In chapter 1.1 Pue 7th ed., Currently operating from January 1, 2003, the following requirements for the identification of conductors are established (allocated to us):
"1.1.29. For the color and digital designation of individual isolated or uninsulated conductors, colors and numbers must be used in accordance with GOST R 50462 "Identifying conductors in colors or digital designations".
Conditions protective grounding
in all electrical installations as well zero protective conductors
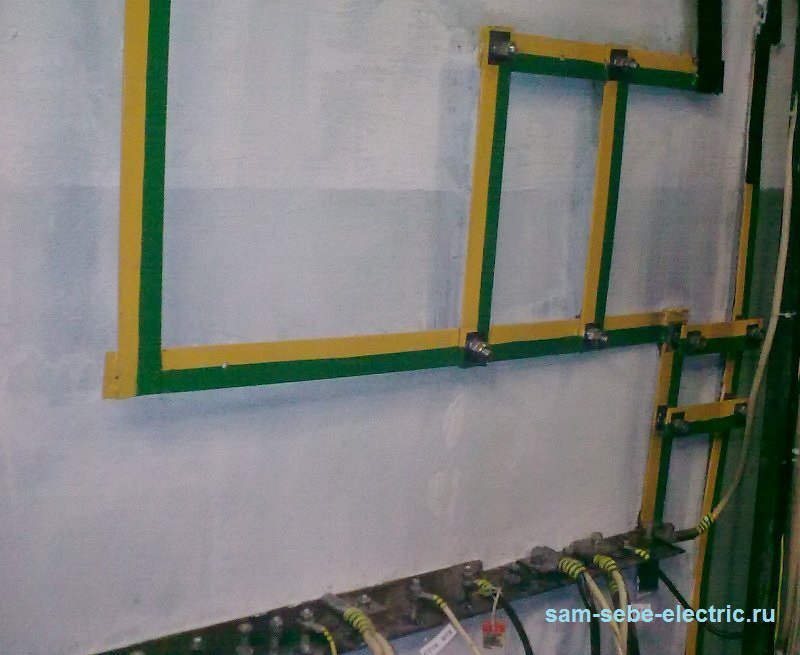
in electrical installations with voltage up to 1 kV from plug-free neutral, including tires, should have an alphabetic designation of re and color designation by alternating longitudinal or transverse stripes of the same width (for tires from 15 to 100 mm) of yellow and green colors.
Zero workers (neutral) conditions denoted by the letter n and blue color. Combined zero protective and zero working conductors Must have an alphabetic designation PEN and color designation: blue Over the entire length and yellow-green stripes at the ends.
1.1.30. The alphanumeric and color designations of the same connections in each electrical installation must be the same.
Tires must be indicated:
1) for variable three-phase current: Tires phase a - yellow, phases in green, phases with - red,
2) for a variable single-phase current tire B.attached by the end of the winding of the power supply - red, tire A.attached to the top winding of the power supply - yellow.
Tires single-phase currentif they are a branch from the three-phase system tires are indicated as the corresponding tires three-phase current;
3) for constant toke.: Positive tire (+) - red, negative (-) - blue and zero working M. – blue color. …».
Credited requirements contain numerous errors. First, a rough mistake should be considered the requirement of paragraph 1.1.30, which prescribes the use of yellow color and green color to identify two phase tires. GOST R 50462-92, which acted from January 1, 1994 until December 31, 2010, forbidden the use of separately yellow color and green, if confusion was possible with yellow-green color. I replaced it by GOST R 50462-2009, which is valid until September 30, 2016, forbidden to apply a separate color and green color to identify conductors. A similar ban contains a new GOST 33542 (see).
The use of yellow and green phase tires is created in low-voltage electrical installations conditions under which you can confuse protective tires with yellow-green marking and phase tires with yellow or green colors. At the same time, the likelihood of erroneous connection to the phase tires of protective conductors of electrical wiring and, as a result, the appearance of voltage on the open conductive parts of the class I electrical equipment, the touch to which becomes fatally dangerous for humans.
Secondly, tires representing one of the options for the execution of conductors are usually used in low-voltage distribution devices that produce and certified according to the requirements of national standards that have established that the color identification of conductors must comply with the requirements of GOST R 50462-92 or GOST R 50462-2009.
Thirdly, the simultaneous use of blue and blue colors for identifying the pole and medium tires will inevitably lead to a dangerous confusion, since the pole tire may be under a voltage of 110, 220, 440 V and more, and the average tire is under voltage, almost equal to zero. Moreover, GOST R 50462-92 considered blue and blue colors as a color.
Fourth, in cited requirements used concepts " single-phase current"And" three-phase current"What is a rough mistake. Single-phase and three-phase can be electrical systems, electrical networks, electrical installations, electrical chains and electrical equipment. Electric current according to GOST R 52002-2003 "Electrical engineering. Terms and definitions of basic concepts "can be variable, constant, pulsating and sinusoidal.
Fifth, in the requirements of the DC electrical circuits under consideration, mentioned zero working tire. However, neutral conductors and, including tires apply in electrical chains alternating current. In the electrical circuits of DC use medium conductors. Therefore, the specified tire must be named medium tire.
Sixth, phase conductors in the requirements are denoted by letters " A, B, with" However, in the standards of IEC and developed on their basis, the national standards, phase conductors designate otherwise - " L1, L2, L3».
Seventh, the analyzed requirements are formulated for electrical installations voltage up to 1 kV, and IEC standards and their relevant national standards establish the requirements for low-voltage electrical installationsoperating at a voltage of up to 1000 V AC and up to 1500 V DC inclusive.
In the eighth, outdated terminology is applied in the requirements, not corresponding to the terminology of GOST 30331.1 (see).
The appearance of errors in the requirements for the color and alphanumeric identification of conductors is explained by the following reasons. Requirements p. 1.1.29 Pue 7th ed. It was formulated based on the requirements of GOST R 50462-92, and the requirements of paragraph 1.1.30 Pue 7th ed. They were rewritten from paragraph 1.1.29 Pue 6th ed. Sample 1985 Thus, the generally accepted principles of the color identification of conductors established by the International Electrotechnical Commission and contained in the requirements of GOST R 50462-92, GOST R 50462-2009 and other national standards developed on the basis of IEC standards have not yet received their correct Reflections in PUE requirements. Although the age of 23, since the introduction of GOST R 50462-92 and replaced it by GOST R 50462-2009, it was more than enough to adjust all national regulatory documentation and, moreover, the correct formulation of the analyzed requirements in Chapter 1.1 Pue 7th ed.
Conclusion. Requirements outlined in paragraph 1.1.29 and 1.1.30 Pue 7th ed., It is necessary to replace the following:
Color and alphanumeric identification of conductors in electrical installations should be performed according to the requirements of GOST 33542-2015
.
Question 32.
What conference and color designation should have a protective grounding conductor in electrical installations?
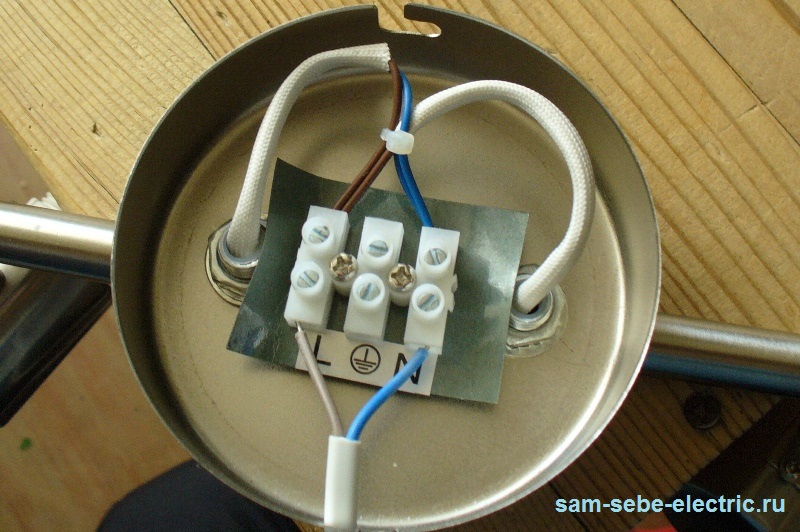
claim 1.1.29.Pue
PE
N. Pen.
Question 33.
What letter and color designation should have combined zero protective and zero working conductors?
claim 1.1.29.Pue
For color and digital designation of individual isolated or uninsulated conductors, colors and numbers should be used in accordance with GOST R 50462 "Identifying conductors in colors or digital designations."
Conditioners of protective grounding in all electrical installations, as well as zero protective conductors in electrical installations with a voltage of up to 1 kV with deaf-marketanenere, including tires, must have an alphabetic designation PE and the color designation by alternating longitudinal or transverse stripes of the same width (for tires from 15 to 100 mm) of yellow and green colors.
Zero workers (neutral) conductors are indicated by the letter N. and blue. Combined zero protective and zero working conductors must have an alphabet designation Pen. and color designation: blue color over the entire length and yellow-green stripes at the ends.
Question 34.
What letter and color notation should have a tire with a variable three-phase current?
clause 1.1.30.Pue
Tires must be indicated:
A. - yellow, phases B. - Green, phases C. - red;
B. A.
M. - Blue.
Question 35.
What letter and color notation should have a bus at a constant current?
clause 1.1.30.Pue
The alphanumeric and color designations of the same connections in each electrical installation must be the same.
Tires must be indicated:
1) with a variable three-phase current: phase tires A. - yellow, phases B. - Green, phases C. - red;
2) with a variable single-phase bus tire B.attached by the end of the power supply winding - red, tire A., attached to the top of the winding of the power supply, is yellow.
Single-phase current tires, if they are a branch from the three-phase system tires, are indicated as the corresponding three-phase current bus;
3) at constant current: positive bus (+) - red, negative (-) - blue and zero working M. - Blue.
The color designation must be performed along the entire length of the tires, if it is also provided for more intensive cooling or anti-corrosion protection.
It is allowed to perform the color notation not along the entire length of the tire, only the color or only alphanumeric designation or color in combination with alphanumeric in the tire connection places. If uninsulated tires are not available for inspection during the period when they are under voltage, it is allowed not to be denoted. It should not decrease the level of security and visibility when servicing electrical installation.
Question 36.
What neutral should the electrical networks of 10 kV voltage should work?
clause 1.2.16.Pue
Work electrical networks 2-35 kV voltage can be provided as with isolated neutraland with neutral, grounded through a gauge reactor or resistor.
Compensation of the capacitive current of the earth closure should be applied at the values \u200b\u200bof this current in normal modes:
in networks with a voltage of 3-20 kV, having reinforced concrete and metal supports on airlines power transmission, and in all networks with voltage of 35 kV - more than 10 A;
in networks that do not have reinforced concrete and metal supports on power lines:
more than 30 A at a voltage of 3-6 kV;
more than 20 A at a voltage of 10 kV;
more than 15 A at a voltage of 15-20 kV;
in the generator voltage diagrams of 6-20 kV blocks, transformer generator - more than 5 A.
The operation of electrical networks with a voltage of 110 kV can be provided with both deaf-free and with effectively grounded neutral.
Electrical networks with a voltage of 220 kV and higher should only work with a deaf-earth vent.
Topic 2. Personnel requirements and its preparation
Question 1.
Which groups are subdivided by electrical personnel of the organization?
1.4.1. PTEEP
The operation of electrical installations must be carried out prepared electrical personnel.
Electrotechnical personnel of enterprises are divided into:
administrative and technical;
operational*;
repair;
operational repair *.
__________________
* In the future, operational and operational and repair personnel, unless separation is required, referred to as operational personnel.
Question 2.
How often is the inspection of electrical safety knowledge for electrical personnel?
p. 1.4.20. PTEEP
Question 3.
What frequency of testing of electrical safety knowledge is installed for the personnel serving electrical installation?
p. 1.4.20. PTEEP
Another check should be made on the following dates:
For electrical personnel, directly organizing and conducting operations for servicing existing electrical installations or performing commissioning, electrical, repair work or preventive tests, as well as for personnel with the right to issue outfits, orders, operational negotiations - 1 time per year;
For administrative and technical personnel, not related to the previous group, as well as for labor protection specialists, admitted to inspection of electrical installations - 1 time every 3 years.
Question 4.
What frequency of advanced training should provide an employer for staff?
clause 1.2.6. Responsible for electricity owes:
to verify the compliance of the power supply schemes to the actual operational, with the mark on them on the inspection (at least 1 time in 2 years); revision of instructions and schemes (at least 1 time in 3 years); control measurements of electrical energy quality indicators (no less often 1 time in 2 years); improving the qualifications of electrical personnel (at least 1 time in 5 years);
clause 1.4.5. Mandatory forms of work with various categories of workers *:
___________________
* Terms of work with staff in electric power organizations Russian FederationApproved by order of the Ministry of Power Energy of Russia from 19.02.2000 No. 49 and registered in the Ministry of Justice of Russia 16.03.2000. Registration number 2150.
clause 1.4.5.1. With administrative and technical staff:
introductory and target (if necessary) labor protection instructions;
With administrative and technical staff with the rights of operational, operational and repair or repair personnel, in addition to these forms of work, all types of preparation provided for operational, operational and repair or repair personnel should be carried out.
clause 14.5.2. With operational and operational and repair personnel:
verification of knowledge of rules, labor protection standards, real rules, fire safety rules and other regulatory documents;
duplication;
special preparation;
control counter-emergency and fire training;
professional additional education for continuous advanced training.
clause 1.4.5.3. With repair personnel:
input, primary in the workplace, repeated, unscheduled and target labor protection instructions, as well as fire safety instructions;
preparing for new post or profession with learning in the workplace (internship);
verification of knowledge of rules, labor protection standards, real rules, fire safety rules and other regulatory documents;
professional additional education for continuous advanced training.
Question 5.
When is an extraordinary test of personnel knowledge?
clause 1.4.23.TEEP
An extraordinary knowledge check is carried out regardless of the period of the previous check:
With the introduction of new or recycled norms and rules into operation;
When installing new equipment, reconstruction or changing the main electrical and technological schemes (the need for an extraordinary check in this case determines the technical leader);
When prescribing or translating to another job, if new responsibilities require additional knowledge of the norms and rules;
In violation by employees, the requirements of labor protection regulations;
At the request of state supervision bodies;
On the conclusion of commissions investigating accidents with people or violations in the work of the energy facility;
With raising knowledge on a higher group;
When checking knowledge after obtaining unsatisfactory assessment;
For a break in work in this position for more than 6 months.
Question 6.
How long from the date of the last test of knowledge workers who have received an unsatisfactory assessment can pass a re-test of knowledge?
clause 1.4.22.TEEP
Employees who received in the next test of knowledge unsatisfactory assessment, the Commission appoints a re-verification no later than 1 month from the date of the last check. The certification period for the employee who has received an unsatisfactory assessment is automatically extended to the period appointed by the Commission for the second inspection, if there is no knowledge verification of the Special Decision of the Commission on the temporary removal of the employee from work in electrical installations
Question 7.
How are the results of testing of knowledge of electrical safety personnel?
clause 1.4.39.TEEP
The results of the test of knowledge are recorded in the molded form and are signed by all members of the Commission. If the test of knowledge of several employees was carried out in one day and the composition of the commission did not change, then members of the Commission can be written 1 time after the end of work; It should be indicated in words total number Workers who have a knowledge check.
Human Resources, who has successfully verified knowledge, issued a certificate of the established form.
Question 8.
For what period should be the internship of electrical personnel in the workplace before appointment on independent work?
p.P. 1.4.8, 1.4.11 PTEP
1.4.8. Electrical personnel before appointing independent work or during the transition to another job (position) related to the operation of electrical installations, as well as during the break in the work as electrical personnel over 1 year is obliged to undergo internship (manufacturing training) in the workplace.
For training, the employee must be granted a term sufficient to familiarize themselves with equipment, equipment, operational schemes and simultaneous study in the amount necessary for this position (profession):
rules of the device of electrical installations, security rules, rules and techniques for first aid in cases of industrial accidents, rules for applying and testing the means of protection, of these Rules;
job and manufacturing instructions;
labor protection instructions;
other rules, regulatory and operational documents operating in this consumer.
1.4.11. The internship is carried out under the guidance of a responsible training personnel and is carried out according to programs developed for each position (workplace) and approved in the prescribed manner. The length of the internship should be from 2 to 14 shifts.
Question 9.
Who has the right to check the knowledge of non-electrotechnical personnel with the assignment of the I admission group?
p.1.4.4. PTEEP
Non-electrotechnical personnel performing work in which the danger of lesion may arise electric shockis assigned a group I on electrical safety. The list of posts and professions requiring assigning personnel I on electrical safety groups, determines the head of the consumer. The personnel who learned the electrical safety requirements belonging to its production activities is assigned a group I with execution in the journal of the established form; The certificate is not issued.
The Assignment of Group I is made by conducting a briefing, which, as a rule, must complete the knowledge check in the form of an oral survey and (if necessary) checking the acquired skills of safe ways to work or the first aid to defeat the electric shock. The assignment of the I group of electrical safety is carried out by an employee from the number of electrical personnel of this consumer with an electrical safety group not lower than III.
The assignment of the I group of electrical safety is carried out with frequency at least 1 time per year.
Question 10.
Who belongs to electrical technological staff?
p.1.4.3. PTEEP
Service of electrical technological installations (electric welding, electrolysis, electrothermia, etc.), as well as complex energy-satisfied production and technological equipment, which requires constant maintenance and adjustment of electrical appliances, electric drives, manual electrical machines, portable and mobile electrical drivers, portable power tools, Must carry out electrical technological staff. It should have sufficient skills and knowledge to safely perform work and maintenance assigned to it.
Electrotechnological staff of production workshops and sections that are not part of the consumer's energy service that performs the operation of electrical technological installations and having a group of electrical safety II and higher, in its rights and responsibilities is equal to electrotechnical; Only, it is subject to the consumer's energy service.
Heads, in direct subordination of which electrotechnological personnel are located, should have a group of electrical safety not lower than that of subordinate staff. They must implement the technical guide to these personnel and control over its work.
The list of posts and professions of electrical * and electrical scientific personnel who need to have an appropriate electrical safety group, approves the head of the consumer.
The head of the consumer, the chief engineer, the technical director, the assignment of an electrical safety group is not required. However, if the specified workers had previously had a group of electrical safety and want to confirm it (promote) or to receive for the first time, the knowledge check is carried out as usual for electrical personnel.
________________
* In the future, electrical personnel is also understood under electrotechnical personnel, if separation is not required.
Question 11.
Who belongs to operational personnel?
Personnel non-electrotechnical | |
Operations staff | |
Operational Staff | |
Staff repair | |
Electrotechnical personnel | |
Question 12.
Who belongs to repair personnel?
Terms used in intersectoral
Rules for labor protection (safety rules)
When operating electrical installations, and their definitions
Administrative staff | Managers and specialists who are charged with the organization of technical and operational services, repair, assembly and commissioning in electrical installations |
Personnel non-electrotechnical | Personnel not falling under the definition of "electrical", "electrotechnological" personnel |
Operations staff | Personnel carrying out operational management and maintenance of electrical installations (inspection, operational switching, workplace preparation, admission and supervision of working, execution of work in the order of current operation) |
Operational Staff | Repair personnel, specially trained and prepared for operational services in the approved volume of electrical installations attached |
Staff repair | Personnel providing maintenance and repair, installation, commissioning and testing of electrical equipment |
Electrotechnical personnel | Administrative and technical, operational, operational repair, repair personnel, organizing and carrying out installation, commissioning, maintenance, repair, control of the operation of electrical installations |
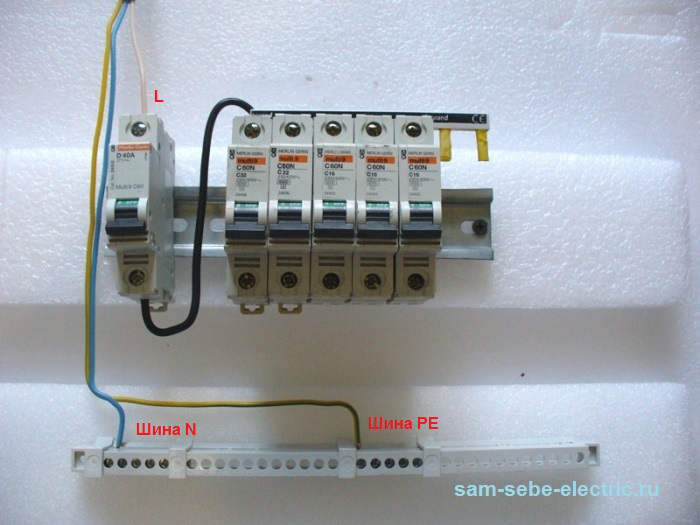
Electrotechnological staff | Personnel whose managed by them technological process The main component is electric Energy (for example, electric welding, electric arc furnaces, electrolysis, etc.), using manual electrical machines, portable power tools and lamps, and other employees for whom the instructions or instructions for labor protection are established by the knowledge of these Rules (where II or Higher Electric Safety Group) For quick reading schemes and easy definition different elements Electrical installations were regulated by the color and letter notation of tires and wires. They are clearly spelled out in Pue Chapter 1.1.29 and 1.1.30 and in Guest P 50462-2009. You should follow these rules. This will allow any electrician to quickly figure out your distribution shield. You still agree that you have more than once asked, and what color to make a "phase", and how "zero". Below you will find answers to your questions. Color marking of tires and wiresColor marking is performed using the storage coloring of conductive livers in different colors. This is done at the factory. Color identification is also possible at the ends of the wire at the site of its connection. Suppose you have a single-core wire of the same color. You can connect all the three phases and mark different phases of the corresponding multi-colored tape. How it is done in the photo below. GOST P 50462-2009 is prohibited from a separate use of green and yellow colors separately when marking conductors. They must be in combination of yellow-green. A combination of yellow-green color is designated a protective conductor.
Blue marked neutral and medium conductors. Combined zero protective and zero working conductors denote yellow-green over the entire length and blue label at the ends at the connection site or vice versa in blue over the entire length and with yellow-green labels at the ends. Preference for phase conductors is given to this colors: black, brown and gray. Although they often come across cables with another marking lived. For alternating current Phase conductors still highlight the following colors: red, purple, pink, orange, white, turquoise. See PUE p.2.1.31.
With three-phase current, the tires are indicated as follows:
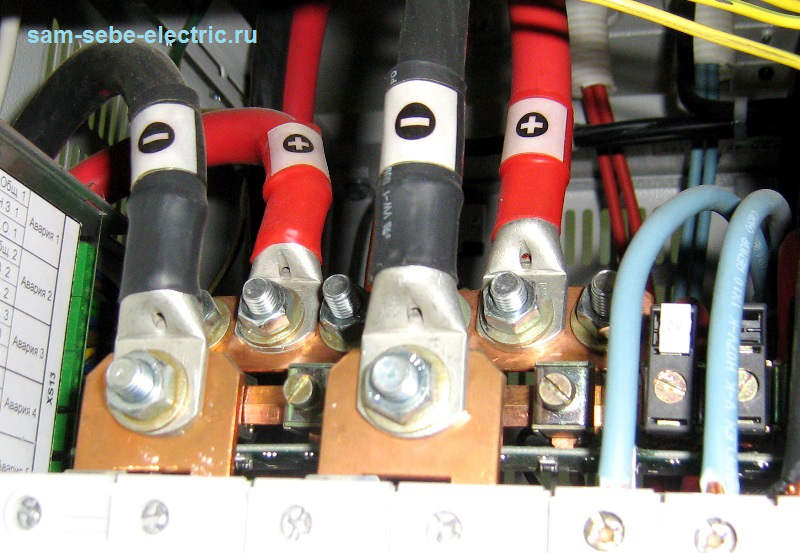
In DC circuits, according to the GOST R 50462-2009, the wires are marked as follows:
According to Pue chapter 1.1.30 tires at constant current are indicated as follows:
Honestly, working with communication equipment, most of which is powered by a constant current, I have never met the wires of brown and gray. I worked for several dozen or even hundreds of communication nodes and there all the "plus" wires were red, and "minus" blue or black.
Constant marking of tires and wiresIn electrical stamps, passports, and on the equipment itself, there are often conductors and contacts for connectivity have alphabetic marking. Below, clarify these letter designations with alternating current.
Deciphering alphabetic designations at constant current:
I think this information will be enough for you enough so that you can determine where the "phase", "zero" and "land" is connected to the chandelmark, and also determine the necessary wires in the scheme.
Do not forget to smile: Entry exam in high school. Examiner: Improving the qualifications includes the following types of training:
Professional retraining and professional development of specialists are carried out on the basis of contracts concluded educational institutions Advanced training with executive authorities, public employment authorities and other legal entities and individuals. Professional retraining and advanced training of civil servants of federal executive bodies are carried out in the manner prescribed by the Government of the Russian Federation. Electric tires are needed to connect separate elements of electrical installations into a single integer. DefinitionTires allow you to combine all electrical installation elements into one. In essence, these are conductors whose resistance is low. With a combination of multiple tires at one point talk about busbars. As a rule, they are installed on insulators, which simultaneously serve as a support. He hides in a special box (channel). Thanks to this, it protects against factors ambient. Busbar should always be resistant to emerging dynamic and thermal loads, electrical shock. Electric tires are performed in several versions. For their division, several classifications are provided for species. According to the method of execution, flexible and rigid tires are distinguished. They are differently called flat and tubular. Flexible tires do not twist. They should not have a high degree of effusion. Moreover, the degree of removal of all wires should be the same. Under the influence of temperature, the length of the tire may vary. Therefore, rigid models are equipped with flexible jumpers that must compensate for these changes. In addition, they are equipped with vibrations. In addition, electrical tires can be isolated and uninsulated. Already from the name it is clear that in the first case, the tire has a layer of insulation, and in the second - no. Classification of tires in the form of sectionIn the form of the cross section, the electric tires are divided into the following types:
Flat tires with rectangular cross section are well discharged. Their use is advisable in a network with high current (from 2 thousand to 4.1 thousand amps). In such cases, they are connected to groups of several pieces. This generates a two- or three-band bus.
Colored tires have a number of shortcomings:
In the network with a voltage of 10-35 kilovolt, box-shaped or flat products can be used. The most effective is the Tubular. It has a number of advantages. It is durable, well removes heat. Electric field Around it is distributed evenly. Thanks to this, no coronation appears. Types of material manufacturing tiresDepending on the material from which the tire is made, the following electrical tires are distinguished:
The last option is a core made of galvanized steel wires around which the wires from aluminum are reitless. Aluminum tires have the following advantages:
They use plastic with minimal impurities. Low all aluminum, magnesium and silicon alloys can be used. Additional elements allow you to increase strength, plasticity, elasticity.
Copper tires may contain in their composition up to 99.9% of copper. Such products possess marking M1. The WTMT and SVTV brands are widely used, which are made from oxygen-free brand. They are distinguished by the degree of softness. The first two letters of the labeling of the SMMM and the SVTT denotes the "copper tire". Further, the letter "M" characterizes soft products, "T" - solid. Marking with variable three-phase currentDetermine the elements of electrical installations will help "prompts", which are expressed in the colors and letter designation of tires and wires. They are not chosen. They are regulated standards. There are two ways of tire color designation. The first implies that the labeling of the electric tire is applied at the stage of manufacture. The manufacturer uses isolation of different colors. The second is suitable in cases where the product has one color. In such situations, the color isolent is used, with which different phases are noted.
In the case of three-phase current, the marking will look like this:
Expert designationGround conductor marked re. It is always referred to as yellow-green. Colors go longitudinal lines. Moreover, the use of these two colors separately is prohibited by GOST. For neutral and medium conductor (worker) with marking N used blue color. When connecting zero protective and working conductors combine all three colors. Marking in this case looks like Pen. The conductor is performed blue, and at its end and in places of connection, a strip of yellow-green color is performed. Currently, it is permissible to perform the opposite color: the yellow-green conductor with a blue stripe at the end.
Letter markingWires and tires electric with alternating current are decoded as follows:
With a constant current of the designation will be as follows:
All these labeling and designations are mandatory. They are regulated by the accepted regulations. Remember all this is immediately difficult. But an experienced electrician knows all this. This marking will allow you to determine where and what is connected. BUT simple man This will be enough to understand, for example, what a tire is needed for electric machines. It may be needed when repairing electrical wiring in the house. It is easy to connect additional sources later. |