coatings). Choosing the roofing material, you should make sure that it has sufficient light-resistance.
The roofs are functionally functioning in fairly hard mode, experiencing the effect of temperature difference. As is known, all materials are in one degree or another are thermal stretching and compression. Therefore, in order to avoid deformations and destruction, it is very important that the materials working in a single construction have had similar temperature expansion coefficients or appropriate technical solutions would be applied to ensure their collaboration. And in other words, when installing the roof, you need to stick to the instructions that the roofing manufacturer offers.
Chemically aggressive substances contained in the air
A number of materials are seriously dangerous to carry frequent, sometimes daily temperature differences from the plus to minus. This, as a rule, occurs in areas with mild and wet winter. Therefore, in such climatic zones, it is necessary to pay close attention to such an important characteristic of materials such as water absorption. With high water absorption under conditions of positive temperatures, the moisture penetrates and accumulates in the pores of the material, and with negative - freezes and, expanding, deforms the structure of the material itself. As a result, the progressive destruction of the material leading to the formation of cracks occurs.
As a rule, in large cities or near large enterprises in the atmosphere, a sufficiently high concentration of chemically aggressive substances, such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide, is observed. Therefore, for all elements of the enclosing structures of buildings in such areas it is necessary to apply materials, resistant to chemical substances present in the air.
Because the roof is considered the end step of building your home, then it should be done very carefully to its device.

After all, from what type of scope roof will be chosen, obeys, not at the very least, the cozy residence of residents of the house.
As can be seen from the name, the scope is called the roof of this type, which consists of one, 2 either more planes placed at a specific angle of slope. The cutting roof device is as follows: it consists of a carrier and coating for the roof, filament so that a bias appear. The magnitude of the slope is taken:
- depending on the volume of annual precipitation in a specific climatic region (the number of drop-down snow, shower),
- depending on the magnitude of the load of the wind.
A very important argument when calculating the angle of slope is considered the material for the roof.
Very often, manufacturers are shown for their own products, with some inclination of the slopes, one or another type of coating can be treated. The main components of the roof of the pitched roofs are considered:
- roof coating
- slinge system.
Of course, all kinds of roofing scit type There are only 2 system options:
- with an attic;
- without a attic.

Scope roof with an attic
In the first embodiment, these are separated roofs, in the second - combined. In other words, if you have an afflicted roof of an attic type, and this room is not considered housing, it is all the same between the overlap of the attic and the roof itself. But for the roofs without premises the attic of the supporting components of the system, the overlappings of the upper floor are considered (if for example, the house consists at least from the 2nd floors).
Types of roofing types
- Single room is a roof with one skate, a bias that can be from one carrier wall to another. Basically, such roofs are necessary for the device canopies, sheds and autogies.
- Double - as seen from the title, the roof has two skates. This kind of scope roof is very popular, due to its own reliability of the design and comparative ease of installation, and is used in the construction of private buildings.
- Four-tight (semi-haul) - has four similar skate (or two pairs of similar slopes in the area). They are mainly used for construction work Rustic or objects outside the city.
- A different variety of four-tie roofs is a tent, the form of which resembles a tent of the skates, whose vertices must come together at one point. Similar types of scanty roofs are used when construeding the objects of capital construction of a square (polygonal) form.
- Study - has several rods formed in the form of a triangle. Skates converge in one vertex.
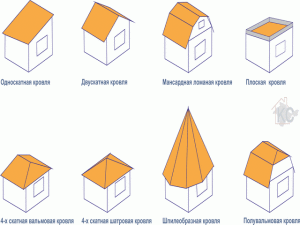
Types of scope roof
Slection type of scope roof
To do this, you need to take into account the following:
- Slope slope So, for a scope roof having an angle of slope 50 degrees and above, snow-covered drifts are not scary. As a rule, the load on the roof system decreases. Therefore, it is possible to slightly reduce the amount of the cross section of the methods used for the occurrence of rafter feet. But for the roof with the angle of inclination of the slope in 2 degrees, the cross section of the rafter legs will have to be up, on the contrary, increase many times. This is manufactured so that the coating can withstand the snow load.
- Cross section of rafter feet. As follows from going to this point, the cross section of Stropilin will need to be received by the limit - so that the solo system itself can withstand the overall load on the roof.
- Requirements that are presented to the durability and reliability of the roof: Fortress, fire resistance, high bearing capacity. From this it follows: the larger cross section of the rafter leg, the longer it will keep the effect of fire. To give similar parameters of resistance to lights of the rafyroids must be held a specialized finish - disinfectant, protective paints resistant to solutions, cement plaster, etc.
- Properties of thermal insulation. Of course, the better the roof is insulating, the high load is obliged to keep the roofing system (core). And therefore, the cross section of Stropilin is obliged to be greater.
Materials and working term of the roof
Of course, the period of exploiting roofs made from different materialswill directly depend not only from the quality of the materials themselves, but also from their properties of operation.
For example, without overhaul, the scope roof system will serve 30-50 years.
The roofs of concrete and iron work approximately the same amount. But the wood roofs have a lifetime of 20-30 years - and then with suitable care, finishing with specialized compositions.
Of course, each type of roofs is selected, if we proceed from the features of the architecture of the structure, as well as depending on the purpose of the roof.
Wood coating

Wood rope roof
A similar type of system is especially famous among developers of low houses. The system consists of farms with different species Stropilin.
Now wood roof can very often be seen in buildings built by technology from Canada. The wood roof rafters system includes: rafting legs, mauerylalat, racks, frame frame and screed.
Basically, similar rafter systems are applied in those buildings, in which two carrier walls - there is no average carrier system.
- relatively small cost
- material is environmentally friendly,
- excellent life.
- low fire resistance and great opportunity to sunbathing
- bad resistance to rotting and different malicious microbes,
- bad corrosion resistance.
Metal Wood Coating
As noticeably from the name, the scope roof of this kind is combined from metal and wood. The latter are collected in the form of frames, arches, farms, while the upper part consists of wood, lower - from the reinforcement. It allows you to work on both compression and stretching.
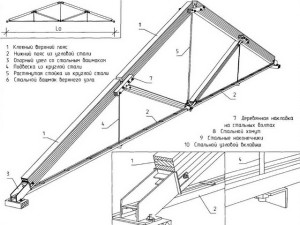
Metal dressing roof
Such roofs are rarely used than simply structures from wood, at least due to their great price. But, metal-treated roofs are often used during the construction of industrial firms.
- the possibility of overlapping spans up to twenty meters long,
- good decorative properties.
Cons: Big price.
Reinforced concrete

Basically, this is a rafter system of concrete and iron. Stropilins are made at the enterprise and are delivered to the construction site. The cross section of the stringlin is rectangular, connect the similar components with welded mortgages.
Apply roofs of the design of this type for the construction of "large-scale" objects: warehouses, hangars, granaries).
- long service life
- customary service
- high coating material fortress for roofing.
Installation of pitched roofing
Specifically, the slope of the pitched roof can be divided into such elements:
- Konk
- Vertex
- Inclined rib
- Speeding
- Gable
- Farmery Sve.
The difficulty of installing a scope roof of a different type depends on the properties of the external and internal structures of the carrier type, and from the accepted angle of slope. If, for example, a scope roof has a too steep slope, the roof coating should be placed only in some particular option to firmly attach the material, the mastering masses are not a big size.
And on the contrary, the smaller the slope of the slope roof, the more decent number of lateral connections will be required.
Carriage elements B. scanty roofsah serve rafal structures - rafter beams or rafting farms with crate or formwork laid on them, or large-sized flat elements - plates and panels.
The choice of bearing structures of pitched roofs affects:
Form (outlines) of the building in the plan;
Roof dimensions (the magnitude of overlapping spans);
Loads (own, snow, wind);
Location in the building of the internal supports (walls, racks, pillars);
Requirements for roof (capital, fire resistance, heat engineering properties, etc.).
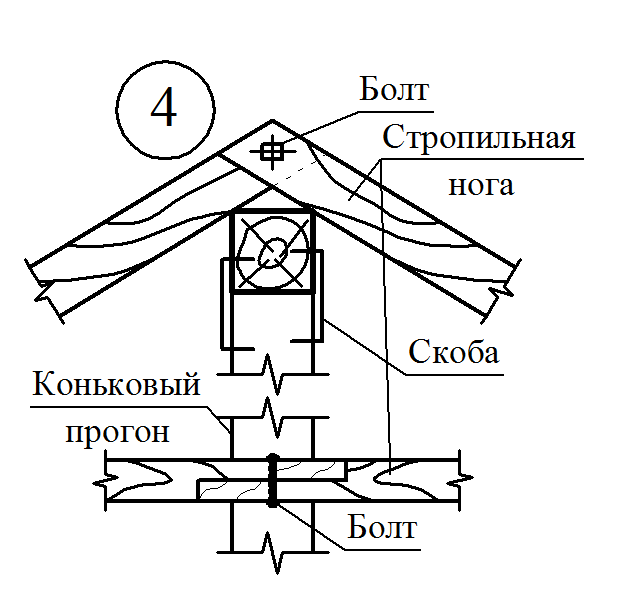
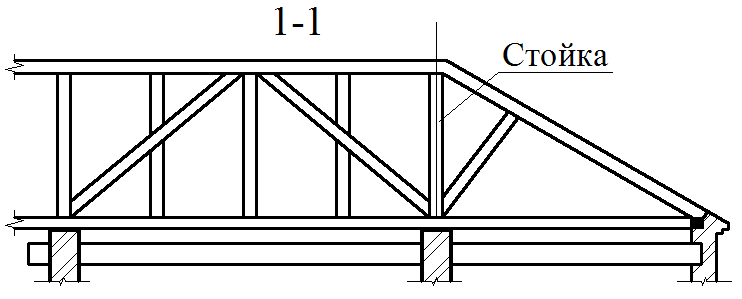
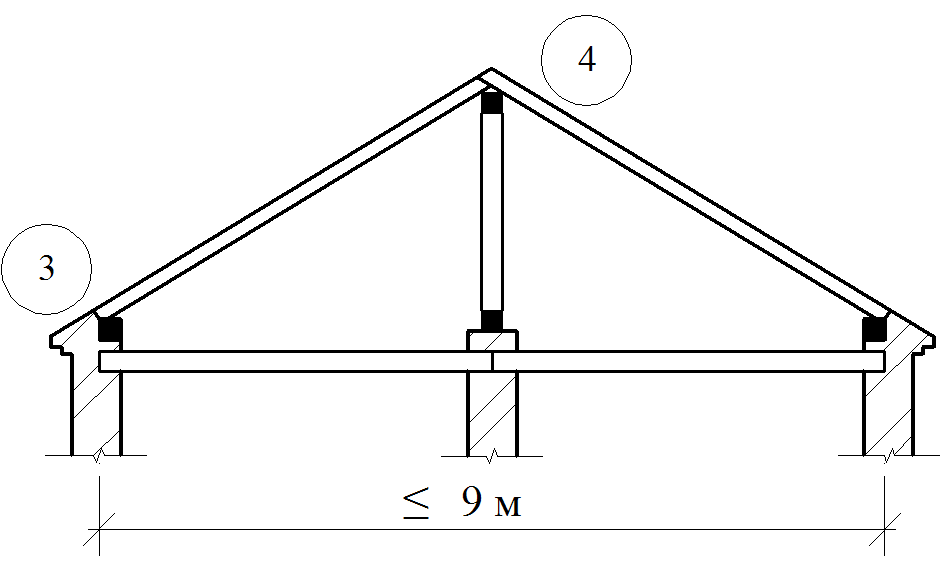
Boy rafter design double roof It can be solved in the form of urinary, hanging or combined rafters, the main element of which are beams, stacked at an angle according to the slope of the roof on the outer walls and internal supports (spots), and in the absence of the latter - only on the outer walls (hanging rafters).
9.5. Curvas System Stropil
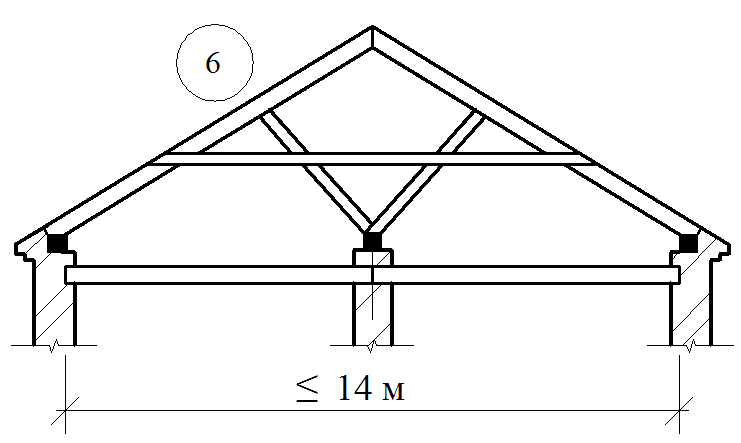
Sweeping rafters are transmitted to support vertically aimed efforts, so easy to manufacture and cheap. In hanging rafters there are significant horizontal efforts, driving walls. To perceive these efforts, it is for eliminating the retrieve, the system is injected into the system that binds the rafting legs between themselves, so that the walls are experiencing only vertical pressure. Under the flights more than 6 meters, in order to avoid dragging in the design of the hanging rafters, include additional elements - suspensions, etc. For large spans, rape farms are used - lattice structures consisting of interconnected elements: lower and upper belts, racks and pods.
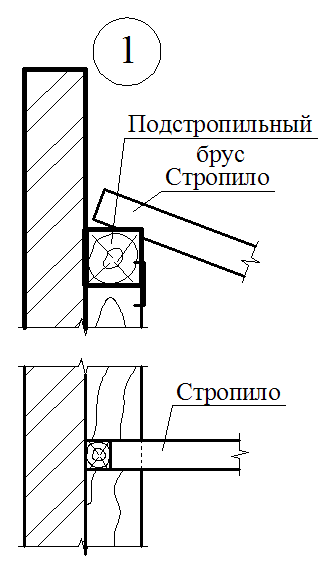
The main elements of the spelling rafters are the rafting legs and supporting their racks, sores, runs and riglels. Stropile feet B. single roofs They are based on a wrinkle on the subcording bars (Mauerlands), stacked on top of the outer walls in their inner face, and in the bounce roofs - the lower end on Mauerlat, the top - on the ski run.
Schedule Sling Roof Stropil Constructions Schemes
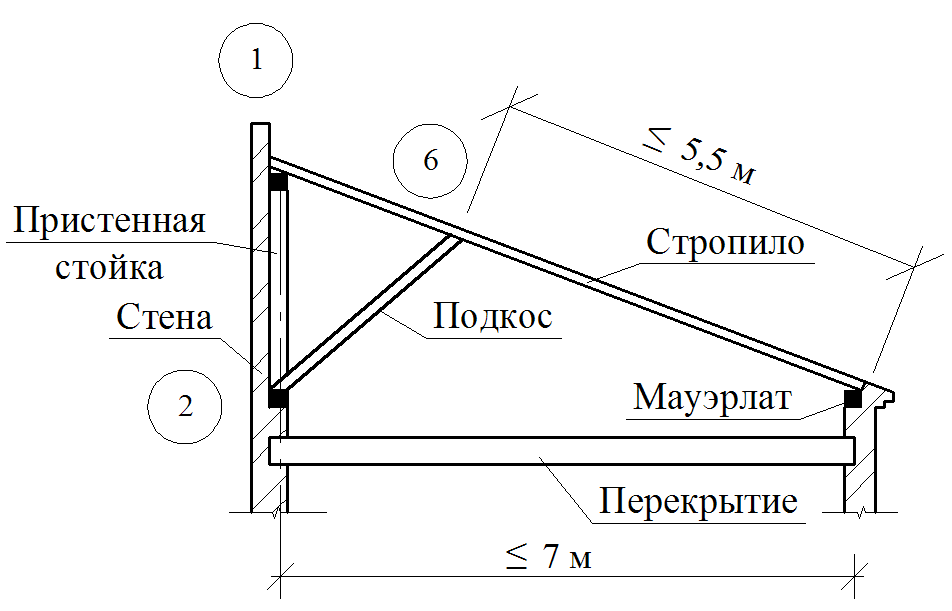
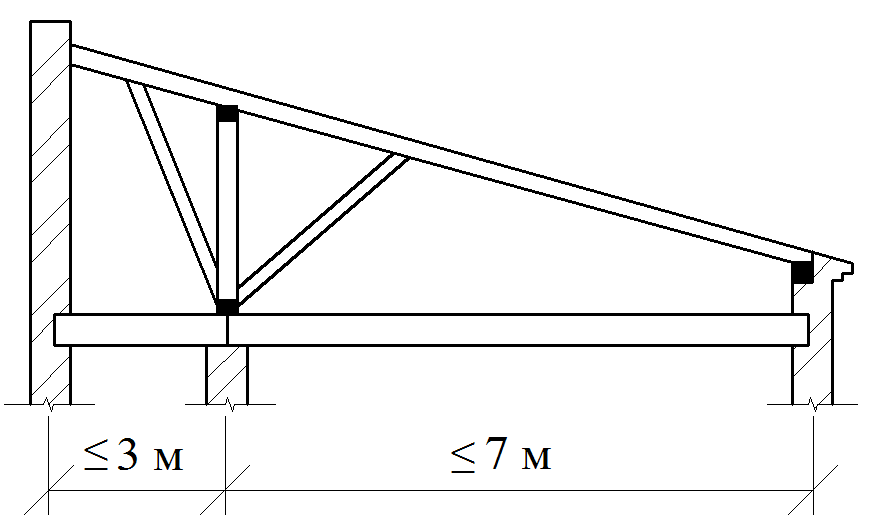
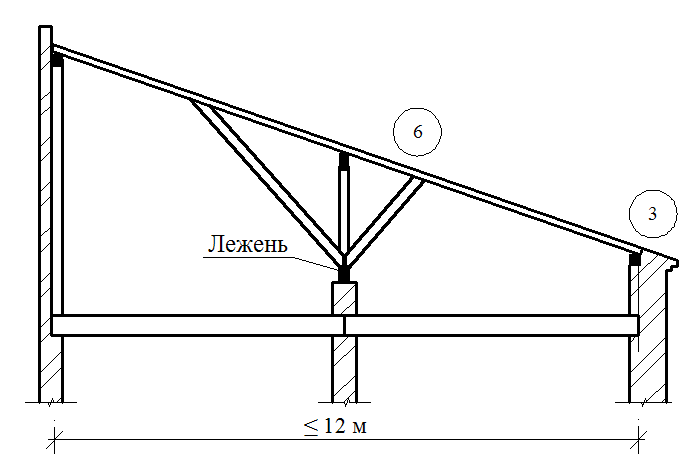
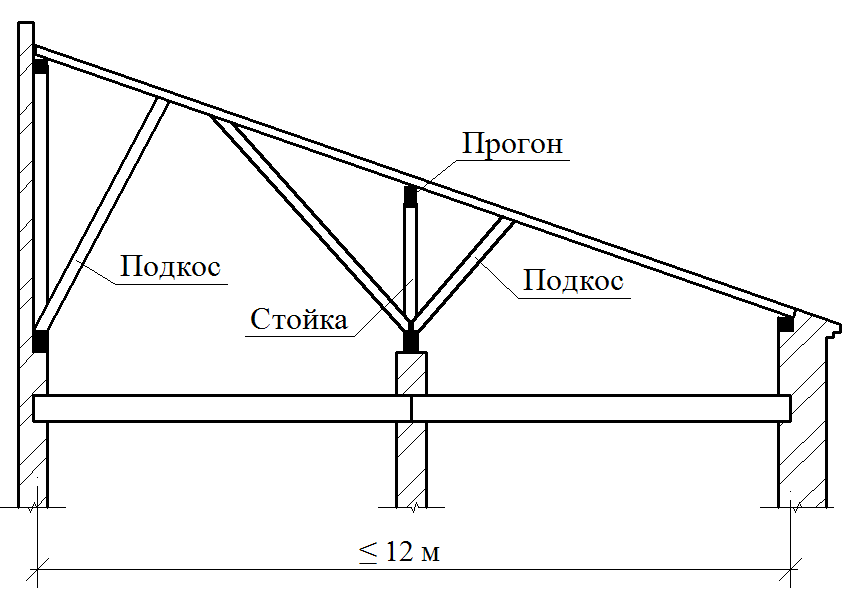
Schemes of the sleeve rafal structures of two-tie roofs
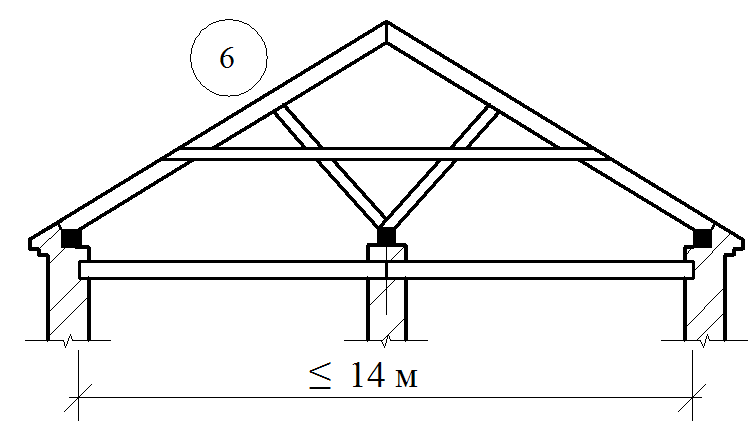
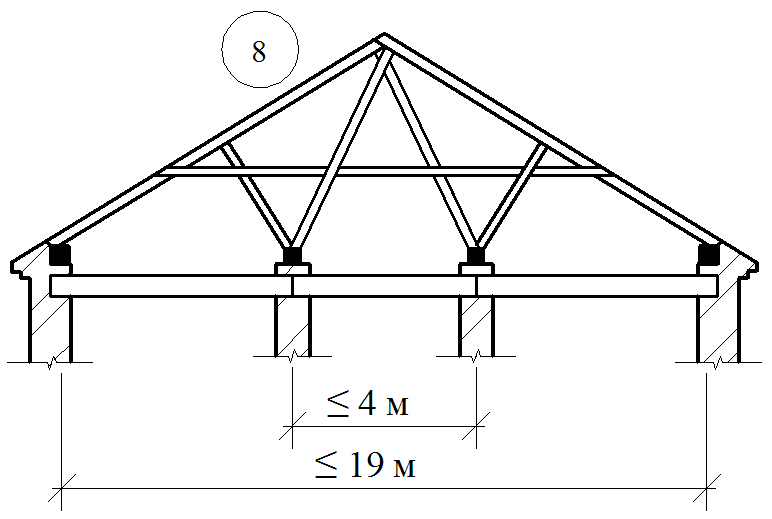
Coupling nodes blocking carrier structures
|
|
|
|
|
Matches of pairing board supporting structures
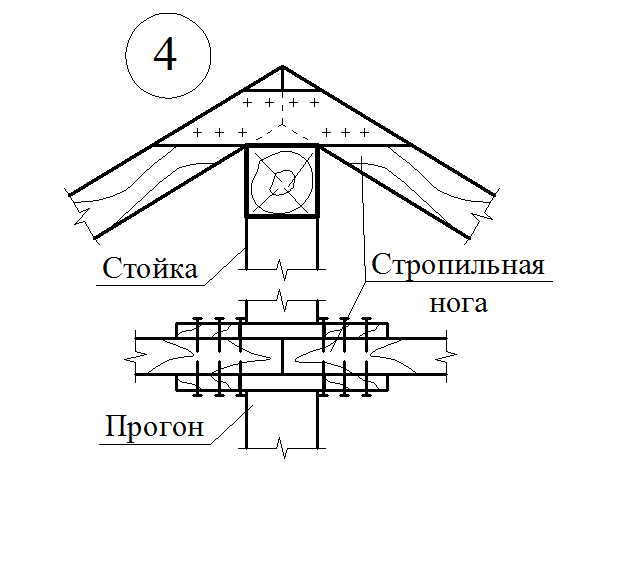
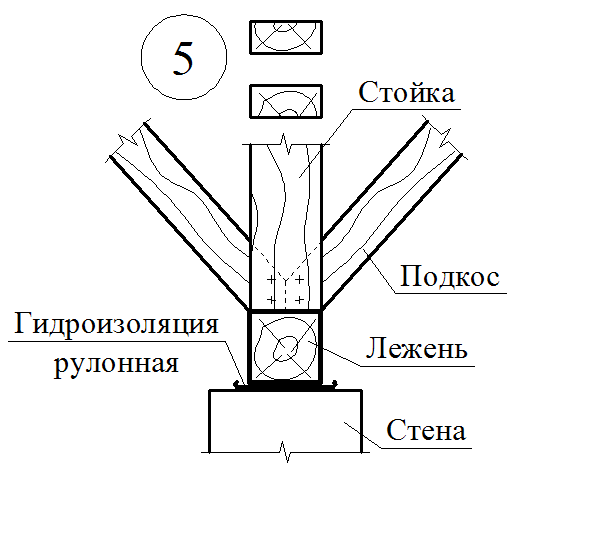
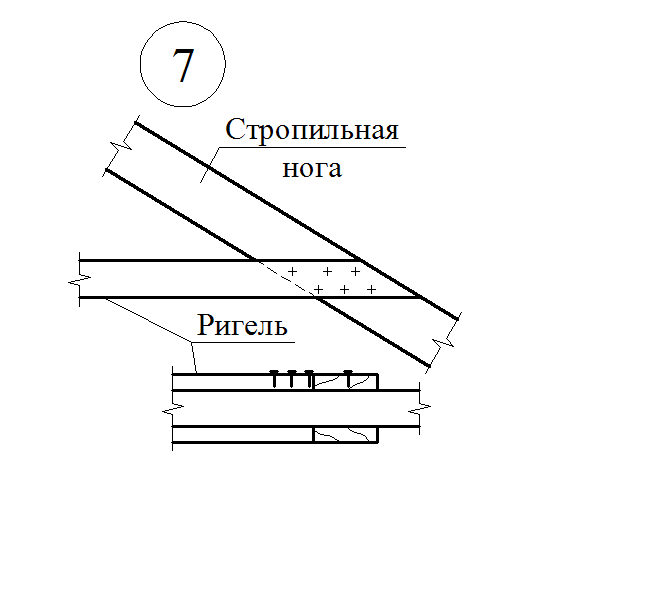
Details of nodes
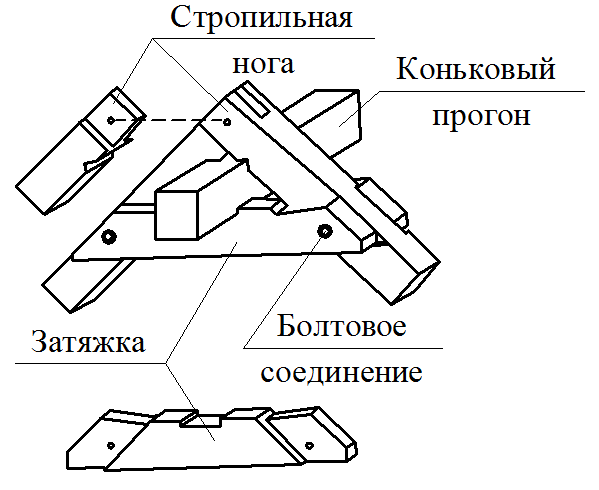
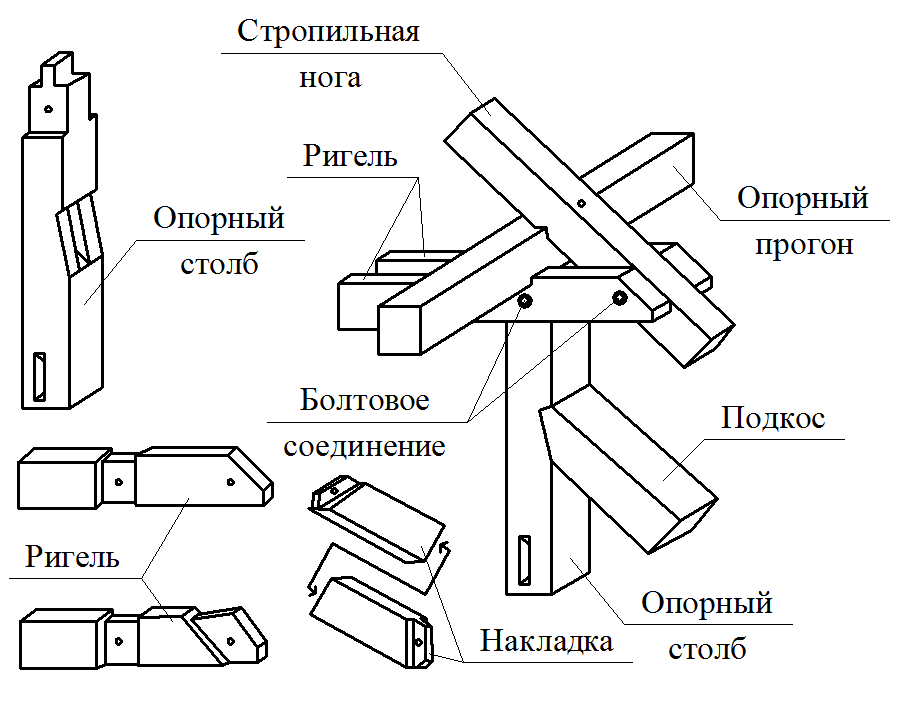
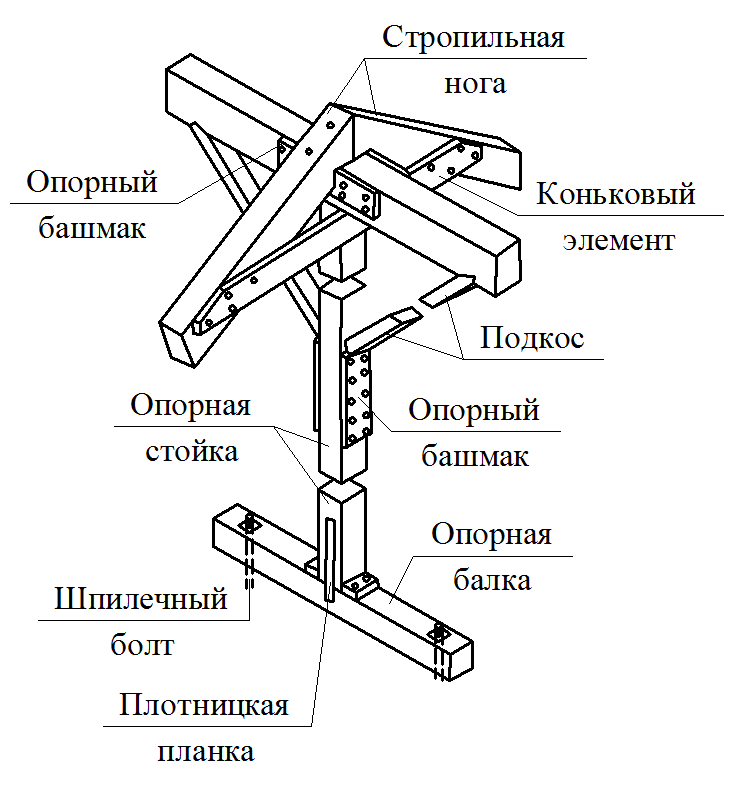
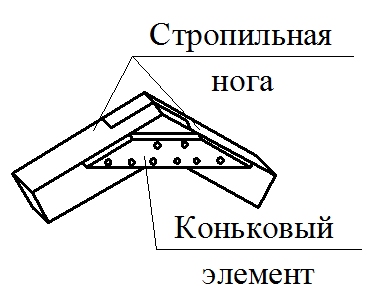
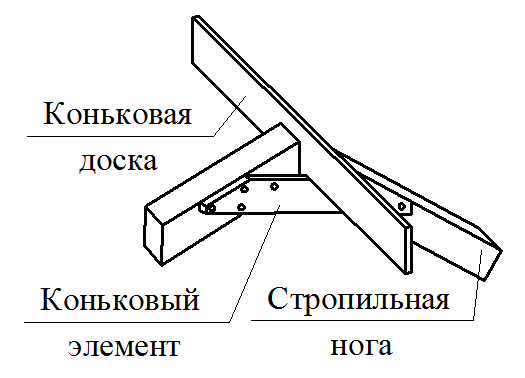
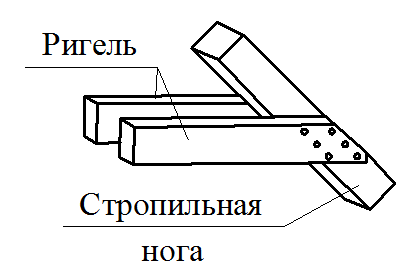
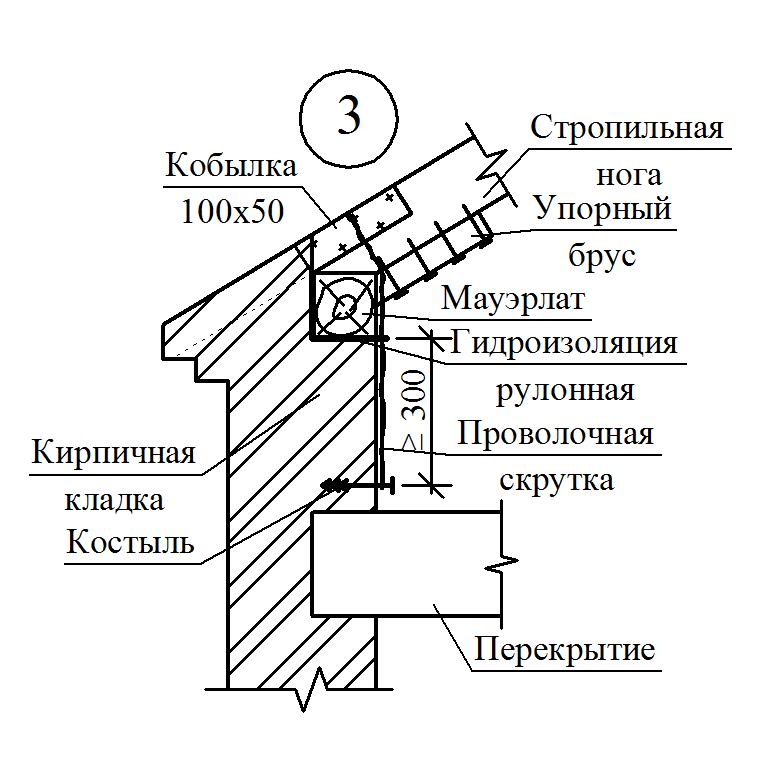
Mauerlat is a support bar serving for transmission and even distribution of pressure from rafted on the walls. For free access to the lower ends of the rafter legs and it is placed above the overlap of Pa 350-500 mm, and in low-rise buildings - by 100-150 mm. Maurylalat is made of logs with a diameter of 160-170 mm or a bars with a cross section of 140x160 mm and more.
With a frequent arrangement of the rafter, as well as with low-force walls, regardless of the received distance between the Mauerlae rafters, they are laid throughout the perimeter of external walls in the form of a continuous tape. With a rare arrangement of rafters and sufficiently strong walls of Mauerlast can be replaced by bars - shorts of 600-700 mm long, stacked under all the rafter legs.
So that the rafters were reloaded, Mauerlands antiseptrate and protect from the walls with rolled insulating material. In buildings with wooden walls, rafting legs are cut directly into the upper element of the wall - into the strapping or the upper crown.
Stropile legs are made of logs dried on one kant (from above), bars and boards on the edge. The cross section of the rafter legs and the distance between them is determined by the calculation depending on the magnitude of the span, the tina and the weight of the roof, snow load, etc. The most commonly used cross sections of BRUSEV 120-140x160-180 mm, boards 40-50x160-180 mm, round forest diameter 120- 160 mm. The distances in the axes between the rafyles of logs and the bars are taken equal to 1500-2000 mm, from the boards - 1000-1500 mm.
The lower ends of the rafter legs, besides wrinkling in Mauerlat, are additionally attached to it with brackets, as well as twigs from the wire (so that the roof with strong winds does not break down). A twist with one end covers Mauerlat, the other is fixed for the crutch, scored in a foot 300-400 mm below the Maurolat.
To the ends of the rafter feet on the magnitude of the coating of the eaves are nailed to the kills - shorts of the boards put on the edge, close in the cornice. By the fifters along the skate throughout the eaves, a formwork is nourished from the board, which serves as the base for the flooring and fastening the roof. If the rafting legs are produced behind Maurylalat and themselves are an element of the eaves, the fake does not apply (in low-rise residential buildings and other buildings).
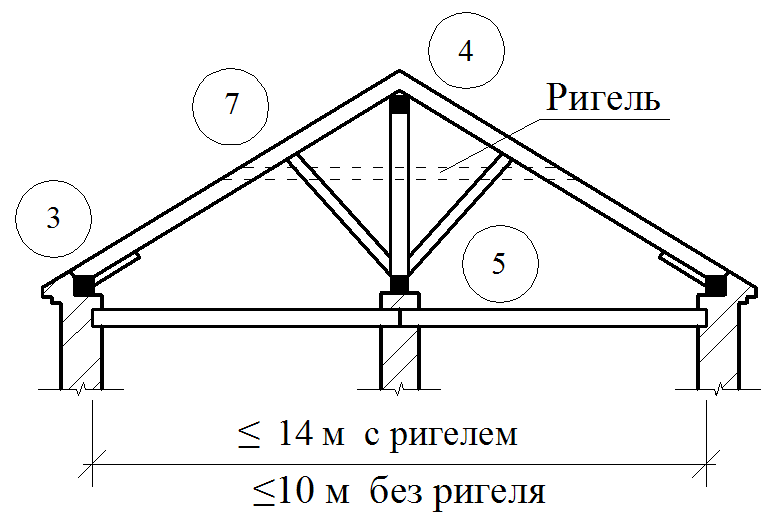
To avoid the returnation, the conjugation of the rafter legs in the skate should be durable, not allowing the shift of the rafter along the slope. The proper strength of the joint is achieved by the word of the upper ends of the rafter footsteps, laying the lining and fastening with bellows and bolts. The pressure from the upper ends of the rafter feet is transmitted to the internal supports by means of runs, racks and pods.
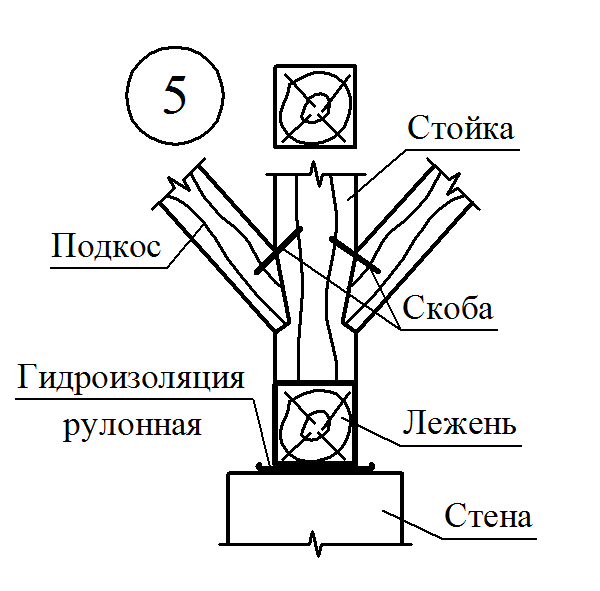
The runs are located in the rod of the roof (skate run) in two-ranking buildings with the central placement of internal supports or sidelines under rafters (side runs) - in three-propellant buildings and two-ranking with the asymmetric arrangement of the internal supports. It is arranged from the logs with a diameter of 180-220 mm, the bars with a cross section of 120x180 mm and more.
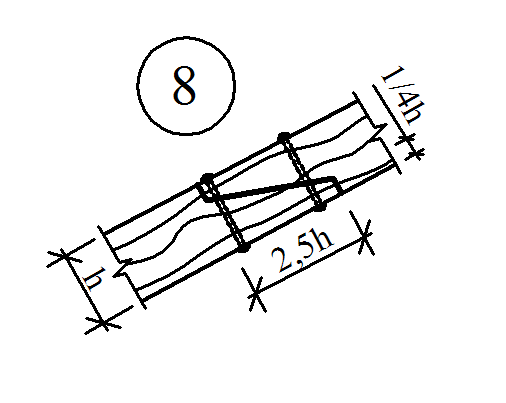
The runs are based on the end walls, and in the interval between them - on the racks installed on the internal bearing walls or pillars. The racks are made of logs with a diameter of 130-200 mm or bars with a cross section of 120x120 mm and more and have 2-3 pairs of rafter feet, which is an average of 4000-5000 mm.
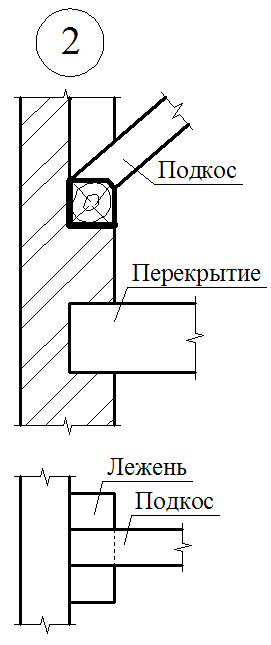
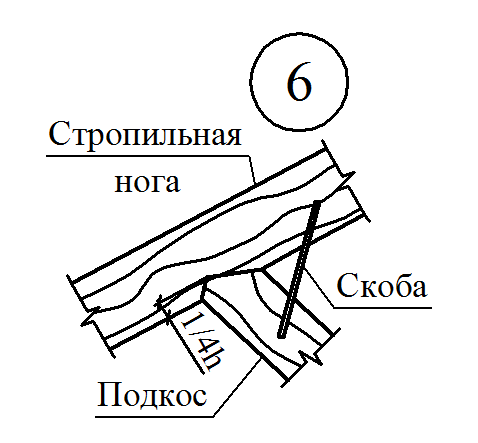
To reduce the deflection of the runs and the rafter feet, they are supported by the longitudinal and transverse subproims of the same section, as well as the rack. Longitudinal struts, in addition, provide roof rigidity in the longitudinal direction.
The installation of the sub-vehicle allows not only to reduce the cross section of the runs supported by them and the rafting legs, but also to increase them in length if you have to overlap big spans. The joint at the same time is performed by a wrinkle (oblique overlay) on the impudent and bolts.
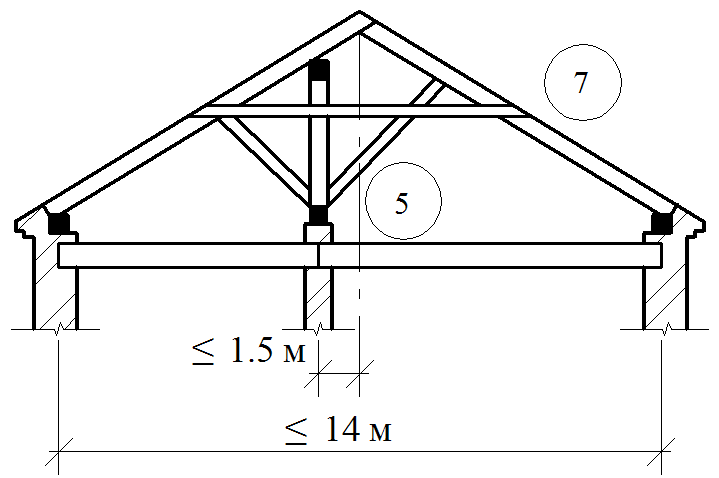
The lower end of the rack is usually based on a longitudinal bar-liter; In it, crossbar is cut. When the distance between the outer walls and the internal supports of more than 4000-4500 mm, transverse crackers are installed under all rapid legs. If the lying in the design of the rafters is not provided, the transverse pumps put only against the racks. At the same time, the sideways are placed on the sideways with the support of the rafter legs on them, and under the racks are resting.
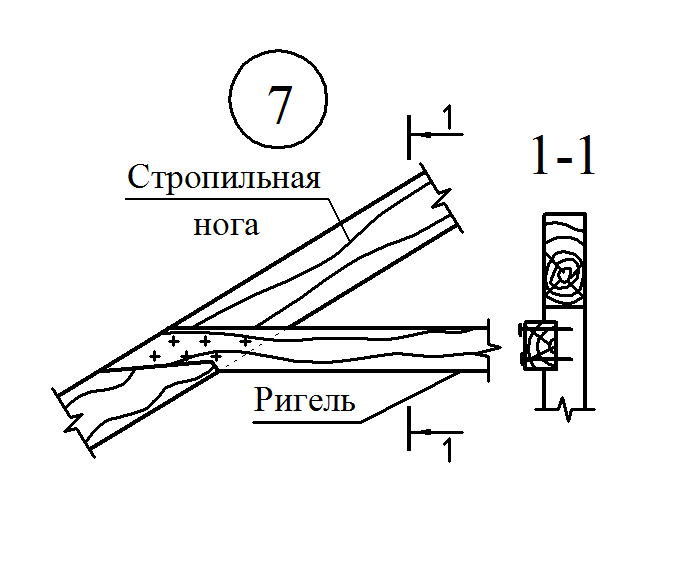
Along with the pink, to increase the rigidity of the rafter of large sizes, cross the riglels (contamination) - horizontal elements connecting the rafting legs. Place them under side runs or above them, but so that the attic can be free to pass. If there is a danger that the racks will be shifted due to the returdation from the ducts, they are, as well as rafters, are seized with horizontal struts attached to the bases of the racks.
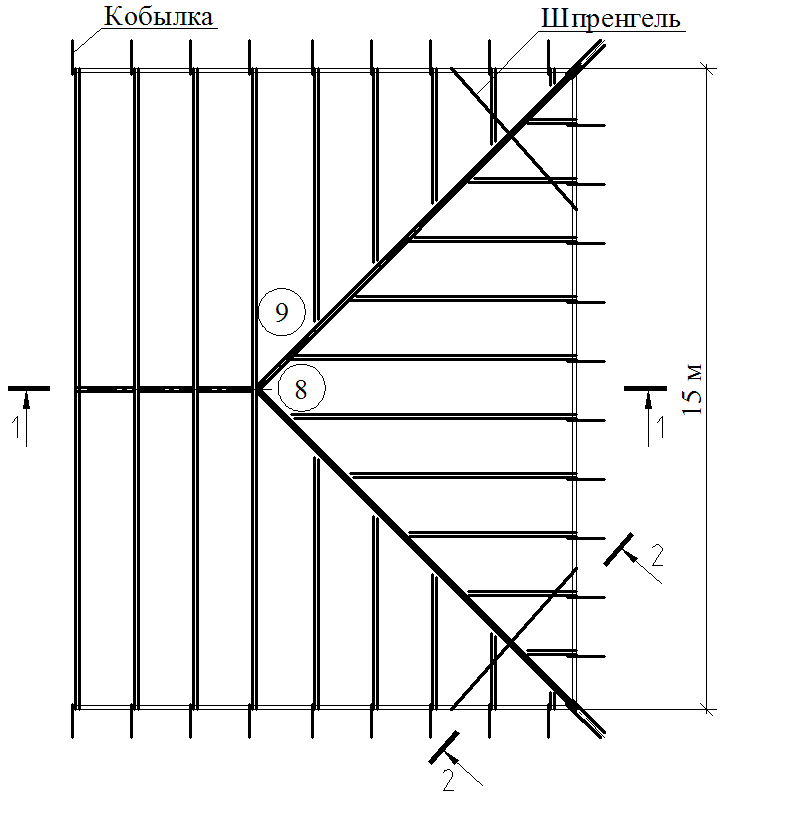
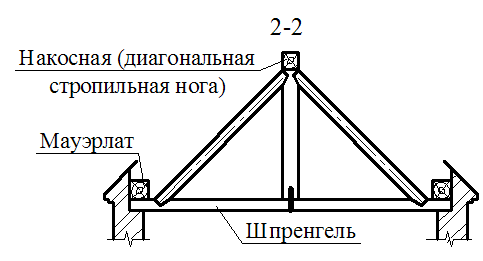
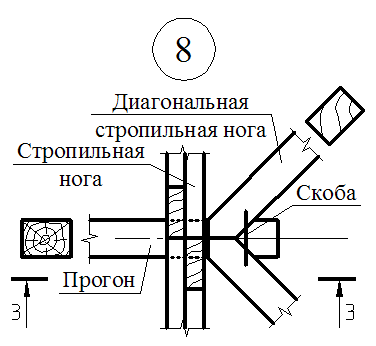
In four-page roofs, in addition to all these elements, sprinkling rafters, additionally install diagonal (savory) strropyl legs and shpregels (designs that support the skates at the end walls).
Diagonal rafting legs are embedded by one end in Mauerlates converging in the corners of the building, and the top is based on the edge of the skate run (in two-ranking buildings with central standing inner supports), and if it is not - on the sumps attached to the upper ends of the nearest pair of rafter (in Three-span buildings, as well as in two-ranking with the asymmetric arrangement of the internal supports).
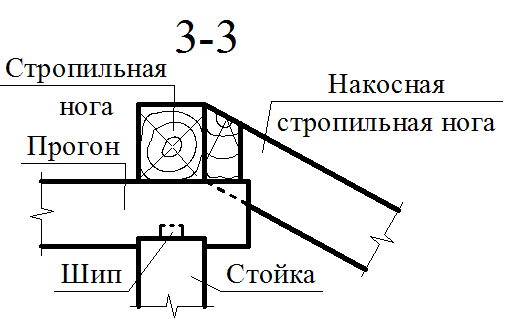
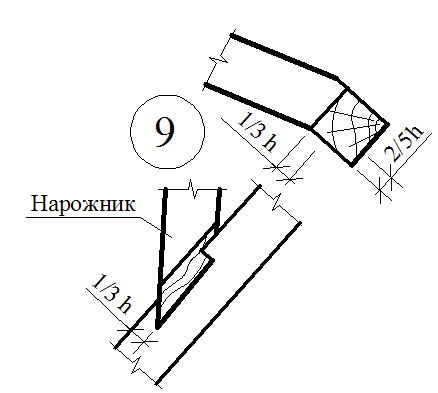
On the diagonal rafting legs, the small rafter legs are described - ninurians - and mate with them (usually frying) flush with the surface of diagonal rafting legs so that the base under the roof in these bridges was in the same plane with skates. Opportuning narigines on diagonal rafting legs make a mistake to reduce the weakening by their wrists. In order to avoid the weakening of the diagonal rafter feet, the narigines sometimes refrigerate on the rails, nailed from the side of the applied rafting legs.
If the spans of apparent rafting legs are large, they are propheted from below with racks that are installed on horizontal beams stacked diagonally on the outer moans. These beams can be embedded by the soaps that support the stoics and forming the Schprengels with them - structures that increase the rigidity of the solo system.
All configuration elements rafter system They are performed by metal mounts - nails, brackets, bolts, stuffed plates, gear discs, rings, knocked with discs, fasteners, etc.
Fragment plan rafted hip roofs
|
|
|
|
|
|
Approximate cross sections of rafters and distances between it |
|
Node 1. Roof adjoining to chimney
- Obsek.
- Slinge foot.
- Insulation.
- Parosolation.
- Board.
- Swirl.
- Plank adjoining.
- Pipe in the roof.
Node 2. Blood adjoining to a round tube
- Roofing Ruflex Super.
- Lining carpet Ruflex K-EL.
- Solid base for laying soft roof (OSP-3, FSF).
- Obsek.
- Bar 50x50 mm (to ensure ventilation).
- Waterproofing, windproof film.
- Slinge foot.
- Bar 50x50 mm (for additional insulation).
- Parosolation.
- Board.
- Swirl.
- Pipe in the roof.
- Sealer.
- SKT seal.
- Clamp.
Node 3. Roof adjoining to a brick wall
- Roofing Ruflex Super.
- Lining carpet Ruflex K-EL.
- Complete base (OSP-3, FSF).
- Plank adjoining.
- Wall of the building.
- End carpet Ruflex Super Pintari.
- Plaster layer.
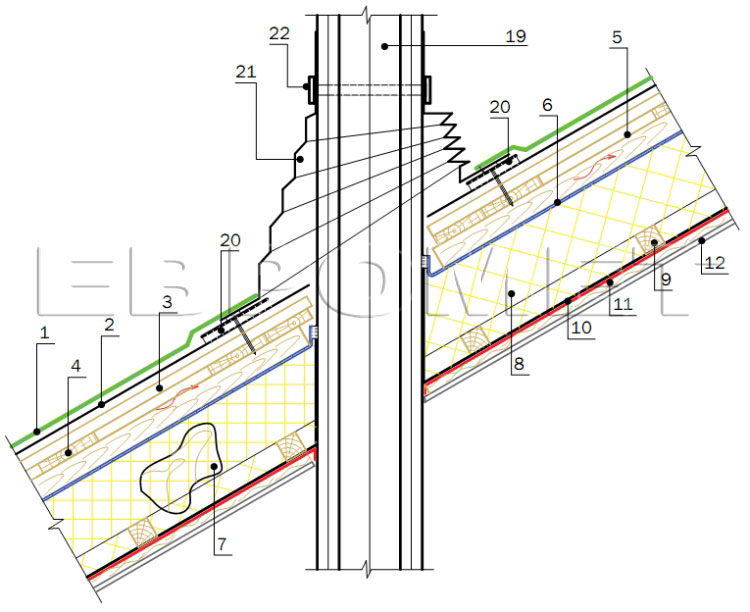
Node 4. Design of the root sills of the attic floor
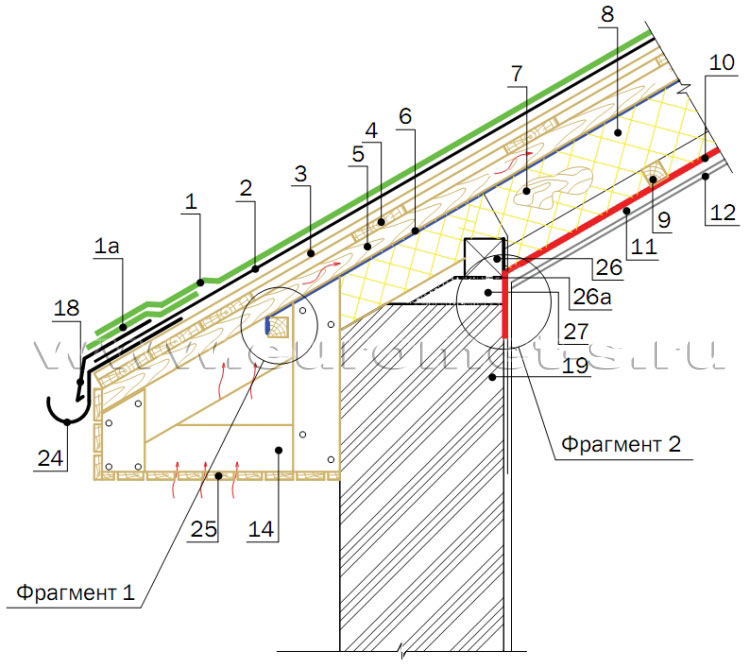
3. Complete base (OSP-3, FSF).
4. Doom.
6. Waterproofing, windproof film.
7. Stropile foot.
8. Insulation.
10. Parosolation.
12. Ceiling liner.
14. Correspond's frame.
18. Ducklock.
19. Wall of the building.
24. Drain bracket.
25. Karnisy firmware
26. Maurylalat.
26a. Waterproofing layer under Maurylalat.
27. Cement-sand reinforced screed.
Note:
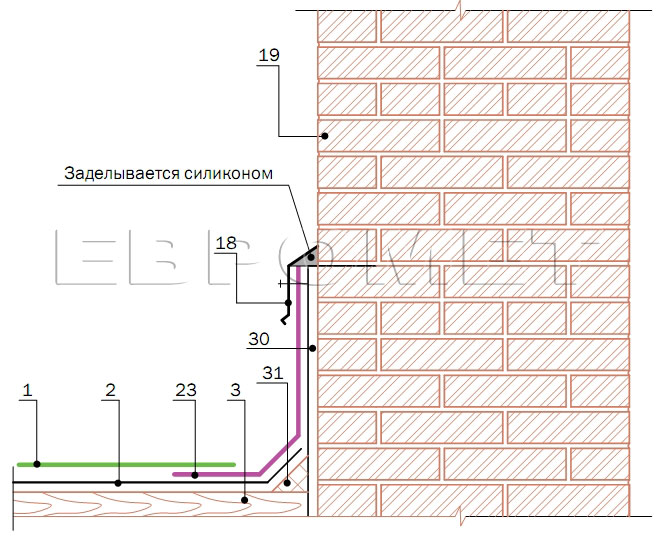
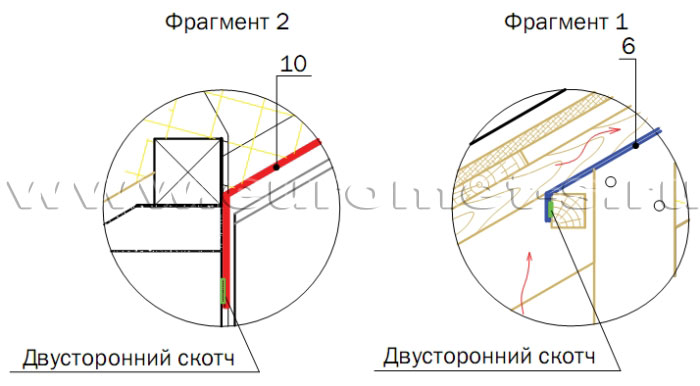
- Waterproofing film (Duke, Izospan, Tyvek, Yutafol or others) should be displayed on the outer edge of the wall and secure on the bar (see Fragment 1).
- Steam barrier film to start on the wall and consolidate it with the help of two-way tape (see Fragment 2).
Node 5. Options for installing a gutter of the drainage system
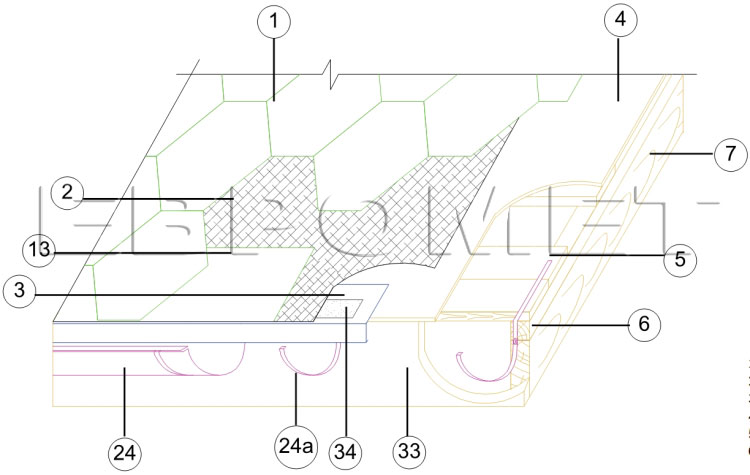
1. Roofing Ruflex Super.
2. Lining carpet Ruflex K-EL.
3. Farmery metal plank.
4. Complete base (OSP-3, FSF).
5. Edged board.
6. counterbus 50x50 mm to provide ventilation gap at least 5 cm.
7. Stropile beam.
13. Ruflex Super Sking Roof Tile.
24 a. Bracket fastening gutter roof drainage systems.
24. Drainage chute.
33. Front board.
34. Glue Ruflex K-36.
Node 6. The ridge of the roof of the attic floor with the Alipai skate deflector

- Roofing Ruflex Super.
- Lining carpet Ruflex K-EL.
- Complete base (OSP-3, FSF).
- Obsek.
- Bar 50x50 (to ensure ventilation).
- Waterproofing, windproof film.
- Slinge foot.
- Insulation.
- Bar 50x50 (for additional insulation).
- Parosolation.
- Board.
- Swirl.
- Alipai skoth fan.
Node 7. The ridge of the roof of the attic floor with roofing fans KTV and VILPE
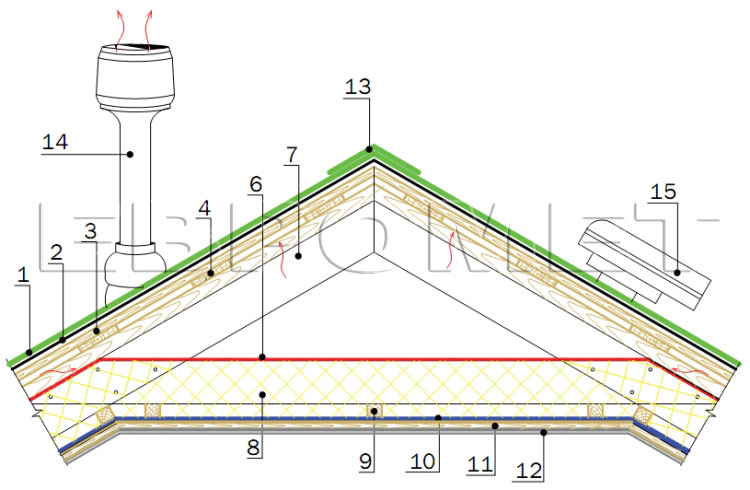
- Roofing Ruflex Super.
- Lining carpet Ruflex K-EL.
- Complete base (OSP-3, FSF).
- Obsek.
- Bar 50x50 (to ensure ventilation).
- Waterproofing, windproof film.
- Slinge foot.
- Insulation.
- Bar 50x50 (for additional insulation).
- Parosolation.
- Board.
- Swirl.
- Ruflex Super Sking Roof Tile.
- Roofing fan type Vilpe.
- Roofing fan of a car type KTV.
Knot 8. Skown node roof roofs of a mansard floor with a wooden aerator
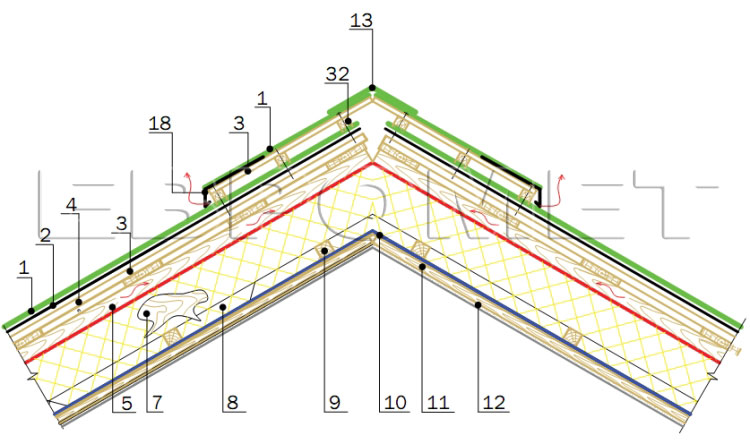
- Soft roofing Ruflex Super.
- Lining carpet Ruflex K-EL.
- Complete base (OSP-3, FSF).
- Roofing dorel.
- Bar 50x50 (to ensure ventilation).
- Waterproofing, windproof film.
- Slinge foot.
- Insulation.
- Bar 50x50 (for additional insulation).
- Parosolation.
- Board.
- Swirl.
- Ruflex Super Sking Roof Tile.
- Drip.
- Skate frame.
Knot 9. Skown node roof roof floor with plastic aerator
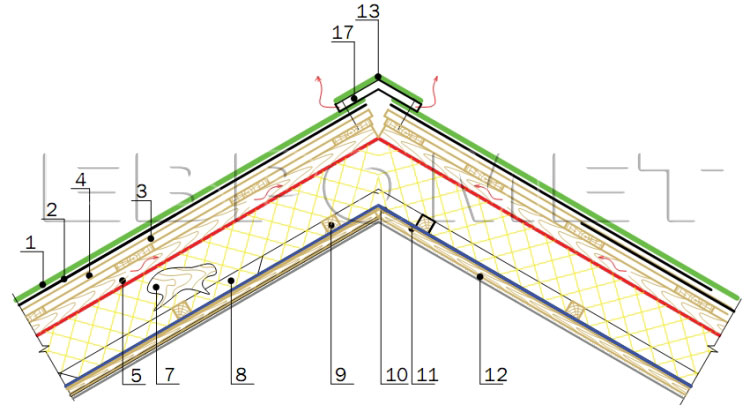
- Soft roofing