The system of charged bodies has a potential energy called electrostatic, because The electrostatic field can move the charged bodies placed in it, while working.
Consider the work of electrostatic forces to move the charge q in a homogeneous electrostatic field with tension E, created by two infinitely large plates with equal modulo and opposite by the sign of charges. We connect the origin of the coordinate axis with a negatively charged plate. On the point charge Q in the field there is power. When moving the charge from T.1 in T.2 by the power line, the electrostatic field does work ![]() .
.
When moving the charge from T.1 in T.3. But ![]() . Hence,
. Hence, ![]() .
.
Work of electrostatic forces when moving electric charge From T.1 to T.3 is calculated according to the derived formula with any form of the trajectory. If the charge moves along the curve, then it can be divided into very small rectilinear areas along the field strength and perpendicular to it. On perpendicular field, the work is not performed. The sum of the projections of the remaining sections on the power line is equal to D 1 -D 2, i.e.
![]() .
.
Thus, work when charging the charge in a homogeneous electrostatic field does not depend on the form of the trajectory, which moves the charge, and depends only on the coordinates of the initial and endpoint paths. This conclusion is valid for inhomogeneous electrostatic field. Consequently, the Coulomb force is a potential or conservative and its work when moving charges is associated with a change in potential energy. The operation of conservative forces does not depend on the form of the body path and is equal to the change in the potential energy of the body, taken with the opposite sign.
![]() .
.
![]() . So.
. So.
Accurate physical meaning not herself potential energybecause Its numerical value depends on the choice of the origin of the coordinates, and the change in potential energy, because Only it is determined uniquely.
The operation of the electrostatic field when the charge is moving along the closed pathway is zero, because D 2 \u003d D 1.
The value equal to the potential energy, which would be on a single positive charge, placed at this point of the electrostatic field, is called the potential of the electrostatic field at this point.
Potential - scalar value. it energy characteristic fields, because Determines the potential charge energy at this point.
The potential is determined with an accuracy of a certain constant, the value of which depends on the selection of the zero level of potential energy. With the removal in an inhomogeneous field from charge, creating a field, the field is weakening. It means that its potential is reduced. J \u003d O is infinitely remote from the charge point. Therefore, the potential of the field at this point of the field is the work performed by electrostatic forces when moving a single positive charge From this point in an infinitely remote. The potential of any point of the field created by a positive charge is positive. In the electrical engineering, the surface of the Earth is taken for the surface with zero potential.
Potential difference is the difference of potential values \u200b\u200bin the initial and endpoints of the trajectory.
![]() .
.
The potential difference between two points is the work of the Coulomb forces to move a single positive charge between them. The potential difference has accurate physical meaning, because It does not depend on the selection of the reference system.
[V] \u003d J / CL \u003d c. 1 Volt is the potential difference between points, when moving between which charges in 1 Kulov's forces are performed in 1J.
Calculate the potential of the points of the field created by a point charge Q.
Let the charge q move in the charge field Q along the radial line. The charge moves in an inhomogeneous field. Consequently, when moving will change the force acting on the charge. But you can smash all the movement on such small areas of DR, on each of which the force can be considered constant. Then. Then work all over the way
Work in the electrostatic field does not depend on the form of the trajectory.
Therefore, if the charge moves from the charge that creates the field, not by a radial line, then you can move from the starting point to the final, moving it first along the arc of the circle of the radius R 1, and then by the radial segment to the end point. On the first plot, work will not be done, because Coulomb force will be perpendicular to the velocity of the body, and on the second it will be above the found formula.
The potential of the resulting field of the charge system at a given point on the principle of the superposition of fields is equal to the algebraic amount of the potentials of the components of the fields at this point.
The geometric location of the points of the equal potential of the potential is called the equipotential surface.. Equipotential surfaces perpendicular to the power lines. The operation of the field when the charge is moving along the equipotential surface is zero. The surface of the conductor in the electrostatic field is equipotential. The potential of all points inside the conductor is equal to the potential on its surface. Otherwise, between the points of the conductor would exist the potential difference, which would lead to the emergence electric current. Equipotential surfaces cannot intersect.
Unlike the remaining magnitudes in electrostatics, the potential difference between the bodies is easy to measure using the electroometer by connecting the housing and the arrow of it with the bodies in these points. In this case, the angle of deflection of the arrow of the electrometer is determined only by the difference between the potentials between the bodies (or that the same is between the arrow and the electrometer housing). Practically the potential difference between points in electrical circuits is measured by a voltmeter connected to these points.
Work on the movement of the electric charge in a homogeneous electrostatic field can be found through the power characteristic of the field - tension, and through the energy - potential. This allows you to establish a link between them.
Hence:
This dependence allows you to introduce a field of field tension in SI. . The tension of the homogeneous electrostatic field is equal if the potential difference between points lying on one power line at a distance of 1m is 1V.
In the electrostatic field, tension is directed towards the reduction of the potential.
It is easy to show that in inhomogeneous fields:
The sign "-" suggests that the potential decreases along the power line.
When moving from one environment to another potential, in contrast to tension, it cannot be changed by jumps.
Electrical capacity.
The potential of a secluded conductor is proportional to the procedure to him. The ratio of charge on the conductor to its potential does not depend on the size of the charge. It characterizes the ability of this conductor to accumulate charges. The electrical capacity of the secluded conductor is called a value equal to an electrical charge, changing the potential of the conductor per unit . To calculate the electrical capacity of a secluded conductor, you need to tell him the charge to divide the potential on it.
1Farade is the electrical capacity of the conductor, the potential of which changes to 1B when the charge is reported to it. Farad is a huge container, so in practice we are dealing with micro and picofarades. The electrical capacity of the conductor depends on its geometric dimensions, shapes and dielectric permeability of the medium in which it is located, as well as from the location of the surrounding bodies.
Bowl potential. Consequently, its electrical capacity
When the charge is transferred from one of the uncharged conductors to another between them there is a potential difference, a proportional value of the charged charge. The ratio of the loss of the transferred charge to the resulting potential difference does not depend on the value of the charged charge. It characterizes the ability of these two bodies to accumulate an electric charge. The mutual electrical capacity of two conductors is called the value equal to the charge, which must be transferred from one conductor to another to change the difference of potentials between them per unit.
Mutual electrical capacity depends on the size and shape of the bodies, on the distance between them, from the dielectric permeability of the medium in which they are located.
Large electrical capacity possess condenters - a system of two or more conductors, called plates separated by a dielectric layer . The charge of the capacitor is the charge module of one of the plates.
To charge the capacitor, its plates are connected to the poles of the current source or, grounding one of the plates, the second attach to any pool of the source, the second pole of which is also grounded.
The electrical capacity of the capacitor is called the charge, the message of which the condenser causes the appearance between the plates of a single potential difference. To calculate the electrical condition of the capacitor, it must be charged to the difference between the potentials between the plates.
Let the distance between the plane condenser D, D are much smaller than their dimensions. Then the field between the plates can be considered homogeneous, and the plates are infinite charged planes. The tension of the electrostatic field from one plug :. Total tension:
The potential difference between the plates:
![]() . =>
. =>
This formula is valid for small d, i.e. With a homogeneous field inside the condenser.
There are capacitors of constant, variable and semi-variable containers (trimmers). Condensers of constant capacity are called, as a rule, by the genus of the dielectric between the plates: mica, ceramic, paper.
In condensers of variable containers, the dependence of the container from the area of \u200b\u200boverlapping area is often used.
Trimmers (or trimming capacitors) changes the container when setting up radio devices, and during operation remains constant.
The sequential and parallel connection of capacitors is practically used, as well as their combination - mixed connection. With a consecutive connection, one pavement of each battery condenser is connected to one plane of another capacitor, i.e. Condenses form a chain. Because , and then ![]()
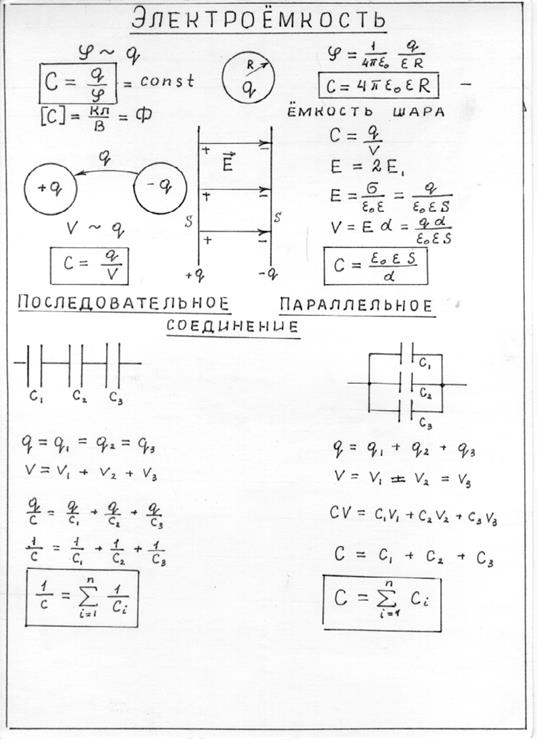
Many living organisms behave like electric dipoles. Electric dipolem They call the system of two equal charges of the opposite sign, located at a distance of L from each other. The vector spent from the negative charge to the positive is called shoulder dipole. The main characteristic of the dipole is an electric dipole moment - a vector physical value equal to the product of a module of one of its charges on the shoulder 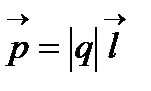 The electrostatic field is potential. This means that the work on the movement of charge in the electrostatic field does not depend on the form of the trajectory, which moves the charge, but is determined only by the initial and ending position of the charge. For any charge, placed in an electrostatic field, the force acts that can move it. Any electrical charge located in the electrostatic field has some potential energy. Therefore, the operation A, which is carried out when the electric charge is moved from one point of the field to another equal to the loss of potential energy W of this charge A \u003d W 1 - W 2 where W 1 and W 2 is the potential charges of charge in the initial and end points, respectively. The most important energy characteristic electric field is the potential. Electric field potential φ is called a scalar physical value, numerically equal to the potential energy of a single positive charge
The electrostatic field is potential. This means that the work on the movement of charge in the electrostatic field does not depend on the form of the trajectory, which moves the charge, but is determined only by the initial and ending position of the charge. For any charge, placed in an electrostatic field, the force acts that can move it. Any electrical charge located in the electrostatic field has some potential energy. Therefore, the operation A, which is carried out when the electric charge is moved from one point of the field to another equal to the loss of potential energy W of this charge A \u003d W 1 - W 2 where W 1 and W 2 is the potential charges of charge in the initial and end points, respectively. The most important energy characteristic electric field is the potential. Electric field potential φ is called a scalar physical value, numerically equal to the potential energy of a single positive charge
Placed at this point 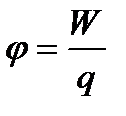 From this formula
From this formula
follows a capacity of potential - volt (B): 1B \u003d 1 J / CL. Under the action of the forces of the field, a positive charge will strive to move from a point with a higher potential to a point with a lower potential, and a negative charge on the contrary. Numerical value and potential sign depends on the selection of the zero level. In physics, it is usually believed that the potential is zero at infinity. In practice in electrical engineering, for zero potential, the potential of the surface of the earth or conductor connected to the ground is usually chosen. When calculating it is important to know not the absolute values \u200b\u200bof potentials, in any two points of the field, and the difference of potentials Δφ. Potential difference It is determined by the following expression Δφ \u003d φ 1 - φ 2 where φ 1 is the potential of the point 1, φ 2 - the potential of the point 2. When the charge q is moved from one point of the electric field to another, the operation is performed a \u003d q (φ 1 - φ 2) of the body In which electrical charges can be moved, called conductors. The transfer of charges in the conductors of the first kind (metals) is due to the movement of electrons, the second kind (gases and liquids) by the movement of ions. In dielectrics, the movement of electrical charges is impossible. The electrostatic field is a special kind of matter, fills all the space surrounding the restricted charges. Charges caused by excess or disadvantage of electrons in each element of the amount of charged body are called free. Charges caused by the polarization of the dielectric are called connected. The potential of this field of the field is the value equal to the work performed by the field with the movement of a single positive charge from this field point to infinitely remote. The potential difference between two points is determined by the work performed when moving a single charge between these points. Equipotential surface is a geometric location of constant potential points.
35.Electility. Condencators. 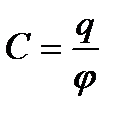 Value FROM called electrical capacity of the conductor. Electrical capacity characterizes the ability of conductors to accumulate electrical charges. Unit of electrical capacity is farad (F) The capacity of such a secluded conductor, to whom the charge of 1 CL reports the potential of 1 to: 1F \u003d 1kl / c. 1 Farad is a very large electrical capacity. EarthFor example, has an electrical capacity of ≈ 711 μF. However, scientists have created devices that are capable of accumulating a fairly large electrical charge with relatively small sizes. They got a name - condencators. The condenser consists of two conductors located at a short distance from each other, separated by a dielectric layer. The exchange processes that are continuously occurring in a living organism lead to the redistribution of charges in the tissues and the emergence of potential differences mentioned biopotentials.To date, it is established that all cells of animals and plant organisms have one or another type of electrical activity. Electrotrix - the phenomenon of the occurrence of stresses in the dielectric under the action of the electric field. The body's electrical capacity is a physical value equal to the number of electricity that increases the potential of this body per unit. Body serve to accumulate electrical charges are called condensers. The condenser is a passive electronic component. It consists of two electrodes in the form of plates separated by a dielectric. Condenser in chains direct current It can carry out current at the time of its inclusion in the chain, at the end of the transient process, the current through the capacitor does not flow. In the chain of the same aCand it conducts vibrations of alternating current by means of cyclic recharging of the condenser, closing the so-called shift current.
Value FROM called electrical capacity of the conductor. Electrical capacity characterizes the ability of conductors to accumulate electrical charges. Unit of electrical capacity is farad (F) The capacity of such a secluded conductor, to whom the charge of 1 CL reports the potential of 1 to: 1F \u003d 1kl / c. 1 Farad is a very large electrical capacity. EarthFor example, has an electrical capacity of ≈ 711 μF. However, scientists have created devices that are capable of accumulating a fairly large electrical charge with relatively small sizes. They got a name - condencators. The condenser consists of two conductors located at a short distance from each other, separated by a dielectric layer. The exchange processes that are continuously occurring in a living organism lead to the redistribution of charges in the tissues and the emergence of potential differences mentioned biopotentials.To date, it is established that all cells of animals and plant organisms have one or another type of electrical activity. Electrotrix - the phenomenon of the occurrence of stresses in the dielectric under the action of the electric field. The body's electrical capacity is a physical value equal to the number of electricity that increases the potential of this body per unit. Body serve to accumulate electrical charges are called condensers. The condenser is a passive electronic component. It consists of two electrodes in the form of plates separated by a dielectric. Condenser in chains direct current It can carry out current at the time of its inclusion in the chain, at the end of the transient process, the current through the capacitor does not flow. In the chain of the same aCand it conducts vibrations of alternating current by means of cyclic recharging of the condenser, closing the so-called shift current.
36. Electrostatic protection.The electrostatic field is a special kind of matter, fills all the space surrounding the restricted charges. Property - transferring the action of one electrical bodies to others; Such an action is manifested in the emergence of forces between charged bodies. Spot charges are such charged bodies whose dimensions are small compared to the distance between them. Each point of the electrostatic field is characterized by tension. Vector electrostatic induction There is a magnitude proportional to the vector of the electrostatic field intensity, and the proportionality coefficient is the dielectric constant The medium showing how many times the electric field strength in the dielectric is smaller than the field strength in vacuum.
37. Current power. EMF. TensionThe tension is a physical value proportional to the strength with which the field is valid for a single positive charge; Direction of tension vector coincides with the direction of the strength vector. Measured in V / m, N / CL. Line of tension is a line, at each point of which the vector of tension characterizing this point is directed by the tangent of the line under consideration. Tension lines come out of a positive electric charge and are included in negative or go into infinity. The number of tension lines is called a stream of tension through the surface. The strength of the current flowing through this conductor site is a physical value measured by the number of electricity tolerable through this platform per unit of time. It is measured in A. Electric current, the value of which does not change in time, is called constant. The electromotive power of the source of the electric current is the value defined as the algebraic amount of the potential jumps encountered when bypassing the chain in which only this source is included. It is equal to the potential difference on the clips of the open source. Electric shockthe directional movement of electrically charged particles is called. For the direction of current, it is considered to refer to the direction of movement of positive charges. Basic characteristic
electric current is current I., numerically equal
charging flowing through the cross section of the conductor
per unit time: 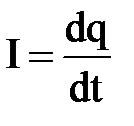 Unit measuring current in si
Unit measuring current in si
is an ampere (a): 1A \u003d 1kl / s. If the current and its direction is not changed over time, such a current is called constant. First prerequisite The existence of electric current is the presence of the potential difference Δφ is not zero. To maintain it, a special device is needed, with which the separation of charges at the ends of the conductor will occur. Such a device is called the generator or current source. Galvanic elements, batteries, thermoelements, photo cells, etc. are used as the current source. The current source simultaneously performs the second condition of the electric current - it closes the electrical circuit, which could be carried out by the continuous movement of charges. The current flows through the outer part of the chain - the conductor and internal - the current source. The current source has two poles: positive (+) with higher potential and negative (-) with lower potential. In the negative pole, an excess of electrons is created, and in positive - disadvantage. The separation of charges in the current source is produced using the forces having non-electrical nature (mechanical, chemical, thermal, etc.), since electrical forces can only be connected, but not separating multi-dimensional charges. Therefore, these forces are called third parties, the work of a third-party force on the separation of charges is equal to: a \u003d and the East + A "where A East \u003d Q (φ 1 - φ 2) work against the power of the electric field; a" - the work performed against the mechanical strength of resistance of the medium Source. The work performed by a third-party force on moving along this section of a single positive charge chain is called electromotive power (EMF) and denotes ε. IN
particular for the current source: 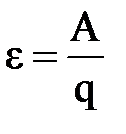 For the current source, we get:
For the current source, we get:
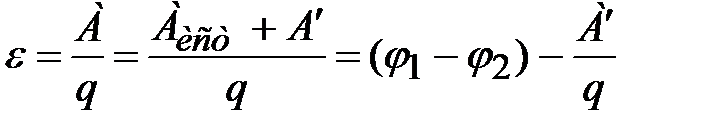 If the source pole is open,
If the source pole is open,
that and "\u003d 0 and ε \u003d φ 1 - φ 2 i.e. EMF of the current source with an open external circuit is equal to the potential difference, which is created on its poles.
Potential difference on the poles of the current source, closed external electrical chain called voltage source U. voltage current source less emf
by magnitude: 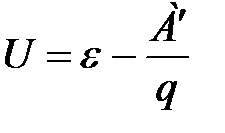 In addition, on any plot
In addition, on any plot
the external electrical circuit there is a certain potential difference, it is called a voltage drop (voltage) U in this section, the voltage and EMF are measured as well as the difference in volt potentials.
38.To in metals.In metal, the current occurs due to the directional movement of the electrons existing in it in the free state in the form of electronic gas. Electric current in metals is an ordered movement of electrons under the action of an electric field. When current flows over the metal conductor of the substance, the substance does not occur, the metal ions do not participate in the transfer of the electric charge. All metals in solid and liquid state are electrical current conductors. When the electric current is passed, the mass of metallic conductors remains constant, does not change and their chemical composition. Under the action of an electric field, free electrons, except for chaotic movement, acquire an ordered movement in one direction, and electric current occurs in the conductor. Free electrons face ions crystal lattice, giving them with each collision kinetic energy. As known carriers of charges in metals are free electrons. Thus, the current in metal conductors is the directional motion of free electrons (despite the fact that the direction of the current is taken direction of movement of positively charged particles). Back in 1826, the German physicist ohm emphasized that the current of the current in the conductor is proportional to the voltage U between the sections of the conductor: i \u003d ku where k is the proportionality coefficient called electrical conductivity or conductivity
explorer. Value 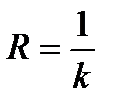 reverse conductivity called
reverse conductivity called
electrical resistance Explorer. Then 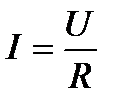 law
law
Ohm for a circuit site (no current source). The unit of measurement of resistance was named OM. From it follows that: 1 ohm \u003d 1 V / and the current resistance to the metal conductor is due to the collision of free electrons with metal ions. It depends on
forms, sizes and substances of the conductor: 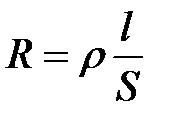 Where L - Length
Where L - Length
explorer, S - The area of \u200b\u200bits cross section, ρ is a specific resistance, the proportionality coefficient characterizing the material from which the material is made. unit of measurement specific resistance Om · m. Experience shows that the current always causes some heating of the conductor. Heating is due to the transition kinetic energy Moving on the conductor of electrons with the ions of the crystal lattice in heat. This amount of heat is determined by the law of Joule - Lenza 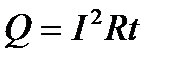 where I is the current of the current in the conductor, R is the resistance, T is the passage time through the conductor. It is on the thermal action of the current that the operation of incandescent lamps, electric furnaces, electric welding, household electric heating devices, etc.
where I is the current of the current in the conductor, R is the resistance, T is the passage time through the conductor. It is on the thermal action of the current that the operation of incandescent lamps, electric furnaces, electric welding, household electric heating devices, etc.
39.t in fluids. Current in gases.Electric current in liquids. The electric current is carried out solutions of many substances in water. Clean water does not conduct an electric current, there are no free carriers of electrical charges. Do not conduct electric current and crystals of the table salt, sodium chloride. When the electric current is passed, chemical changes occur, as a result of which gas is released. The conductors of the second kind are called electrolytes, and the phenomenon occurring in the electrolyte when the electric current is passed through it - electrolysis. Metal plates, lowered in electrolyte, are called electrodes; One of them, connected to the positive pole of the current source, is called an anode, and the other, connected to the negative pole, is a cathode. Particles of the molecule having an electric charge are called ions. The phenomenon of electrolysis was opened in 1837 B. S. Jacobi, who made numerous experiments on the study and improving the chemical sources of current. Jacobi found that one of the electrodes placed in a solution of copper sulfate when the electric current passes through it is covered with copper. This phenomenon called by galvanoplasty, for example, the coating of metal objects with a thin layer of other metals - gilding, silvering. Electric current in gases.
In the gases there are unhappiecked and independent electrical discharges. The phenomenon of the flow of electric current through the gas is called an independent electrical discharge. The process of separation of an electron from an atom is called an atom ionization. The minimum energy that needs to be expensive for the separation of an electron from an atom is called ionization energy. Partially or completely ionized gas, in which the density of positive and negative charges The same, called plasma. Electric current carriers with poor discharge are positive ions and negative electrons. Spark discharge It occurs between the two electrodes charged different charges and having a greater potential difference .. Spark discharge short-term, its mechanism is an electronic shot. Lightning is the type of spark discharge. Between the wire of the power line and the surface of the earth, there is a special form of self-discharge in gases, called crown discharge. Electric current carriers in the arc are positively charged ions and electrons. Discharge occurring under reduced pressure is called glow discharge
40.Magnetic field and its characteristics. In the space surrounding the electric current, the magnetic field occurs. It is manifested by the forces acting on the conductors made in it with the current. The magnetic field is created only by moving charges and acts only on the electrical charges moving in this field. The magnetic field is characterized by a magnetic induction vector. The induction of the magnetic field is the value equal to the moment of forces acting on the frame with a current having a single magnetic moment. Unit of measurement of the induction of the magnetic field - Tesla (TL). The magnetic field is vortex (the operation performed when bypassing the charge of the current on the closed path is not zero). The magnetic field of the direct permanent magnet is similar to the magnetic field of the solenoid (the power lines come out from the North Pole and are included in the south). The magnetic properties of some iron ores (the ability to attract iron objects) are known with deep antiquity and obtained use in a magnetic compass device. It turned out that a permanent magnet has two poles - northern (denotes the letter N) and south (denotes s). Motionic magnet poles are mutually attracting, and the same is repelled, an idea of \u200b\u200bexistence has arisen in science. magnetic charges (positive and negative). It is impossible to divide the poles of the magnet. In 1820, the Danish physicist Ersted found that the wire for which electric current flows on the magnetic arrow located near it. The magnetic arrow turns perpendicular to the wire, the French ampere physicist discovered the magnetic interaction of two conductors with a current around moving electrical charges (electric currents) Another type of field occurs - a magnetic fieldis generated by moving electric charges and an alternating electric field. Magnetic field is power field - It acts with some force on moving charges, conductors with current, permanent magnets, are depicted graphically by silest lines. The power lines of the magnetic field are always closed they have no beginning, no end. Therefore, the magnetic field is vortex. The tangent to the magnetic power line at any point coincides in the direction with the so-called magnetic induction vector. Therefore, the power lines of the magnetic field are typically called magnetic induction lines. Vector magnetic induction - Main power characteristic Magnetic field: proportional to power that acts on the northern end of an infinitely small magnetic arrow placed in
this magnetic field point. The unit of magnetic induction is Tesla (TL): 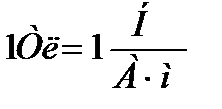 Induction (with other things being equal) depends on the properties of the medium (substance). Induction in substance and induction in vacuum are related to the following relationship
Induction (with other things being equal) depends on the properties of the medium (substance). Induction in substance and induction in vacuum are related to the following relationship 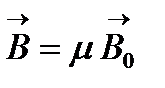 where μ is magnetic permeability of the substance, dimensionless physical quantity characterizing the magnetic properties of the medium. For vacuum μ \u003d 1. Along with the induction, there is another characteristic of the magnetic field - the tension associated with magnetic induction by the ratio
where μ is magnetic permeability of the substance, dimensionless physical quantity characterizing the magnetic properties of the medium. For vacuum μ \u003d 1. Along with the induction, there is another characteristic of the magnetic field - the tension associated with magnetic induction by the ratio 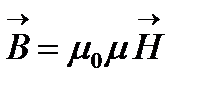 where μ 0 is a magnetic constant, depending on the selection of the system of units. It does not have physical meaning as well as ε 0 in electrostatics. In the international system units
where μ 0 is a magnetic constant, depending on the selection of the system of units. It does not have physical meaning as well as ε 0 in electrostatics. In the international system units 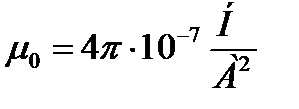 The value does not depend on the properties of the medium and is the characteristic of the magnetic field created by external with respect to the sources under consideration. Unit of measuring the tension of the magnetic field - a / m.
The value does not depend on the properties of the medium and is the characteristic of the magnetic field created by external with respect to the sources under consideration. Unit of measuring the tension of the magnetic field - a / m.
41. Ampere Law- The law of interaction of permanent currents. Andre Marie Ampera is installed in 1820. From the AMPER law it follows that parallel conductors with constant currents flowing in one direction are attracted, and in the opposite - repel. The AMPER's law is also called the law that determines the force with which the magnetic field acts on a small segment of the conductor with a current. F \u003d BI. l.sINA (A is the angle between the current direction and the induction of the magnetic field). This formula of the Ampere Law turns out to be fair for a straight line conductor and uniform field. If the conductor has an arbitrary formula and an inhomogeneous field, then the amper's law takes the form: DF \u003d I * B * dlsinaThe ampere force is directed perpendicular to the plane in which the DL and B vectors lie to determine the direction of force acting on the conductor with a current placed in the magnetic field, the rule of the left hand is applied. The direction of force is determined by the rule of the calculation of the vector product, which is convenient to remember using the rule of the right hand. Ampere Module can be found by the formula:
42.Magnetic properties of substances. Nature of magnetism.The substance capable of influence the magnetic field is called a magnet. The molecular current is a circular current, flowing into molecules of substance. Molecular currents exist in molecules and are excited under the action of an external magnetic field. The appearance in the substance of an additional magnetic field under the action of an external magnetic field is called magnetization. The magnetization will be the magnitude characterized by the medium magnetization and the unit of its volume is equal to the magnetic moment. The ratio of the magnetization vector to the vector of the external field tension is called the susceptibility of the magnetic. Substances, the field of magnetization of which is determined by the orientation of the molecular currents existing in molecules are called paramagnets. Diamagnetics This substance in which the magnetization field is determined by currents arising from the resulting molecular currents under the action of an external field. Substances in which the field of magnetization occurs by orientation of magnetization domains is called ferromagnetic. The magnetic properties of some iron ores (the ability to attract iron objects) are known with deep antiquity and received the use of more than a thousand years before our era in the magnetic compass device. It turned out that a permanent magnet has two poles - northern (denotes the letter N) and south (denotes s). The Northern Pole magnet, which is given the opportunity to freely navigate, turns to the north, and southern - to the south, the variety of magnets are mutually attractive, and the same are repelled. As a result, in science an idea of \u200b\u200bthe existence of magnetic charges (positive and negative), two new magnets always turn out of the cut magnet. It is impossible to divide the poles of the magnet. In 1820, the Danish physicist Ersted found that the wire for which electric current flows on the magnetic arrow located near it. The magnetic arrow rotates perpendicular to the wire. At the same time, the French ampere physicist discovered the magnetic interaction of two conductors with a current (mutual attraction or repulsion depending on the direction of currents flowing into them). Subsequent experiments have shown that the magnetic properties have a current in liquids, gases, any moving electrical charge. Thus, it turned out that there is another type of field around moving electrical charges (electric currents) - a magnetic field. No magnetic charges exist, the magnetic field is generated by moving electric charges and an alternating electric field. The magnetic field is a power field - it acts with some force on moving charges, conductor with current, constant magnets. Since the magnetic field is a power field, it is depicted graphically by means of power lines as well as an electric field. The power lines of the magnetic field are always closed they have no beginning, no end. Therefore, the magnetic field is vortex.
43.Thenage charged particles in a magnetic field. The Lorentz power is the force acting on a charged particle when it moves in a magnetic field. The ratio of the charge of a particle (electron, ion) to its mass is called a specific charge of this particle. Knowing the direction of Lorentz's force and the direction of the charged particle caused by it in a magnetic field can be found a sign of the charge of particles that move in magnetic fields.
If the charged particle in the magnetic field moves with a velocity V along the magnetic induction lines, the angle α between vectors V and B is 0 or π. Lorentz's power is zero, i.e. the magnetic field on a particle does not act and it moves evenly and straightly. If the charged particle moves in a magnetic field with a velocity V, which is perpendicular to the vector B, then the Lorentz force f \u003d q is constant in the module and perpendicular to the particle path. According to Newton's second law, Lorentz's strength creates a centripetal acceleration. It means that the particle will move around the circumference. The period of rotation of the particle, i.e. the time T, for which it makes one full turn. As well as on the conductor with a current, the magnetic field is valid for a separate charge moving in it. The process of interaction of moving charges with an external magnetic field was studied by Danish physicome Lorenz. As a result of the generalization of the experimental data, it derived a formula for calculating the force acting from the magnetic field to a moving charged particle. This force was named lorentz power: 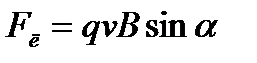 where q is a particle charge, V is its speed, B is a magnetic induction, α is the angle between vectors and. Being perpendicular to the speed, the Lorentz power changes only the direction of the speed of the particle and does not change its magnitude. If the particle flies into a homogeneous magnetic field parallel to the magnetic induction lines, it continues to move in a straight line at the initial speed (α \u003d 0, sinα \u003d 0 and therefore f l \u003d 0). If the vector of the initial velocity of the particle is perpendicular to the magnetic induction lines, then in this field, the particle will move around the circumference of some radius with a constant period. In this case, the period of circulation depends only on the specific charge of Q / M particles. If the particle flies into a homogeneous magnetic field under a certain angle α to the magnetic induction vector, then its trajectory is a screw helix. Features of the movement of charged particles in magnetic and electric fields are widely used in modern techniques. They underlie the operation of the radar, electron microscope, televisions and monitors with electronolic tubes, accelerators of charged particles, etc. The mass spectrometry is based on the same physical phenomena - the method of determining the masses of particles and their relative content in complex substances, which is widely used in chemistry and biology.
where q is a particle charge, V is its speed, B is a magnetic induction, α is the angle between vectors and. Being perpendicular to the speed, the Lorentz power changes only the direction of the speed of the particle and does not change its magnitude. If the particle flies into a homogeneous magnetic field parallel to the magnetic induction lines, it continues to move in a straight line at the initial speed (α \u003d 0, sinα \u003d 0 and therefore f l \u003d 0). If the vector of the initial velocity of the particle is perpendicular to the magnetic induction lines, then in this field, the particle will move around the circumference of some radius with a constant period. In this case, the period of circulation depends only on the specific charge of Q / M particles. If the particle flies into a homogeneous magnetic field under a certain angle α to the magnetic induction vector, then its trajectory is a screw helix. Features of the movement of charged particles in magnetic and electric fields are widely used in modern techniques. They underlie the operation of the radar, electron microscope, televisions and monitors with electronolic tubes, accelerators of charged particles, etc. The mass spectrometry is based on the same physical phenomena - the method of determining the masses of particles and their relative content in complex substances, which is widely used in chemistry and biology.
44. Equating electromagnetic induction.The phenomenon of the occurrence of an electric current in a closed conductive circuit when the magnetic induction flow changes through the area bounded by this circuit is called electromagnetic induction. The current current is called induction. The induction current has such a direction that the magnetic induction stream created by it compensates for the change in the flow of magnetic induction, which caused this current. Electromotive force
(EMF) induction current is called EMF induction. It is proportional to the change in the flow of magnetic induction in time.
45.The induction and self-induction.The occurrence of induction emfs in the circuit, due to the change in current in the same circuit, is called self-induction. Self-induction currents occurring in conductors when the electric current is turned on and turned off, they are referred to as the closure and opening extracts. The property of the contour has more or less pronounced self-induccus is characterized by self-induction coefficient. The self-induccus coefficient is equal to self-induction EMF, which occurs in the circuit when the current changes in it per unit per unit of time. The appearance of the induction current in the circuit caused by the change in the electric current in the adjacent circuit is called mutually induction. It is characterized by a mutual induction coefficient, which is determined by the geometric shape, size and mutual position of the contours, and in the presence of ferromagnetic bodies and the power of the current in the circuit. Induction currents arising in solid conductors who cannot be considered as linear contours are called Foucault currents. The phenomenon of self-induction of Foucault currents in the conductors for which alternating current flows is called the skin effect.
46. \u200b\u200bAlternating current.Alternating current is a current, whose value changes over the law of cosine or sinus. AC current, the value of which at every given time is the same for all sections of the chain under consideration, is called a quasistationary. Constant current resistance is called ohmic or active. Electrical circuits have alternating current inductive and capacitive resistance due to the presence in these circuits of capacitors and inductors of inductance. Inductive resistance is equal to the product of the circuit inductance per circular current frequency, capacitive resistance is inversely proportional to the product of the tank to the frequency of the current. The resistance exerted by the electrical circuit of the variable current is called the impedance of the chain.
Effective AC power is equal to DC power, the thermal action of which is equivalent to the action of the alternating current under consideration
47. The concept of an electromagnetic field. Electromagnetic waves.The presence of electrical oscillations in the oscillatory circuit causes a magnetic field in the surrounding space in the surrounding space. Electric I. magnetic fieldarising from electrical oscillations exist inextricably come from each other and are called electromagnetic field. The electromagnetic field that occurs in any place of space, over time applies to all other parts of the space, if it changes periodically, then these changes are transmitted to the surrounding space. This is called an electromagnetic wave. In the electromagnetic wave, the vectors of the electric and magnetic fields, as well as the vector indicating the direction of the propagation of the wave, are mutually perpendicular. Such a wave is called transverse. Electromagnetic waves are used for wireless transmission of various signals, which is used in radio engineering, television, radar.
48. Electric oscillations.Machines serving for electricity by using electromagnetic phenomena are called generators; They convert mechanical energy into electric. Machines converting electrical energy into mechanical, are called electric motors. The oscillating circuit is a closed chain consisting of a container, inductance and inevitably present ohmic resistance in which electrical oscillations can occur. Electric oscillations in such a circuit are performed due to the transitions electrical Energy Condenser in magnetic energy inductance coil. The presence of electrical oscillations in the oscillatory circuit causes a magnetic field in the surrounding space, which is vortex.
49 On the nature of light.The light simultaneously has wave and corpuscular properties. It extends in the form of short electromagnetic waves. The energy of the wave particles (a quantum of light or photon) is proportional to the frequency of light. The ratio of proportion is the constant plank. Photon energy decreases with a reduction in frequency. The speed of light in emptiness does not depend on the state of the speed of reference systems. It is a universal global constant C \u003d 3.8 × 10 -8 m / s. Papping on the border of the section of two media, the light beam is partially reflected, partially passes into a new medium (refracted). The angles compiled by the norm conducted to the interface of the media, with the incident, reflected and refracted rays, are called respectively angles of falling, reflection and refraction.
50. Recovery and refraction of light.The ratio of the sinus of the angle of falling to the sinus of the refractive angle is called the relative indicator of the refractiveness of the substance. If the beam originally spread in emptiness, then the refractive index is called absolute. The optical density of the substance determines its refractive index. The phenomenon consisting in the reflection of the entire energy incident on the border (there is no refracted beam) is called the phenomenon of complete internal reflection. It occurs when light passes in an optically more dense medium on the border with an optically less dense medium. The angle of falling, in which the complete internal reflection occurs, is called the limit angle of complete internal reflection. With mirror reflection, the reflection angle is equal to the angle of fall. Surface, evenly in all directions, the lighting light falling on it is called absolutely matte.
51. Thin lenses. Lens - Detail of an optically transparent homogeneous material bounded by two polished refracting rotation surfaces. If the thickness of the lenses itself is small compared to the radii of curvature of spherical surfaces, then the lens is called thin. Lenses are there gathering and scattering. Gathering lens in the middle thicker than the edges, scattering lens, on the contrary, in the middle side thinner in the case of thin lenses it can be assumed that the main optical axis intersects with the lens at one point, which is called Optical Center for Lenses O. All direct passing through optical center called by-optical axes. If on the lens to send a beam of the rays parallel to the main optical axis, then after passing through the lens, the rays will be gather at one point F, which is called main focuslenses. The thin lens has two main focus, symmetrically located relative to the lens on the main optical axis. In collecting lenses, the tricks are valid, imaginary. Property lenses ability to give images of objects. Optical force measurement unit 1 diopter. Thin lenses have a number of shortcomings that do not allow to receive high-quality images.
One of the main concepts in electricity is an electrostatic field. Its important property is considered to work on the movement of charge in electric fieldwhich is created by a distributed charge that does not vary in time.
Terms of performance
The force in the electrostatic field moves the charge from one place to another. It does not completely affect the form of the trajectory. Determining the power depends only on the position of the points at the beginning and end, as well as, on the total size of the charge.
Based on this, you can draw the following conclusion: if the trajectory when moving the electric facility is closed, then all the work of forces in the electrostatic field has a zero value. At the same time, the form of the trajectory does not matter because the Coulomb forces produce the same work. When the direction in which the electric pressure moves, changes to the opposite, then the force itself also changes its sign. Therefore, a closed trajectory, regardless of its form, determines all the work produced by Coulomb forces equal to zero.
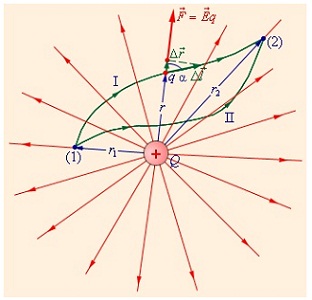
If there are several in the creation of the electrostatic field spot charges, their overall work will develop from the amount of work produced by the Coulomb fields of these charges. The overall work, regardless of the form of the trajectory, is determined exclusively by the location of the initial and endpoints.
The concept of potential charge energy
Peculiar to the electrostatic field, allows you to determine the potential energy of any charge. In addition, it is more accurately installed work on the movement of charge in the electric field. To get this value, in space you need to select a specific point and potential charge energy located at this point.

The charge placed anywhere has potential energy, equal workperformed by the electrostatic field during the movement of the charge from one point to another.
IN physical senseThe potential energy is a value for each of the two different points of space. At the same time, the work on the movement of the charge is regardless of the paths of its movement and the selected point. The potential of the electrostatic field in this spatial point is equal to the work performed electrical forcesWhen a single positive charge is removed from this point into an infinite space.
Electrical field work
| Potential. Potential difference. Voltage. | |
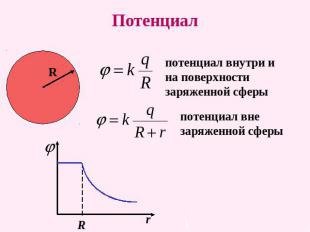
| Potential The electrostatic field is a scalar value equal to the ratio of the potential energy of charge in the field to this charge: - the energy characteristics of the field at the point. The potential does not depend on the size of the charge placed in this field. | |
| Because Potential energy depends on the choice of the coordinate system, the potential is determined up to constant. The potential reference point is chosen depending on the problem: a) the potential of the Earth, b) the potential of an infinitely remote point of the field, c) the potential of the negative condenser plate. | |
| - The consequence of the principle of superposition of fields (the potentials are developing algebraically). | |
| Potential numerical equal to work Fields to move a single positive charge from this point of the electric field to infinity. In the C potential is measured in Volta: | |
| Potential difference | |
| | |
| Voltage - The difference of potential values \u200b\u200bin the initial and end-screen trajectories. Voltage Numerically equal to the operation of the electrostatic field when moving a single positive charge along the power lines of this field. The potential difference (voltage) does not depend on the choice coordinate systems! | |
| The difference unit of potentials | |
| Communication between tension and voltage . | |
| Tension is equal to the rate of change of potential along the direction d. | |
| From this ratio you can see: |  |
| Equipotential surfaces. EPP - surface of equal potential. EPP properties: - Work when moving the charge along the equipotential surface is not performed; - vector of tension is perpendicular to the EPP at each point. | 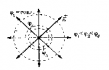 |
2. Model of the structure of the atomic nucleus. Nuclear power. Communication energy. Nuclear reactions.
In 1932 After the opening of Proton and Neutron, scientists D.D. Ivanenko (USSR) and V. Heisenberg (Germany) was put forward proton-neutron model of the nucleus of the atom.

According to this model:
- the kernels of all chemical elements consist of nucleons: protons and neutrons
- the nucleus charge is due only by protons
- the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the sequence number of the element
- The number of neutrons is equal to the difference between the mass number and number of protons (N \u003d A-Z)
Conditional designation of the core of the atom of the chemical element:
X - symbol of chemical element
A is a mass number that shows:
- Mass of the nucleus in the whole atomic units of mass (A.E.M.)
(1A.E.m. \u003d 1/12 mass of carbon atom)
- the number of nucleons in the kernel (a \u003d n + z), where n is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom
Z - the charge number that shows:
- the charge of the nucleus in elementary electrical charges (e.e.z.)
(1E.F. \u003d Electron Charge \u003d 1.6 x 10 -19 CB)
- Number of protons
- the number of electrons in the atom
- Serial number in the Mendeleev Table
Nuclear power - graduation forces connecting protons and neutrons in the kernel.
Properties:
1. Discipers of about 10 -13 cm. Strong interactions correspond to attraction, with a decrease in distance - repulsion.
2. Only dependent on the presence of an electric charge (the property of the charge independence) the same force acts on the proton and the neutron.
3. Intelligence with a limited number of nucleons (saturation property).
4. Interactive: Quickly decrease, starting with R ≈ 2.2. 10 -15 m.
Energy that is necessary for the complete cleavage of the kernel into individual nucleons is called communication energy. Communication energy is very large. In the synthesis of 4 g of helium, the same amount of energy is distinguished as when combining two coal cars.
The mass of the nucleus is always less than the sum of the masses of the rest of the protons and neutrons, its components.
The difference between the mass of the kernel and the sum of the masses of protons and neutrons is called the mass defect.
Formula for calculating the energy of communication:
![]() - Mass defect.
- Mass defect.
m P - the mass of the proton; M N is a neutron rest mass. M I - the mass of the nucleus of the atom.
In atomic physics, mass is conveniently expressed in atomic units of the mass:
1 AEM \u003d 1.67 · 10 -27 kg. Energy and mass communication coefficient (equal to 2): c 2 \u003d 931.5 MeV / A · E · m.
Nuclear reactions - transforming atomic nuclei caused by their interactions with different particles or each other.
Symbolic recording: A + A \u003d B + B. When writing nuclear reactions, the laws of preservation of charge and mass number (number of nucleons) are used.
Examples:
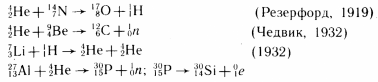
The energy yield of the nuclear reaction is the difference between the total binding energy of particles involved in the reaction and reaction products.
Reactions occurring with energy release, called. Exothermic, with an absorption - endothermic.




